doc - University of Rochester
... Ghost imaging with entangled photon pairs (biphotons) has been extensively discussed in the literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this ...
... Ghost imaging with entangled photon pairs (biphotons) has been extensively discussed in the literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this ...
GGN PUBLIC SCHOOL, LUDHIANA XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT
... 2. The radius of curvature of the faces of a double concave lens are 10cm and 15 cm. if focal length is 12 cm, what is the refractive index of the glass?[1.5] 3. A biconvex lens has a focal length half the radius of curvature of either surface. What is the refractive index of lens material? [2] 4. T ...
... 2. The radius of curvature of the faces of a double concave lens are 10cm and 15 cm. if focal length is 12 cm, what is the refractive index of the glass?[1.5] 3. A biconvex lens has a focal length half the radius of curvature of either surface. What is the refractive index of lens material? [2] 4. T ...
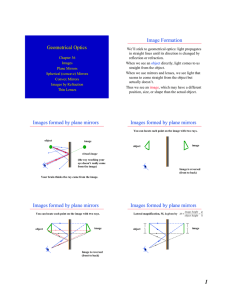
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
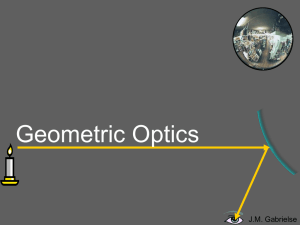
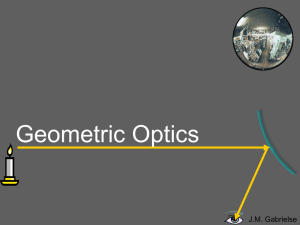
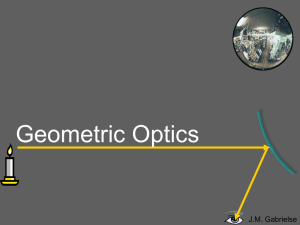
... Parabolic Mirrors • These present the concept of a focal point the point to which the optic brings a set of parallel rays together. • Parallel rays come from objects that are very far away. • Parabolas are hard to make. It’s much easier to make spherical optics, so that’s what we’ll examine next. ...
... Parabolic Mirrors • These present the concept of a focal point the point to which the optic brings a set of parallel rays together. • Parallel rays come from objects that are very far away. • Parabolas are hard to make. It’s much easier to make spherical optics, so that’s what we’ll examine next. ...
Metamaterials
... Bloch wave fcn: Product of phase factor and periodic fcn. Mentioned before in Kenneth’s presentation. ...
... Bloch wave fcn: Product of phase factor and periodic fcn. Mentioned before in Kenneth’s presentation. ...
Stops: Finite nature of lenses affects the energy and... and imaged by optical systems
... determines the light gathering ability of the lens. Field Stop (F.S.) – Limits the size or angular breadth of the object. In a camera, the edge of the film itself bounds the image plane and becomes the F.S. Entrance Pupil – Image of the A.S. as seen from the object side of the lens system (below). E ...
... determines the light gathering ability of the lens. Field Stop (F.S.) – Limits the size or angular breadth of the object. In a camera, the edge of the film itself bounds the image plane and becomes the F.S. Entrance Pupil – Image of the A.S. as seen from the object side of the lens system (below). E ...
How I discovered phase contrast
... first case, the diffraction is caused by the unequal amplitudes of the light passing the strips, in the second case by the unequal light paths, i.e. by the unequal phases. I therefore distinguish the two by calling the first kind an amplitude grating, the second a phase grating. Or in the general ca ...
... first case, the diffraction is caused by the unequal amplitudes of the light passing the strips, in the second case by the unequal light paths, i.e. by the unequal phases. I therefore distinguish the two by calling the first kind an amplitude grating, the second a phase grating. Or in the general ca ...
Lenses: Bending Light
... Create: Your task is to prepare an engaging visual presentation about how lenses have changed the world. You may choose to focus on one particular scientist or one type of optical technology. In setting the scene for your presentation, you should include a brief summary of the historical and politic ...
... Create: Your task is to prepare an engaging visual presentation about how lenses have changed the world. You may choose to focus on one particular scientist or one type of optical technology. In setting the scene for your presentation, you should include a brief summary of the historical and politic ...
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section XII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... where n ≡ index of refraction of the lens, f ≡ focal length (i.e., distance from the lens to the focal point F ), R1 ≡ radius of curvature of front surface, and R2 ≡ radius of curvature of back surface. 6. The variables in Eqs. (XII-10, 11, 12) take on positive or negative values based upon their re ...
... where n ≡ index of refraction of the lens, f ≡ focal length (i.e., distance from the lens to the focal point F ), R1 ≡ radius of curvature of front surface, and R2 ≡ radius of curvature of back surface. 6. The variables in Eqs. (XII-10, 11, 12) take on positive or negative values based upon their re ...
Intraocular Lenses
... concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference with waves from some of the zones (OPD = m, m=intege ...
... concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference with waves from some of the zones (OPD = m, m=intege ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
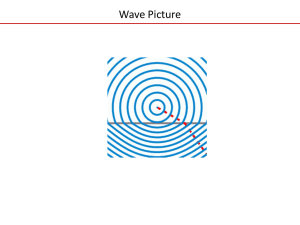
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Glencoe Physics Chapter 16
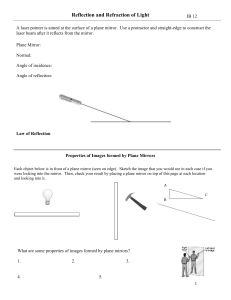
... 3. the same size - no enlargement or reduction 4. located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror - image gets smaller as you move away 5. virtual - not real, appears to be behind the mirror Page 463; 6,9,10 ...
... 3. the same size - no enlargement or reduction 4. located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror - image gets smaller as you move away 5. virtual - not real, appears to be behind the mirror Page 463; 6,9,10 ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.