Document
... 3.18. Defects caused by reflections • We have assumed that the paraxial approximation applies in that all rays make small angles with respect to the optical axis. We also assume that the rays strike close to th e centre of the mirror. • In real systems the rays hit the whole mirror. We find that ray ...
... 3.18. Defects caused by reflections • We have assumed that the paraxial approximation applies in that all rays make small angles with respect to the optical axis. We also assume that the rays strike close to th e centre of the mirror. • In real systems the rays hit the whole mirror. We find that ray ...
Technical Information on Optics
... Mechanical device which limits the path of light rays between the object and image planes of an optical imaging forming system. Astigmatism Aberration which occurs in an image formation due to skew rays. Astigmatism is characterized by two different focal positions in two perpendicular planes (merid ...
... Mechanical device which limits the path of light rays between the object and image planes of an optical imaging forming system. Astigmatism Aberration which occurs in an image formation due to skew rays. Astigmatism is characterized by two different focal positions in two perpendicular planes (merid ...
TAPERED OPTICAL FIBER PLATFORM FOR HIGH SENSITIVITY
... due to hardware misalignments, atmospheric turbulence, and many other causes of optical path differences (OPD). Common synthesis techniques include incoherent and coherent methods. Incoherent methods utilize passive illumination and adaptive optics while coherent methods rely on active illumination ...
... due to hardware misalignments, atmospheric turbulence, and many other causes of optical path differences (OPD). Common synthesis techniques include incoherent and coherent methods. Incoherent methods utilize passive illumination and adaptive optics while coherent methods rely on active illumination ...
Transformation-designed optical elements
... The transformation method allows one to design continuous media that exert precise and arbitrary control over a field, particularly the electromagnetic field[1][2][3][4]. Even the challenging problem of reflectionless design in arbitrary geometries is quite straight foward. The resulting material sp ...
... The transformation method allows one to design continuous media that exert precise and arbitrary control over a field, particularly the electromagnetic field[1][2][3][4]. Even the challenging problem of reflectionless design in arbitrary geometries is quite straight foward. The resulting material sp ...
Principles and Clinical Applications of Ray-Tracing
... of degradation: A) Diffraction B) Scattering and c) Optical Aberration. Optical aberrations are the most important source of impairment of the quality of the optical system. The definition of an optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxia ...
... of degradation: A) Diffraction B) Scattering and c) Optical Aberration. Optical aberrations are the most important source of impairment of the quality of the optical system. The definition of an optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxia ...
Physics 212: General Physics II
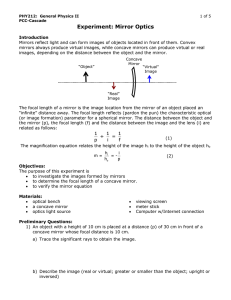
... (or image formation) parameter for a spherical mirror. The distance between the object and the mirror (p), the focal length (f) and the distance between the image and the lens (i) are related as follows: ...
... (or image formation) parameter for a spherical mirror. The distance between the object and the mirror (p), the focal length (f) and the distance between the image and the lens (i) are related as follows: ...
Low-Cost Tunable Adaptive Optics.pdf
... be tuned by simply varying the amplitude of the driving signal. This has applications in many fields including machine and weapon vision where it is an advantage to have a single compact and versatile optical element that can be electrically adjusted without any moving parts. Similarly, a variable f ...
... be tuned by simply varying the amplitude of the driving signal. This has applications in many fields including machine and weapon vision where it is an advantage to have a single compact and versatile optical element that can be electrically adjusted without any moving parts. Similarly, a variable f ...
5377 17paper
... It is desirable to design an aberration test target so that it will sample a lens pupil in the most beneficial way. Since aberrations have unique character in the manner which they influence specific portions of a lens pupil, the test target can be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular ...
... It is desirable to design an aberration test target so that it will sample a lens pupil in the most beneficial way. Since aberrations have unique character in the manner which they influence specific portions of a lens pupil, the test target can be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular ...
CE-PHY II - OPTICS
... A rear-view driving mirror may be either plane or convex. Which of the following is/ace the advantage(s) of using a convex mirror over a plane mirror ? ...
... A rear-view driving mirror may be either plane or convex. Which of the following is/ace the advantage(s) of using a convex mirror over a plane mirror ? ...
Review of paper entitled “Athermalization of optical instruments from
... equal - of the mount. In a simple two mirror Cassegrain system, the author suggests that any design can be athemalized. The simplest method of accomplishing this is to utilize the same material for the mirrors as the housing. In other words, if you use aluminum mirrors and an aluminum housing, your ...
... equal - of the mount. In a simple two mirror Cassegrain system, the author suggests that any design can be athemalized. The simplest method of accomplishing this is to utilize the same material for the mirrors as the housing. In other words, if you use aluminum mirrors and an aluminum housing, your ...
Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2
... To use this result you need to have the object at a distance more than 10f 2 (f is the focal length of the positive lens) or use a collimated laser beam. In this formula either f1 or f2 could be the focal length of the diverging lens. If the first lens is the positive lens then the separation distan ...
... To use this result you need to have the object at a distance more than 10f 2 (f is the focal length of the positive lens) or use a collimated laser beam. In this formula either f1 or f2 could be the focal length of the diverging lens. If the first lens is the positive lens then the separation distan ...
Adaptive Optics and the cone mosaic
... Additionally, "high-order aberrations", such as coma, spherical aberration, and trefoil, must also be corrected in order to achieve microscopic resolution. High-order aberrations, unlike low-order, are not stable over time, and may change with frequencies between 10 Hz and 100 Hz. The correction of ...
... Additionally, "high-order aberrations", such as coma, spherical aberration, and trefoil, must also be corrected in order to achieve microscopic resolution. High-order aberrations, unlike low-order, are not stable over time, and may change with frequencies between 10 Hz and 100 Hz. The correction of ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.


















![Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008539460_1-d375c81ee0822c3c0b88887d5bbb056f-300x300.png)