Direct index of refraction measurement at extreme
... Examining the first order terms in both the grating and zoneplate, i.e. (m, n) = (±1, 1), its efficiency is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which t ...
... Examining the first order terms in both the grating and zoneplate, i.e. (m, n) = (±1, 1), its efficiency is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which t ...
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
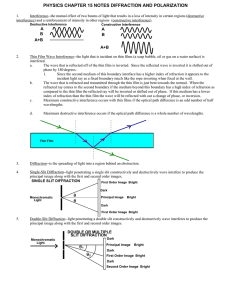
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
Young`s Double Slits
... Place the slide saddle back on the track in the same position as before. You should observe a similar diffraction pattern. ...
... Place the slide saddle back on the track in the same position as before. You should observe a similar diffraction pattern. ...
Why is the sky purple? - Little Shop of Physics
... color of sunrises and sunsets. At sunrise or sunset, sunlight passes through a thickness of atmosphere 12 times that at midday, so light passes through 12 times more atmosphere at sunrise and sunset. When we greet the day or say goodnight, we see beautiful sights in the yellow, orange, and red part ...
... color of sunrises and sunsets. At sunrise or sunset, sunlight passes through a thickness of atmosphere 12 times that at midday, so light passes through 12 times more atmosphere at sunrise and sunset. When we greet the day or say goodnight, we see beautiful sights in the yellow, orange, and red part ...
Incandescence Light bulb has a wire filament (tungsten) that is
... Neon light has glass tubes filled with a gas like neon, argon or krypton at low pressure. At both ends of the tube there are metal electrodes. When you apply an electric current, the gas ionizes and electrons flow through the gas. The electrons excite the gas’ atoms and cause them to emit light. Dif ...
... Neon light has glass tubes filled with a gas like neon, argon or krypton at low pressure. At both ends of the tube there are metal electrodes. When you apply an electric current, the gas ionizes and electrons flow through the gas. The electrons excite the gas’ atoms and cause them to emit light. Dif ...
Chapter 27: Summary
... a warm object. An example is the red-orange glow given off by a toaster element. Black body radiation is historically significant, because Max Planck explained it in terms of quantized energy levels, the first time quantized energy levels had been used. The Photoelectric effect When light is inciden ...
... a warm object. An example is the red-orange glow given off by a toaster element. Black body radiation is historically significant, because Max Planck explained it in terms of quantized energy levels, the first time quantized energy levels had been used. The Photoelectric effect When light is inciden ...
supplemental_material
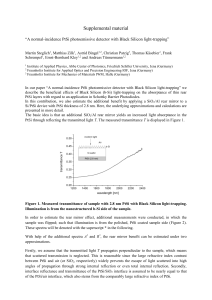
... Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with t ...
... Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination is from the polished, PtSi coated sample side (Figure 2). These spectra will be denoted with t ...
Absorption of Radiation
... wavelength of plane polarized light, concentration & number of symmetric molecules •circularly polarized light: the electric field vector is rotating around the axis of light propagation. • electric field vector can rotate in either the right or left direction, and the light is called right (Clockwi ...
... wavelength of plane polarized light, concentration & number of symmetric molecules •circularly polarized light: the electric field vector is rotating around the axis of light propagation. • electric field vector can rotate in either the right or left direction, and the light is called right (Clockwi ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum Web Quest
... Use http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/thermal/3-what-makes-em-radiation.html to answer the following (the general site http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/Communications/2-more-about-radio-waves.html can also be used on other questions) 15) Why do materials absorb some ...
... Use http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/thermal/3-what-makes-em-radiation.html to answer the following (the general site http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/Communications/2-more-about-radio-waves.html can also be used on other questions) 15) Why do materials absorb some ...
BSA
... It is convenient to express the concentration in terms of parts per million (ppm) instead of using molar concentrations since the initial weights and the final volumes of the unknowns and standards are equal to each other. It takes about 1-1.5 mL of solution in the sample cell to obtain a reading. F ...
... It is convenient to express the concentration in terms of parts per million (ppm) instead of using molar concentrations since the initial weights and the final volumes of the unknowns and standards are equal to each other. It takes about 1-1.5 mL of solution in the sample cell to obtain a reading. F ...
Light Tasks
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
... New experiences that don’t fit the patterns they are familiar with o Refraction: Spear fishing demonstration, coin in cup o Force and motion: Falling objects, weight in a vacuum, cart with constant force o Buoyancy: Alka-Seltzer demonstration o Color, reflection, or intensity: ???? New patterns ...
Lect 4 - Components - Sonoma State University
... • Each Slit becomes a secondary source of light • A constructive interference will be created on the image plane only for specific WLs that are in phase high light intensity • Narrow slits are placed next to each other • The spacing determines the pitch of the gratings • Angles are due to phase sh ...
... • Each Slit becomes a secondary source of light • A constructive interference will be created on the image plane only for specific WLs that are in phase high light intensity • Narrow slits are placed next to each other • The spacing determines the pitch of the gratings • Angles are due to phase sh ...
IBM-finalrev - Madison Public Schools
... 19. Explain what is necessary to make light refract? 20. Identify the color that would be seen when these opaque objects are seen on the following colors of light. a. white object in yellow light e. green object in red light b. white object in white light d. green object in white light c. green obje ...
... 19. Explain what is necessary to make light refract? 20. Identify the color that would be seen when these opaque objects are seen on the following colors of light. a. white object in yellow light e. green object in red light b. white object in white light d. green object in white light c. green obje ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.