Holographic optics for a matched-filter optical
... with increasing u I in the filter plane and is maximum for u coordinates at the edge of the filter plane. The justification for the space-invariance approximation is as follows. Since the purpose of the matched filter optical processor is to produce a sharp peak in the output plane, it is the value ...
... with increasing u I in the filter plane and is maximum for u coordinates at the edge of the filter plane. The justification for the space-invariance approximation is as follows. Since the purpose of the matched filter optical processor is to produce a sharp peak in the output plane, it is the value ...
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope
... professional phase contrast devices, but it can serve its purpose quite well. Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the si ...
... professional phase contrast devices, but it can serve its purpose quite well. Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the si ...
Ref. “Optical Materials”
... fiber can be used for the in-situ detection of contaminants and water in soil. A chalcogenide fiber is connected to a headened optical analysis system (top and center), and is inserted into the soil to be tested. The IR signals reflected from the soil and transmitted through the fiber to the FTIR in ...
... fiber can be used for the in-situ detection of contaminants and water in soil. A chalcogenide fiber is connected to a headened optical analysis system (top and center), and is inserted into the soil to be tested. The IR signals reflected from the soil and transmitted through the fiber to the FTIR in ...
Optics - MIT Fab Lab
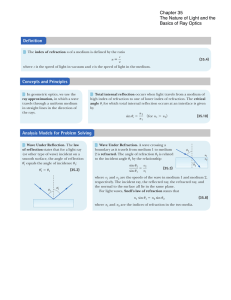
... This is Snell’s Law, discovered experimentally by Willebrord Snell around 1621. Light rays bend when they cross the interface between media with different indices of refraction. The index of refraction can depend on wavelength and so different colors are bent in different directions; this gives rise ...
... This is Snell’s Law, discovered experimentally by Willebrord Snell around 1621. Light rays bend when they cross the interface between media with different indices of refraction. The index of refraction can depend on wavelength and so different colors are bent in different directions; this gives rise ...
Lens Effectivity (WP)
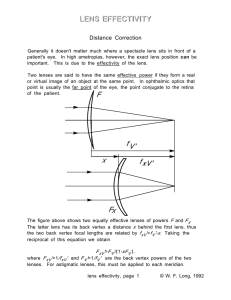
... The emmetrope accommodates 1/b =1/(0.33m+0.017m)=+2.88D. For the eight diopter myope, the vergence leaving the spectacle lens is B G '=-8.00D+1/(-0.33m)=-11.00D. The vergence of light reaching the first principal plane of the eye is B P =-11D/[1-(0.017m)(-11D)]=-9.267D. The ocular refraction (princi ...
... The emmetrope accommodates 1/b =1/(0.33m+0.017m)=+2.88D. For the eight diopter myope, the vergence leaving the spectacle lens is B G '=-8.00D+1/(-0.33m)=-11.00D. The vergence of light reaching the first principal plane of the eye is B P =-11D/[1-(0.017m)(-11D)]=-9.267D. The ocular refraction (princi ...
2 Fabry-Perot resonator
... 3 Beam Tracing and Mirror Resonators Ray tracing is an practical implementation of paraxial ray analysis in optical system design. It’s foundation is the paraxial approximation of Snell, that is sin θ ≃ θ. The thin lens equation 1/ f = 1/a + 1/b is only valid in that case. ...
... 3 Beam Tracing and Mirror Resonators Ray tracing is an practical implementation of paraxial ray analysis in optical system design. It’s foundation is the paraxial approximation of Snell, that is sin θ ≃ θ. The thin lens equation 1/ f = 1/a + 1/b is only valid in that case. ...
Document
... - Structure. Less dense polymorphs of a particular material will have a more open structure and thus a lower n than their denser counterparts. We can illustrate this with the case of SiO2, which can exist as a glass or in several crystallographic forms: nglass = 1.46, ntridymite = 1.47, ncristobalit ...
... - Structure. Less dense polymorphs of a particular material will have a more open structure and thus a lower n than their denser counterparts. We can illustrate this with the case of SiO2, which can exist as a glass or in several crystallographic forms: nglass = 1.46, ntridymite = 1.47, ncristobalit ...
P3.7.4.5 - LD Didactic
... filled with quartz sand is investigated (see Fig. 2). The microwave ray impinges vertically on the outer surface, which has a circular curvature, so that no refraction takes place there. Refraction does take place at the flat outer surface in the direction of air as medium, whose refractive index n2 ...
... filled with quartz sand is investigated (see Fig. 2). The microwave ray impinges vertically on the outer surface, which has a circular curvature, so that no refraction takes place there. Refraction does take place at the flat outer surface in the direction of air as medium, whose refractive index n2 ...
Optics Studio Manual - Department of Physics
... observation screen. • Form an image of the object on the screen using a positive lens. Measure the image and object distances. Compare to the paraxial formula. Vary your object distances from much greater than the focal length f to twice the focal length (the “2f point,” an important point of symmet ...
... observation screen. • Form an image of the object on the screen using a positive lens. Measure the image and object distances. Compare to the paraxial formula. Vary your object distances from much greater than the focal length f to twice the focal length (the “2f point,” an important point of symmet ...
Active Aperture Control and Sensor Modulation for Flexible Imaging
... blur caused by the filter mask. Because the blurred masks on the SLM overlap, a special control algorithm is required to find the optimal mask which can detect all the scene points. In contrast, the third design is capable to control the response of individual pixels on the sensor due to the fact th ...
... blur caused by the filter mask. Because the blurred masks on the SLM overlap, a special control algorithm is required to find the optimal mask which can detect all the scene points. In contrast, the third design is capable to control the response of individual pixels on the sensor due to the fact th ...
14_04_2014 - IB Phys..
... • The light that enters an optic fibre travels down the length of the fibre and the arrival of light is registered by a photodiode • In the absence of any light, falling on the photodiode, the current is zero • When light of a specific wavelength falls on the photodiode, a current flows. The magnitu ...
... • The light that enters an optic fibre travels down the length of the fibre and the arrival of light is registered by a photodiode • In the absence of any light, falling on the photodiode, the current is zero • When light of a specific wavelength falls on the photodiode, a current flows. The magnitu ...
Powerpoint Slides
... The maximas in intensity occur when the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
... The maximas in intensity occur when the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
Optical Mineralogy: Introduction
... maximum illumination. Note that this is the opposite of regular interference discussed earlier, the reasons being that the two waves are vibrating in perpendicular directions, and that we still have to deal with an additional layer represented by the analyzer. When white light is used instead of mon ...
... maximum illumination. Note that this is the opposite of regular interference discussed earlier, the reasons being that the two waves are vibrating in perpendicular directions, and that we still have to deal with an additional layer represented by the analyzer. When white light is used instead of mon ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.