chapter9-Section4
... Rays striking the lens at different points do not cross the optical axis at the same place. ...
... Rays striking the lens at different points do not cross the optical axis at the same place. ...
CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
... gather more light from distant objects. As a result, images appear to be much ____________ and therefore can be magnified to a greater extent, revealing more detail. o Have ____________ focal lengths than lenses in a microscope in order to view objects far away. o ____________ telescopes – bend ...
... gather more light from distant objects. As a result, images appear to be much ____________ and therefore can be magnified to a greater extent, revealing more detail. o Have ____________ focal lengths than lenses in a microscope in order to view objects far away. o ____________ telescopes – bend ...
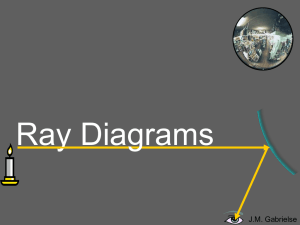
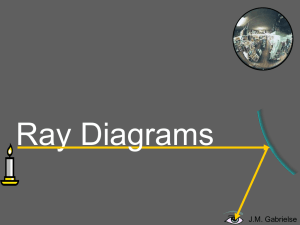
Ray Diagrams Powerpoint
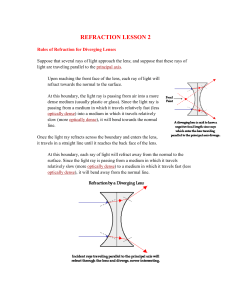
... θr When light passes back out of the glass into the air, it is refracted away from the normal. ...
... θr When light passes back out of the glass into the air, it is refracted away from the normal. ...
Document
... θr When light passes back out of the glass into the air, it is refracted away from the normal. ...
... θr When light passes back out of the glass into the air, it is refracted away from the normal. ...
Material and design choices for a small movement +
... the precision optical platform needs to be able to be moved and then moved back to the same location within the range of motion throughout the life time of the system. Orientation Independence; many times it is unknown what orientation relative to the gravity field will be the final orientation of t ...
... the precision optical platform needs to be able to be moved and then moved back to the same location within the range of motion throughout the life time of the system. Orientation Independence; many times it is unknown what orientation relative to the gravity field will be the final orientation of t ...
Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle File
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
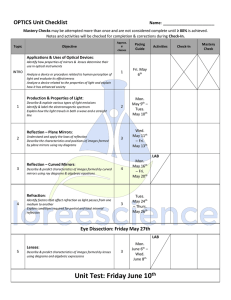
Student Checklist
... ALL mastery checks should be completed, demonstrating mastery (≥ 80%), by the dates indicated. If they are not completed by this time they must be completed after school. Check-Ins must also be completed by the dates indicated. ...
... ALL mastery checks should be completed, demonstrating mastery (≥ 80%), by the dates indicated. If they are not completed by this time they must be completed after school. Check-Ins must also be completed by the dates indicated. ...
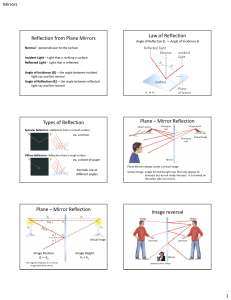
Reflection from Plane Mirrors Law of Reflection Types of Reflection
... • Incident rays parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focal point upon reflection. • Incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection. • The Normal Lines always go through the C ...
... • Incident rays parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focal point upon reflection. • Incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection. • The Normal Lines always go through the C ...
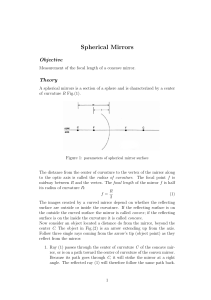
Spherical Mirrors
... Figure 2: concave mirror All three of these reflected rays intersect at a single point. This is the image point (the tip of the arrow). The three rays diverge as they continue beyond this image point. If you place your eye in that region (beyond the image), the diverging rays will create another ima ...
... Figure 2: concave mirror All three of these reflected rays intersect at a single point. This is the image point (the tip of the arrow). The three rays diverge as they continue beyond this image point. If you place your eye in that region (beyond the image), the diverging rays will create another ima ...
Optics Ic
... camera, placed at the end of the rail opposite the mirror. 3) For our first experiments, mount the LED near the end of the track by the mirror. Place the small mounted screen about 30 cm down the track from the LED. Place a plano-convex lens of focal length (f) 50 mm (labeled PCX50) on the track bet ...
... camera, placed at the end of the rail opposite the mirror. 3) For our first experiments, mount the LED near the end of the track by the mirror. Place the small mounted screen about 30 cm down the track from the LED. Place a plano-convex lens of focal length (f) 50 mm (labeled PCX50) on the track bet ...
Lecture-6-Optics
... determines the light gathering ability of the lens. Field Stop (F.S.) – Limits the size or angular breadth of the object. In a camera, the edge of the film itself bounds the image plane and becomes the F.S. Entrance Pupil – Image of the A.S. as seen from the object side of the lens system (below). E ...
... determines the light gathering ability of the lens. Field Stop (F.S.) – Limits the size or angular breadth of the object. In a camera, the edge of the film itself bounds the image plane and becomes the F.S. Entrance Pupil – Image of the A.S. as seen from the object side of the lens system (below). E ...
Reduction of ocular chromatic aberration by a blue light filtering
... • The blue light filtering chromophore was designed to protect the retina against phototoxicity mediated by blue light1 • Among wavelengths in the visible spectrum, blue light is most phototoxic2 and the most strongly aberrated longitudinally (versus chromatic mean)3 • The correction of chromatic ab ...
... • The blue light filtering chromophore was designed to protect the retina against phototoxicity mediated by blue light1 • Among wavelengths in the visible spectrum, blue light is most phototoxic2 and the most strongly aberrated longitudinally (versus chromatic mean)3 • The correction of chromatic ab ...
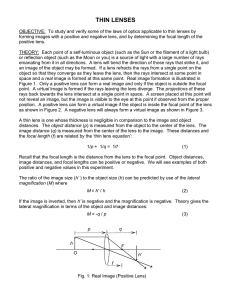
Thin Lenses
... OBJECTIVE: To study and verify some of the laws of optics applicable to thin lenses by forming images with a positive and negative lens, and by determining the focal length of the positive lens. THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflect ...
... OBJECTIVE: To study and verify some of the laws of optics applicable to thin lenses by forming images with a positive and negative lens, and by determining the focal length of the positive lens. THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflect ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.