* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MIRRORS reflect light and obey the law
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
Magic Mirror (Snow White) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese sun and moon mirrors wikipedia , lookup
Mirrors in Mesoamerican culture wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
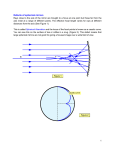
Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Reflection: Definition: Law of Reflection: MIRRORS reflect light and obey the law _____________________________________ There are three types of mirrors. Plane Mirror Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Optics - Ray Tracing Definition: How can wave be a ray? 1 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Plane Mirrors – Flat Surface Law of Reflection: Draw a ray diagram and label all parts. Name the Optical Image: Nature: Orientation: Size: Plane Mirrors – Flat Surface Draw a diagram of a Plane Mirror. Name the IMAGE. Practice Problem: Two plane mirrors are at right angles to each other as shown. If a pin is placed on the shiny side of each, how many images are formed? Hint: Images can form images, too. 2 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Spherical Mirrors Two Types: Optics – SPHERICAL CONCAVE MIRROR Draw a ray diagram of the concave mirror. Describe the characteristics. Optics – SPHERICAL CONVEX MIRROR Draw a ray diagram of the convex mirror. Describe the characteristics. 3 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ MIRROR PROPERTIES When rays reflect from a mirror and ______________________________, they pass through the image. The image can be seen on a __________________________ or a piece of paper. This image is called a _________________ ___________________. If the rays are coming from __________________________ source, they are striking the mirror as ________________________________. They will reflect, converging at the ____________________________________________, forming an IMAGE. When the rays reflect from a mirror and _______________________ from a point ________________ the mirror, the image is ________________________ which means the image cannot be pictured or projected on a screen. MIRROR EQUATION The equation that shows a relationship between the focal length (f), distance to object (do), and distance to image (di) can be written: For a concave mirror, the focal length is __________________________. For a convex mirror the focal length is ____________________________. If the image is real, in front of the mirror, the distance to image is __________________________. If the image is virtual, behind the mirror, the distance to image is __________________________. 4 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ MAGNIFICATION EQUATION The relationship of image size compared to object size represents magnification. Also the relationship between the negative of the image distance compared to the object distance represents magnification. These relationships can be written as: When the image size is ________________________, the image is upright (virtual). When the image size is ______________________, the image is inverted (real) Practice Problem: An object 2.0 cm high is 30.0 cm from a concave mirror. The radius of curvature of the mirror is 20.0 cm. What is the location of the image? What is the size of the image? Practice Problem: Find the location of the image in a concave mirror if the object is 2.0 cm in height and is 5.0 cm from the mirror with a focal length of 10.0 cm. How large is the image? 5 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ MIRROR PROPERTIES – The Focus of a Spherical Concave Mirror Draw a ray diagram When parallel rays of a concave (spherical) mirror ______________________ so that they __________________________converge at the focal point, the image appears as a ________________________ or ___________________________, not a point creating the effect of ________________________ ______________________________. To prevent the effect, the mirror is constructed to be ____________________________, causing all the rays to ____________________ through one point, the ______________ ____________________________. Examples of parabolic mirrors that behave in this manner are: __________________________________, _________________________________ ___________________________________, and_________________________________ Ray Tracing of the Spherical Concave Mirror - Three types of principal rays: p-ray: f-ray: c-ray: 6 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Spherical Concave Mirror – Ray Tracings to locate image Object > Center of Curvature (2F) Object = Center of Curvature (2F) Object between Center of Curvature (2F) and Focus (F) Object = Focus (F) Object < Focal Length (f) 7 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Practice Problem: a) Construct 2 ray diagrams to illustrate what happens to the size of the image as an object is brought nearer to a spherical concave mirror when the object is outside the focus. b) Construct 2 ray diagrams to illustrate what happens to the size of the image as an object is brought nearer to a spherical concave mirror when the object is inside the focus. Practice Problem: A spherical concave mirror, focal length 20 cm, has a 5 cm high object placed 30 cm from the mirror. Draw a ray diagram, construct the image and name the image. 8 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Spherical Convex Mirror Construct the image for an object located outside a spherical convex mirror and name the image. Practice Problem: Construct 2 ray diagrams to illustrate what happens to the size of the image as an object is brought nearer to a spherical convex mirror. Practice Problem: A spherical convex mirror, focal length 15 cm, has a 4 cm high object placed 10 cm from it. a) Draw a ray diagram, construct the image and name the image. b) Use the mirror equation to calculate: i. The position of the image ii. The magnification iii. The size of the image 9 Physics - Chapter 18 Mirrors and Lenses Name___________________ Optics – Sign Conventions for Mirrors Focal Length: Magnification: Image Distance: CONCAVE MIRRORS produce REAL IMAGES when the VIRTUAL IMAGES are produced by: object is: _________________________________________________ __________________________________ _________________________________________________ __________________________________ _________________________________________________ __________________________________ _________________________________________________ Optics – Concave vs. Convex Mirrors Concave Convex 10