24.1 Physics 6C Geometrical Optics
... A concave makeup mirror with radius of curvature 0.5m is held 0.2m from a woman’s face. Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then ...
... A concave makeup mirror with radius of curvature 0.5m is held 0.2m from a woman’s face. Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then ...
Off-axis focal shift for rotationally nonsymmetric screens
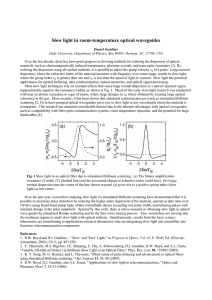
... the off-axis line. The second factor is the amplitude representation of the inverse-square law and is responsible for the focal-shift effect along the abovementioned straight lines. For our present discussion, we start by considering a spherical monochromatic wave emerging from a rotationally nonsym ...
... the off-axis line. The second factor is the amplitude representation of the inverse-square law and is responsible for the focal-shift effect along the abovementioned straight lines. For our present discussion, we start by considering a spherical monochromatic wave emerging from a rotationally nonsym ...
LM Ch 8: Bright Field
... from one to another, even to the oil objectives. The idea of parfocality of objectives was invented by Abbe. One precaution: avoid getting oil on your dry objectives. This will make an image through them very hazy and irregular. Remember to adjust the field iris and the aperture iris when changing f ...
... from one to another, even to the oil objectives. The idea of parfocality of objectives was invented by Abbe. One precaution: avoid getting oil on your dry objectives. This will make an image through them very hazy and irregular. Remember to adjust the field iris and the aperture iris when changing f ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
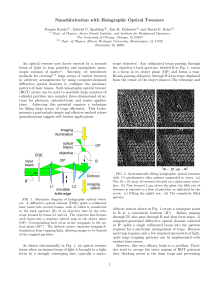
... materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adjust the group velocity υg of a pulse. Large normal dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increas ...
... materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adjust the group velocity υg of a pulse. Large normal dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increas ...
Velocity of sound in liquids
... Fig. 2 shows the relationship between variations in sound pressure %p and the location x for four phases of a stationary wave. The refractive index of the liquid also changes because of the pressure variations, and the change in refractive index %n can be regarded as proportional to the pressure var ...
... Fig. 2 shows the relationship between variations in sound pressure %p and the location x for four phases of a stationary wave. The refractive index of the liquid also changes because of the pressure variations, and the change in refractive index %n can be regarded as proportional to the pressure var ...
op_bessel1 - School of Physics
... UNIFORMLY ILLUMINATED CIRCULAR APERTURE Diffraction in its simplest description is any deviation from geometrical optics (light travels in straight lines) that result from an obstruction of a wavefront of light. A hole in an opaque screen represents an obstruction. On an observation screen placed af ...
... UNIFORMLY ILLUMINATED CIRCULAR APERTURE Diffraction in its simplest description is any deviation from geometrical optics (light travels in straight lines) that result from an obstruction of a wavefront of light. A hole in an opaque screen represents an obstruction. On an observation screen placed af ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction from a circular aperture
... UNIFORMLY ILLUMINATED CIRCULAR APERTURE Diffraction in its simplest description is any deviation from geometrical optics (light travels in straight lines) that result from an obstruction of a wavefront of light. A hole in an opaque screen represents an obstruction. On an observation screen placed af ...
... UNIFORMLY ILLUMINATED CIRCULAR APERTURE Diffraction in its simplest description is any deviation from geometrical optics (light travels in straight lines) that result from an obstruction of a wavefront of light. A hole in an opaque screen represents an obstruction. On an observation screen placed af ...
Abstract : Fiber interfaces between single atoms and single photons Sébastien Garcia,
... miniaturization, stability et flexibility provided by optical fibers as light wave-guides, we present two experiments where optical fibers are used as interfaces for single atoms trapping and single photons collection into their guided modes. The first experiment combines a singlemode fiber with an ...
... miniaturization, stability et flexibility provided by optical fibers as light wave-guides, we present two experiments where optical fibers are used as interfaces for single atoms trapping and single photons collection into their guided modes. The first experiment combines a singlemode fiber with an ...
Lecture 21 Wave Optics
... Resolution limit -- Rayleigh’s criteria For circular aperture, slightly different: ...
... Resolution limit -- Rayleigh’s criteria For circular aperture, slightly different: ...
Expressive Chromatic Accumulation Buffering for Defocus Blur
... displace along the line from the sensor center. In other words, the transverse magnification is chromatic. Incorporation of the lateral aberration in the thinlens model can done in two ways. We can shift the lens so that chief rays pass through the shifted lens center (Fig. 6a), or scale objects to ...
... displace along the line from the sensor center. In other words, the transverse magnification is chromatic. Incorporation of the lateral aberration in the thinlens model can done in two ways. We can shift the lens so that chief rays pass through the shifted lens center (Fig. 6a), or scale objects to ...
Chapter 33
... A convex meniscus lens is made from glass with n = 1.50. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is 22.4 cm and that of the concave surface is 46.2 cm. (a) What is the focal length? (b) Where will the image be for an object 2.00 m away? ...
... A convex meniscus lens is made from glass with n = 1.50. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is 22.4 cm and that of the concave surface is 46.2 cm. (a) What is the focal length? (b) Where will the image be for an object 2.00 m away? ...
Measuring the Real Point Spread Function of High Numerical
... Pupil Function P(r, q), where r is the normalized radial coordinate in the pupil plane and m is the azimuthal angle in the same plane. Both amplitude and phase aberrations can be present in a lens, but it is the latter that usually play the dominant role. The amplitude aberrations are typically limi ...
... Pupil Function P(r, q), where r is the normalized radial coordinate in the pupil plane and m is the azimuthal angle in the same plane. Both amplitude and phase aberrations can be present in a lens, but it is the latter that usually play the dominant role. The amplitude aberrations are typically limi ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.