acknowledgements
... between two adjacent lines in the scale is 50 m. b) Reconstruction of DOE in a) given by He-Ne laser light (transmission mode). The micropositioning device can displace the substrate by linear increments as small as 10 m. However, due to the hole dimensions and the film distortions, a high qualit ...
... between two adjacent lines in the scale is 50 m. b) Reconstruction of DOE in a) given by He-Ne laser light (transmission mode). The micropositioning device can displace the substrate by linear increments as small as 10 m. However, due to the hole dimensions and the film distortions, a high qualit ...
The Fresnel Biprism
... tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was meant to be at the centre of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib wa ...
... tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was meant to be at the centre of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib wa ...
Representation of Wavefront Aberrations
... In everyday life we measure distances in physical units of meters. However, in optics it is common to measure distances with a ruler that is calibrated in wavelengths of light. Such a ruler effectively measures the number of times light must oscillate in traveling from the object to the image. If al ...
... In everyday life we measure distances in physical units of meters. However, in optics it is common to measure distances with a ruler that is calibrated in wavelengths of light. Such a ruler effectively measures the number of times light must oscillate in traveling from the object to the image. If al ...
Structure and optical properties of reconstructed Si and Ge surfaces
... School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin December 5, 2013 ...
... School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin December 5, 2013 ...
Experiment 15
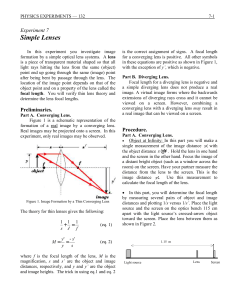
... clear image of the crossed-arrow object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. Measure the object size and the image size for this position of the lens. 2. Without moving the screen or the light source, move the lens to a second position where the image is in fo ...
... clear image of the crossed-arrow object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. Measure the object size and the image size for this position of the lens. 2. Without moving the screen or the light source, move the lens to a second position where the image is in fo ...
ray_optics_su2014
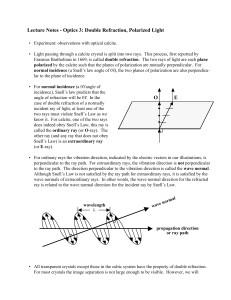
... normal when enters media with lower wavespeed (i.e. higher index of refraction) ...
... normal when enters media with lower wavespeed (i.e. higher index of refraction) ...
Vision Improvement by Correcting Higher
... and visual acuity under white light condition with the AO system. Even though the AO system is a powerful and noninvasive tool to correct the higherorder aberrations, it is an impractical correction method because of the size of the entire system. Laser refractive surgery is also available for custo ...
... and visual acuity under white light condition with the AO system. Even though the AO system is a powerful and noninvasive tool to correct the higherorder aberrations, it is an impractical correction method because of the size of the entire system. Laser refractive surgery is also available for custo ...
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light - FSU
... quarter-wave plate is rotated through an angle α so that its axis lies along one of the axes of the ellipse, it will add or subtract a phase difference of π/2 to the existing phase difference of π/2 between the component simple harmonic motions along OB and OC. Then we will have two simple harmonic ...
... quarter-wave plate is rotated through an angle α so that its axis lies along one of the axes of the ellipse, it will add or subtract a phase difference of π/2 to the existing phase difference of π/2 between the component simple harmonic motions along OB and OC. Then we will have two simple harmonic ...
Rev.Sci.Instrum.
... as an inhomogeneity of the state of polarization of the reflected beam, leading to a dark-bright pattern at the CCD camera. Also waveguide modes or surface plasmons can be used for the visualization of inhomogeneities using similar instrumentation. An example was provided in Ref. 14, where the effic ...
... as an inhomogeneity of the state of polarization of the reflected beam, leading to a dark-bright pattern at the CCD camera. Also waveguide modes or surface plasmons can be used for the visualization of inhomogeneities using similar instrumentation. An example was provided in Ref. 14, where the effic ...
Optical aberration
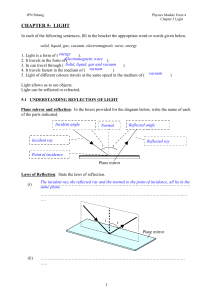
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.