Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... that direction cannot move the electrons very much, does no work, and passes through. ...
... that direction cannot move the electrons very much, does no work, and passes through. ...
The Michelson Interferometer and Its Applications
... Measurement of the Wavelength and Coherence Length of an LED Source ...
... Measurement of the Wavelength and Coherence Length of an LED Source ...
Chapter 4 - Rothschild Science
... When emitted light from excited atoms is passed through a prism a spectrum of discrete lines of separate colors (separate energies) is observed rather than a continuous spectrum of ROY G ...
... When emitted light from excited atoms is passed through a prism a spectrum of discrete lines of separate colors (separate energies) is observed rather than a continuous spectrum of ROY G ...
1 - RosedaleGrade10Science
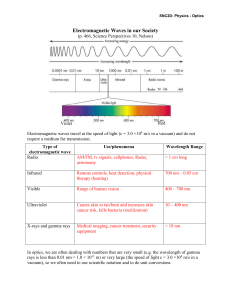
... rays is less than 0.01 nm = 1.0 × 1011 m) or very large (the speed of light c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum), so we often need to use scientific notation and to do unit conversions. ...
... rays is less than 0.01 nm = 1.0 × 1011 m) or very large (the speed of light c = 3.0 ×108 m/s in a vacuum), so we often need to use scientific notation and to do unit conversions. ...
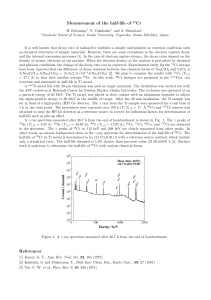
Measurement of the half-life of
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...
Unit 1 VCE Physics: Sample Timeline, 2004
... The use of “dot-points” in the sample timeline does not imply a “you must cover all this information” approach to teaching physics. It is, perhaps, more important to mix the supply of information with space for discussion of the “big questions” and mysteries surrounding physics. There should be ro ...
... The use of “dot-points” in the sample timeline does not imply a “you must cover all this information” approach to teaching physics. It is, perhaps, more important to mix the supply of information with space for discussion of the “big questions” and mysteries surrounding physics. There should be ro ...
Document
... electron from the metal (here, W is the energy necessary to eject the electron), then energy of the photon absorbed (hυ) goes into ejecting the electron (W) plus any extra energy left over which would show ...
... electron from the metal (here, W is the energy necessary to eject the electron), then energy of the photon absorbed (hυ) goes into ejecting the electron (W) plus any extra energy left over which would show ...
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
... differences between allowed levels Modern model has electron “cloud” rather than ...
... differences between allowed levels Modern model has electron “cloud” rather than ...
n - LSU Physics
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
Nuclear and Modern Physics
... The liberated electrons are attracted to the positive plate and produce a measurable current. Current can be sent out as electrical power or used to ...
... The liberated electrons are attracted to the positive plate and produce a measurable current. Current can be sent out as electrical power or used to ...
Sample
... photons. Then I introduce refraction and refractive index, which leads to total internal reflection, and how it can explain light guiding in a multimode step-index optical fiber. That explanation of light guiding takes the traditional optical perspective of tracing the paths of light rays, rather th ...
... photons. Then I introduce refraction and refractive index, which leads to total internal reflection, and how it can explain light guiding in a multimode step-index optical fiber. That explanation of light guiding takes the traditional optical perspective of tracing the paths of light rays, rather th ...
1 Janaky Narayanan PC 5213 AY 2004
... chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determined by the three dimensional arrangement of the atoms in space. The word “conformation” de ...
... chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determined by the three dimensional arrangement of the atoms in space. The word “conformation” de ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.