* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
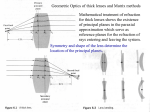
Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of Mirrors and Lenses Plane Mirror – a mirror with a flat, reflective surface Convex Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves outward Concave Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves inward Lens – a transparent device with at least 1 curved surface that changes the direction of light passing through it (refracts light) *Rays are refracted at the surfaces of lenses according to Snell’s Law* Converging Lens – a lens that causes parallel light rays to come together, so that they cross at a single focal point (convex lenses) Diverging Lens – a lens that causes parallel light rays to spread apart, so that they appear to emerge from the virtual focal point (concave lenses) Terms for Ray Diagrams Optical Centre (O) / Vertex (V) – the geometric centre of all lenses Optical Axis (OA) – an imaginary vertical line through the optical centre Principle Axis (PA) – a horizontal line drawn through the optical centre Focal Point (F) – the point on the principal axis through which a group of rays parallel to the principal axis are refracted *F = ½ C Focal length (f) – the distance between the focal point and the optical centre, measured along the principle axis Centre / Radius of Curvature (C) – the centre of a sphere whose surface has been used to make the mirror or lens OA O or V PA C F F f C Drawing Mirrors and Lenses 1. Plane Mirror 4. Convex Lens 2. Convex Mirror 3. Concave Mirror 5. Concave Lens 4 Image Characteristics – SALT S – Size or Magnification Is the image smaller, larger, or the same size in comparison to the object? A – Attitude Which way is the image oriented compared to the object: upright or inverted? L – Location Where is the image relative to the mirror or lens? Is the image behind or in front of the mirror or lens? Where is the image in relation to C and F? T – Type Is the image real or virtual? *Real images can be projected onto a screen. *Virtual images cannot be projected onto a screen. Ray Diagrams 1. Images in a Plane Mirror Ray diagrams as per our SONG F and C do not exist, as there is no radius of curvature Memorize SALT for a plane mirror S – image is the same size as the object A – image is upright L – image is the same distance behind the mirror, as the object is in front of the mirror T – image is virtual (image is behind mirror – rays converge behind mirror) 2. Images in a Convex Mirror F and C are on the right side of the mirror Always draw rays starting from the top of the object Solid lines are used on the left; dotted lines are used on the right Steps for Locating Image Draw a ray // to PA, stopping at the mirror. From the edge of the mirror, angle ruler through F on the right side of the mirror. Extend this ray backwards on the left. Draw a ray through C. Place a dot where the first 2 rays intersect. Draw a ray to O, until the mirror is reached. Angle the ruler downwards towards the left, so that the ruler intersects the point. Draw this ray. S – smaller A – upright L – behind mirror (between O and F) T – virtual ( rays converge behind mirror) See example on DOV Camera. 3. Images in a Concave Mirror 1 2 3 4 5 Steps for Locating Image For (1-3): Draw ray #1 // to PA, stopping at the mirror. Angle ruler, so the same ray is refracted through F. Draw ray #2 through F, touching mirror below PA. Continue this ray // to PA. Place a dot at the intersection. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that this ray reaches the point of intersection. All rays will be on left side of mirror with solid lines. For 4: Draw ray #1. Ray #2 cannot be drawn. Draw ray #3 to O, and then continue this ray // to ray #1. For 5: Draw ray #1. Extend the ray intersecting F backwards on the right side of the mirror using a dotted line. Ray #2 cannot be drawn. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that ray #1 and ray #3 are skew rays. Extend ray #3 backwards with a dotted line. Draw image. S A L T 1 Smaller than object 2 Same size Inverted At C 3 Larger than object Between F Beyond C &C Real (rays converge in front of mirror) See 5 DOV Camera examples. 4 No image (reflected rays are // and never converge) 5 Larger than object Upright Behind mirror Virtual (rays converge behind mirror) 4. Images in a Convex Lens 1 2 3 C 4 5 F F C Steps for Locating Image For (1-3): Draw ray #1 // to PA, stopping at lens. Extend this ray through F on the right side. Draw ray #2 through O, intersecting through ray #1. Place a dot where the 2 rays intersect. Draw ray #3 through F on the left side, stopping at lens. Continue ray // to PA, through the intersection point. For 4: Draw ray #1. Draw ray #2 through O, realizing rays will never converge (// rays). Ray #3 cannot be drawn. For 5: Draw ray #1. Extend the ray intersecting F backwards on the left side of the lens using a dotted line. Draw ray #2 through O, ensuring ray #1 and ray #2 are skew rays. Extend ray #2 backwards with a dotted line. Draw image. S A L T 1 Smaller than object Between F &C 2 Same size Inverted At C 3 Larger than object Beyond C Real (rays converge after going through lens) See 5 DOV Camera examples. 4 No image (refracted rays are // and never converge) 5 Larger than object Upright Same side as object (left of object) Virtual (rays must be extended back to converge) 5. Images in a Concave Lens Steps for Locating Image Draw ray #1 // to PA, stopping at lens. Angle ruler so that ray passes through F on the left side with a dotted line. Extend this ray backwards on the right side with a solid line. Draw ray #2 through F on the right side. This ray will be solid on the left, and dotted on the right. Angle ruler to create ray #3 // to PA, ensuring there is a POI with the lens. Ray must be dotted on left and solid on the right. Draw ray #4 through O with a solid line. Ray #1, 3, and 4 will intersect. S – smaller than object A – upright L – same side as object (between F and lens) T – virtual (rays must be extended back to converge) See DOV Camera example.