Key Words: Reflection: Light returning from a
... the wire the core becomes magnetic. Step up Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step up transformer increase the voltage. Step down Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step down transformer decrease the ...
... the wire the core becomes magnetic. Step up Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step up transformer increase the voltage. Step down Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step down transformer decrease the ...
Optical Fibres
... The first bundle is used to shine light into the stomach. The second is used to see the inside of the stomach; a tiny lens over the bundle forms an image on the ends of the fibres, and the image can then be seen directly. ...
... The first bundle is used to shine light into the stomach. The second is used to see the inside of the stomach; a tiny lens over the bundle forms an image on the ends of the fibres, and the image can then be seen directly. ...
optics(conceptuals)
... (ii) Object is placed in front of a convex mirror. Q.53 The radii of curvature of both the surfaces of a lens are equal. If one of the surfaces is made plane, how will the focal length and power change? Q.54 Give reason: (i) Stars twinkle at night. (ii) Sun can be seen for several minutes after it h ...
... (ii) Object is placed in front of a convex mirror. Q.53 The radii of curvature of both the surfaces of a lens are equal. If one of the surfaces is made plane, how will the focal length and power change? Q.54 Give reason: (i) Stars twinkle at night. (ii) Sun can be seen for several minutes after it h ...
image
... trace back the two reflected rays to P' Point P' is the point where the rays appear to have originated The image formed by an object placed in front of a flat mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror ...
... trace back the two reflected rays to P' Point P' is the point where the rays appear to have originated The image formed by an object placed in front of a flat mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror ...
RAY OPTICS I
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolutio ...
... A variable slit is provided to the students. They are supposed to select a doublet lens of the proper focal length from a catalog such that for a typical source the lens is substantially illuminated. This in turn will illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolutio ...
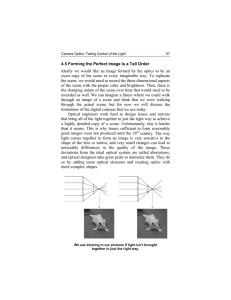
4.5 Forming the Perfect Image Is a Tall Order Ideally we would like
... 4.5 Forming the Perfect Image Is a Tall Order Ideally we would like an image formed by the optics to be an exact copy of the scene in every imaginable way. To replicate the scene, we would need to record the three-dimensional aspects of the scene with the proper color and brightness. Then, there is ...
... 4.5 Forming the Perfect Image Is a Tall Order Ideally we would like an image formed by the optics to be an exact copy of the scene in every imaginable way. To replicate the scene, we would need to record the three-dimensional aspects of the scene with the proper color and brightness. Then, there is ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... wavelength of the light in the object medium and the aperture angle of the lens. The extent of the PSF decreases with decreasing wavelength and with increasing aperture angle. Since the use of wavelengths below 360 nm is limited by the performance of the optical components, the resolution is further ...
... wavelength of the light in the object medium and the aperture angle of the lens. The extent of the PSF decreases with decreasing wavelength and with increasing aperture angle. Since the use of wavelengths below 360 nm is limited by the performance of the optical components, the resolution is further ...
Ray Optics - Sakshi Education
... separates this medium from another, then a part of the light comes back into the first medium in a definite direction. This is called reflection of light. The surface from which reflection takes place is called a reflector. The amount of light reflected depends on (i) the angle of incidence and (ii) ...
... separates this medium from another, then a part of the light comes back into the first medium in a definite direction. This is called reflection of light. The surface from which reflection takes place is called a reflector. The amount of light reflected depends on (i) the angle of incidence and (ii) ...
2-Day Intensive Training
... • The optical core and planar waveguide layers are made of Silica (SiO2) which is deposited unto a Silicon (Si) wafer ...
... • The optical core and planar waveguide layers are made of Silica (SiO2) which is deposited unto a Silicon (Si) wafer ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 39 – Review
... (a) Write the Mueller matrices for each component (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmit ...
... (a) Write the Mueller matrices for each component (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmit ...
ECEN 4616/5616 “Optoelectronic System Design” MWF 1:00 → 1:50
... Slower than Fourier, but more adaptable to complex objects. ...
... Slower than Fourier, but more adaptable to complex objects. ...
Instructions - Physics Internal Website
... in the figure. (δ is the angle the reflected ray makes with the incident ray.) 9. (10 pts.) Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation similar to visible light in every way other than their lower frequency. When radio waves travel through ice, you can consider to be the same as light travel ...
... in the figure. (δ is the angle the reflected ray makes with the incident ray.) 9. (10 pts.) Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation similar to visible light in every way other than their lower frequency. When radio waves travel through ice, you can consider to be the same as light travel ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.