Fusion Review Byzantine Russia
... The Byzantines at first followed Roman ways. Constantinople was known as the ‘New Rome.’ Its public buildings and palaces were built in the Roman style. The city even had an oval arena called the Hippodrome, where chariot races and other events were held. Byzantine political and social life also wer ...
... The Byzantines at first followed Roman ways. Constantinople was known as the ‘New Rome.’ Its public buildings and palaces were built in the Roman style. The city even had an oval arena called the Hippodrome, where chariot races and other events were held. Byzantine political and social life also wer ...
Name:
... Who was Constantine? year ________. Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire What two important things after his death in 395 CE. In ________ he moved the capital of the Empire from did he do? ___________ to the city of ________________. _____________ later came to be known as _ ...
... Who was Constantine? year ________. Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire What two important things after his death in 395 CE. In ________ he moved the capital of the Empire from did he do? ___________ to the city of ________________. _____________ later came to be known as _ ...
11.1 The Byzantine Empire
... • Christianity develops differently in Eastern and Western Roman Empires. • Two churches disagree over many issues, including the use of icons. • Icons are two-dimensional religious images used to aid in prayer. • Leading bishop of Eastern Christianity is known as a Patriarch. • In the West, the pop ...
... • Christianity develops differently in Eastern and Western Roman Empires. • Two churches disagree over many issues, including the use of icons. • Icons are two-dimensional religious images used to aid in prayer. • Leading bishop of Eastern Christianity is known as a Patriarch. • In the West, the pop ...
Chapter 11 - SeymourSocialStudiesDepartment
... Institutes—Told law students how to use the laws ...
... Institutes—Told law students how to use the laws ...
The Byzantine Empire and Russia
... What was the Byzantine Empire? • The predominantly Greek-speaking continuation of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. • Initially the eastern half of the Roman Empire, it survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and continued to thrive • Its capital city was Constantinople, originall ...
... What was the Byzantine Empire? • The predominantly Greek-speaking continuation of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. • Initially the eastern half of the Roman Empire, it survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and continued to thrive • Its capital city was Constantinople, originall ...
- Sweet Home Central School District
... Empire brought autocratic rule (through the establishment of the Czar), the Eastern Orthodox religion, the dome (onion-shaped), and the Cyrillic alphabet to Russia. ...
... Empire brought autocratic rule (through the establishment of the Czar), the Eastern Orthodox religion, the dome (onion-shaped), and the Cyrillic alphabet to Russia. ...
The Byzantine Empire
... • Constantinople is in middle of trade routes. • City was naturally protected. • Controlled the water between the Aegean and Black Sea. • City became rich from taxes on trade. ...
... • Constantinople is in middle of trade routes. • City was naturally protected. • Controlled the water between the Aegean and Black Sea. • City became rich from taxes on trade. ...
Byzantine Empire - Essays on the Dot
... The Byzantine Empire is the longest running empire in the history of man kind that ruled for over a thousand years. The term Byzantine Empire was conventionally used during the 19th century depicting the Greek – speaking Roman Empire during the middle ages. Byzantine Empire derived from the original ...
... The Byzantine Empire is the longest running empire in the history of man kind that ruled for over a thousand years. The term Byzantine Empire was conventionally used during the 19th century depicting the Greek – speaking Roman Empire during the middle ages. Byzantine Empire derived from the original ...
The Byzantine Empire
... survive within the Byzantine Empire? What factors produced the division within the Christian church? Why did the Byzantine Empire have so much influence on religion, culture, and trade in Russia and Eastern Europe? ...
... survive within the Byzantine Empire? What factors produced the division within the Christian church? Why did the Byzantine Empire have so much influence on religion, culture, and trade in Russia and Eastern Europe? ...
Justinian and Theodora
... once capital moved to Constantinople 3. Services conducted in Greek or local languages ...
... once capital moved to Constantinople 3. Services conducted in Greek or local languages ...
Byzantine Empire
... Diocletian thought it would be easier to govern an eastern and a western half Constantine named his city Constantinople (modernday Istanbul) ...
... Diocletian thought it would be easier to govern an eastern and a western half Constantine named his city Constantinople (modernday Istanbul) ...
The Byzantine Empire
... – Priests may be married – Divorce is allowed under certain circumstances – Church is centered in Constantinople ...
... – Priests may be married – Divorce is allowed under certain circumstances – Church is centered in Constantinople ...
The Byzantine Empire
... conquered nearly as much land as they had maintained when in the days when the Roman Empire was united. • Justinian also encouraged the teaching of classical Greek texts, preserving the epic stories and philosophical breakthroughs of the Greeks. • Justinian’s passion was church building • His greate ...
... conquered nearly as much land as they had maintained when in the days when the Roman Empire was united. • Justinian also encouraged the teaching of classical Greek texts, preserving the epic stories and philosophical breakthroughs of the Greeks. • Justinian’s passion was church building • His greate ...
Lesson 1: Geography of the Byzantine Empire
... culture. It mixed Greek languages and Roman customs. Like the Romans, most Byzantines lived in wooden houses. As in Roman cities, the city offered public baths, steam rooms, and swimming pools. A hippodrome is an ancient Greek stadium that was used for horse and chariot racing. Chariot racing was a ...
... culture. It mixed Greek languages and Roman customs. Like the Romans, most Byzantines lived in wooden houses. As in Roman cities, the city offered public baths, steam rooms, and swimming pools. A hippodrome is an ancient Greek stadium that was used for horse and chariot racing. Chariot racing was a ...
Byzantine Empire
... rules and customs. Extravagant circuses and chariot races continued on Constantinople, along with such traditions as the emperor's distribution of bread to the citizens. The army followed Roman military traditions. Some of Rome’s class-based standards of punishment and dress for the rich and poor re ...
... rules and customs. Extravagant circuses and chariot races continued on Constantinople, along with such traditions as the emperor's distribution of bread to the citizens. The army followed Roman military traditions. Some of Rome’s class-based standards of punishment and dress for the rich and poor re ...
CHAPTER 14 : THE GREAT SCHISM AND THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
... empire but turning attention to Europe when Asia was the primary concern. For awhile the empire survived simply because the Muslims were too divided to attack, but eventually the Ottomans overran all but a handful of port cities. Constantinople was initially considered not worth the effort, but with ...
... empire but turning attention to Europe when Asia was the primary concern. For awhile the empire survived simply because the Muslims were too divided to attack, but eventually the Ottomans overran all but a handful of port cities. Constantinople was initially considered not worth the effort, but with ...
Byzantine empire - Ms. Mcatee`s Site
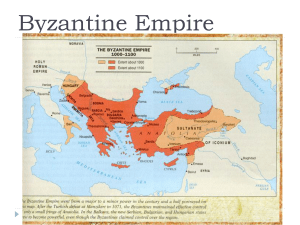
... At its height, the Byzantine empire covered an area from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
... At its height, the Byzantine empire covered an area from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
The Byzantine Empire - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Umm…. Not quite. • Eastern and Western halves were officially split into two distinct empires in 395 CE • 5th century (476 CE): Rome is sacked by the invading Germanic tribes, but only the Western Empire falls. • The Eastern Empire exists for 1,000 more years. • Capital is Constantinople (modern n ...
... • Umm…. Not quite. • Eastern and Western halves were officially split into two distinct empires in 395 CE • 5th century (476 CE): Rome is sacked by the invading Germanic tribes, but only the Western Empire falls. • The Eastern Empire exists for 1,000 more years. • Capital is Constantinople (modern n ...
Byzantine Empire and Russia
... Empire (West) & Byzantine Empire (East) Greeks=most of Byzantine Empire’s population Wealthy families moved to Constantinople when barbarians invaded Rome ...
... Empire (West) & Byzantine Empire (East) Greeks=most of Byzantine Empire’s population Wealthy families moved to Constantinople when barbarians invaded Rome ...
The Byzantine Empire & the Eastern Orthodox Church
... Liturgy conducted in Greek was sacred rite of worship Architecture and art represented religious symbols ...
... Liturgy conducted in Greek was sacred rite of worship Architecture and art represented religious symbols ...
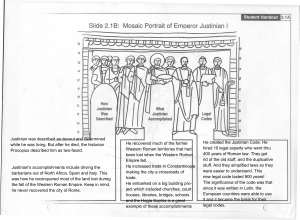
What is the name given to someone who digs up and studies
... convinced Justinian not to flee Constantinople, but to fight against the Nika rebellion. Theodora ...
... convinced Justinian not to flee Constantinople, but to fight against the Nika rebellion. Theodora ...
He created the Justinian Code. He hired 10 legal experts who went
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
Music Report - St Faith`s Crosby
... had to be memorised, which limits how music you can sing. With the emergence of written music, musical ideas were recorded for others to study and learn, and more importantly without the composer having to be present. Without this notation system musicians wouldn't be able to share and expand on mus ...
... had to be memorised, which limits how music you can sing. With the emergence of written music, musical ideas were recorded for others to study and learn, and more importantly without the composer having to be present. Without this notation system musicians wouldn't be able to share and expand on mus ...
The Byzantine Empire
... survived. It began the Byzantine Empire. • The Byzantine Empire survived for one thousand years after the fall of Rome. ...
... survived. It began the Byzantine Empire. • The Byzantine Empire survived for one thousand years after the fall of Rome. ...