Reflecting And Refracting Light
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears – Always inverted ...
... Reflection Vocabulary • Real Image – – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL – Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears – Always inverted ...
Optical Prescriptions Spectacle Lenses
... “High index” Glass n = addition of titanium oxides. ...
... “High index” Glass n = addition of titanium oxides. ...
Reflection,Refraction, Lenses
... their patients. Optical fibres can also carry enormous amounts of information as pulses of light. ...
... their patients. Optical fibres can also carry enormous amounts of information as pulses of light. ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the ...
... imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the ...
The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
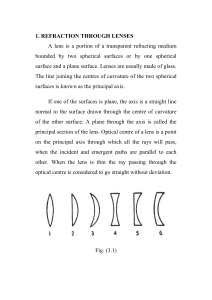
... beginning, lenses were simply biconvex (both surfaces are convex) or biconcave (both surfaces are concave). These lenses corrected refractive errors, but also produced aberrations. Aberration is the failure of a mirror or lens to bring light rays to a single focal point, producing a defective image. ...
... beginning, lenses were simply biconvex (both surfaces are convex) or biconcave (both surfaces are concave). These lenses corrected refractive errors, but also produced aberrations. Aberration is the failure of a mirror or lens to bring light rays to a single focal point, producing a defective image. ...
Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of
... Types of Mirrors and Lenses Plane Mirror – a mirror with a flat, reflective surface Convex Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves outward Concave Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves inward Lens – a transparent device with at least 1 curved surface that changes the di ...
... Types of Mirrors and Lenses Plane Mirror – a mirror with a flat, reflective surface Convex Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves outward Concave Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves inward Lens – a transparent device with at least 1 curved surface that changes the di ...
lecture5web
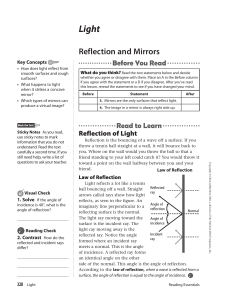
... hits that surface (and will be reflected or refracted) – First draw a tangent line to the curve (or tangent plane to the surface) – The normal is perpendicular to that line or plane and going through the point – Once you have drawn the normal you can draw the reflected or refracted ray ...
... hits that surface (and will be reflected or refracted) – First draw a tangent line to the curve (or tangent plane to the surface) – The normal is perpendicular to that line or plane and going through the point – Once you have drawn the normal you can draw the reflected or refracted ray ...
Laser Vibrometer Measurements of Objects Immersed
... enough light from the object to make an accurate measurement. In air, the index of refraction is close to one, the same as in a vacuum, and can be neglected. In a fluid, the index is much greater and must be taken into account by dividing the measured value by this factor. For example, a velocity me ...
... enough light from the object to make an accurate measurement. In air, the index of refraction is close to one, the same as in a vacuum, and can be neglected. In a fluid, the index is much greater and must be taken into account by dividing the measured value by this factor. For example, a velocity me ...
Chapter Notes
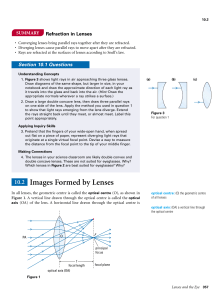
... Step 1: Draw an incident ray parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray of this will always be through the focus point. (note that the reflected ray had to be extended in order to go through the focus.) Step 2: Draw the next incident ray through the focus and point on the object into the mirr ...
... Step 1: Draw an incident ray parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray of this will always be through the focus point. (note that the reflected ray had to be extended in order to go through the focus.) Step 2: Draw the next incident ray through the focus and point on the object into the mirr ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... will be formed by a single ray, forming an inverted image that is in focus. ...
... will be formed by a single ray, forming an inverted image that is in focus. ...
Convolution in Imaging and the Optical Transfer Function Process
... What exactly is the modulation transfer function? How does it help us analyze the quality of an optical system? Well, we’ll first by looking at a very important concept, the Optical Transfer Function (OTF). The OTF of an optical system describes how the components of the system project light from an ...
... What exactly is the modulation transfer function? How does it help us analyze the quality of an optical system? Well, we’ll first by looking at a very important concept, the Optical Transfer Function (OTF). The OTF of an optical system describes how the components of the system project light from an ...
Light microscopy
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.