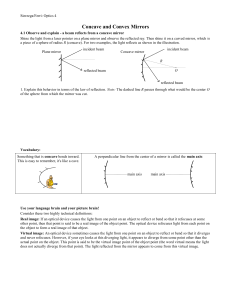
In the figure shown above, an object is placed a distance in front of a
... determine the location of the image due to the lens (technically two rays should suffice): 1. Parallel to the optical axis through the focus 2. Through the focus and then parallel to the optical axis 3. Through the optical center ...
... determine the location of the image due to the lens (technically two rays should suffice): 1. Parallel to the optical axis through the focus 2. Through the focus and then parallel to the optical axis 3. Through the optical center ...
Rejection of two-photon fluorescence background in
... beam in the back aperture of the focusing objective. While most TPEF applications involving deformable mirrors aim at improving the quality of a laser-beam focus in thick tissue using adaptive optics [9, 10], our strategy is just the opposite: we purposefully degrade the quality of the focus by intr ...
... beam in the back aperture of the focusing objective. While most TPEF applications involving deformable mirrors aim at improving the quality of a laser-beam focus in thick tissue using adaptive optics [9, 10], our strategy is just the opposite: we purposefully degrade the quality of the focus by intr ...
Critical angle - Kelso High School
... 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out about interference in this unit. Tutorial ques ...
... 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out about interference in this unit. Tutorial ques ...
pp. 273
... match the diffraction angle of the orders to be spatially filtered. Thus, when first order spectra are being filtered, a prism is selected with a diopter number of 100 X/p. In this case, the spatial filter aperture remains fixed on the optical axis of the field lens and separation of the various ima ...
... match the diffraction angle of the orders to be spatially filtered. Thus, when first order spectra are being filtered, a prism is selected with a diopter number of 100 X/p. In this case, the spatial filter aperture remains fixed on the optical axis of the field lens and separation of the various ima ...
Optics_pal_mac_2012
... (17) A hydrogen electron transitions from n=3 to n=1. The electron ______ a photon. (18) The photon has an energy of ________ eV. (19) The photon has an energy of _______ J. (20) The frequency of the photon is __________ Hz. (21) The wavelength o f the photon is ________ m. (22) The photon (is/is n ...
... (17) A hydrogen electron transitions from n=3 to n=1. The electron ______ a photon. (18) The photon has an energy of ________ eV. (19) The photon has an energy of _______ J. (20) The frequency of the photon is __________ Hz. (21) The wavelength o f the photon is ________ m. (22) The photon (is/is n ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... All large modern telescopes are reflectors • Since light passes through the lens of a refracting telescope, • You need to make the lens from clear, highquality glass with precisely shaped surfaces • It is easier to make a high-quality mirror than a ...
... All large modern telescopes are reflectors • Since light passes through the lens of a refracting telescope, • You need to make the lens from clear, highquality glass with precisely shaped surfaces • It is easier to make a high-quality mirror than a ...
lecture23
... Summary of Sign Conventions Here’s a summary of the mirror and lens (coming soon) sign conventions Object Distance. When the object is on the same side as the incoming light, the object distance is positive (otherwise is negative). Image Distance. When the image is on the same side as the outgoing ...
... Summary of Sign Conventions Here’s a summary of the mirror and lens (coming soon) sign conventions Object Distance. When the object is on the same side as the incoming light, the object distance is positive (otherwise is negative). Image Distance. When the image is on the same side as the outgoing ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Keeps the slide in place on the stage. Stage clips Location where the slide is placed. Contains an opening that lets light pass through. Stage Controls the amount of light that enters the stage. Diaphragm Provides light for viewing the specimen. Light This is the bottom of the microscope and it supp ...
... Keeps the slide in place on the stage. Stage clips Location where the slide is placed. Contains an opening that lets light pass through. Stage Controls the amount of light that enters the stage. Diaphragm Provides light for viewing the specimen. Light This is the bottom of the microscope and it supp ...
Much Physics - Little Effort
... In order to have object and image in focus at the same time, they must be placed at an equal distance to the eye. In this case object distance and image distance are the same and the magnification factor is 1. It may be proved quite accurately, whether magnification 1 has in fact been obtained, if o ...
... In order to have object and image in focus at the same time, they must be placed at an equal distance to the eye. In this case object distance and image distance are the same and the magnification factor is 1. It may be proved quite accurately, whether magnification 1 has in fact been obtained, if o ...
C. Huang, X. Wu, H. Liu, B. Aldalali, J.A. Rogers and H. Jiang
... exposure to the image. In general, the focusing behavior of our artificial RSCEs is equivalent to that by a spherical mirror with the same radius of curvature r (see the bottom half of the sphere in Figure S1a). Since the height of each square tube (i.e. 60 µm) is much smaller than r (i.e. 1.1 cm) o ...
... exposure to the image. In general, the focusing behavior of our artificial RSCEs is equivalent to that by a spherical mirror with the same radius of curvature r (see the bottom half of the sphere in Figure S1a). Since the height of each square tube (i.e. 60 µm) is much smaller than r (i.e. 1.1 cm) o ...
Lecture 16 - Purdue Physics
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
document
... • The image that is formed by the concave mirror is not virtual. • Rays of light pass through the location of the image. • A real image is formed when light rays converge to form the image. • When an object is farther from a concave mirror than twice the focal length, the image that is formed is rea ...
... • The image that is formed by the concave mirror is not virtual. • Rays of light pass through the location of the image. • A real image is formed when light rays converge to form the image. • When an object is farther from a concave mirror than twice the focal length, the image that is formed is rea ...
OPTICAL MODELING
... The design of a complete system level modeling and simulation tool for optical micro-systems is the focus of our research . We use a rigorous optical modeling technique based on the rigorous Scalar Rayleigh-Sommerfeld formulation, which is efficiently solved with an angular spectrum approach. Our cu ...
... The design of a complete system level modeling and simulation tool for optical micro-systems is the focus of our research . We use a rigorous optical modeling technique based on the rigorous Scalar Rayleigh-Sommerfeld formulation, which is efficiently solved with an angular spectrum approach. Our cu ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.