* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Byzantine Empire
Law school of Beirut wikipedia , lookup
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine flags and insignia wikipedia , lookup
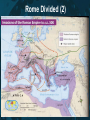
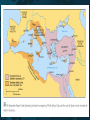
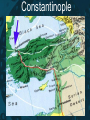
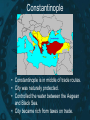
The Byzantine Empire Rome Has Fallen! • • • • Umm…. Not quite. Sure, Rome is sacked by barbarians. But only the Western Empire crumbles! The Eastern Empire exists for 1,000 more years. • Capital is Constantinople • Called the Byzantine Empire Rome Divided By… Into… Rome Divided (2) Constantine -rebuilt the old Greek port of Byzantium -renamed it Constantinople Constantinople Constantinople Constantinople Constantinople • Constantinople is in middle of trade routes. • City was naturally protected. • Controlled the water between the Aegean and Black Sea. • City became rich from taxes on trade. Back to The Byzantines • At first, this Empire controlled only a small area around the eastern Mediterranean • but during the reign of Justinian (527-565), it started to recover much of the territory of the old Roman empire. Emperor Justinian • Comes from a poor family. • He retakes some Roman provinces. • Is a tremendous ruler. • Builds the Hagia Sophia. (more on this later) Autocrat • Justinian rules as an Autocrat which means a ruler with absolute power Justinian’s Code • Preserved Roman law. • Forms the basis of medieval and modern legal systems. • Called the “Body of Civil Law” • His work inspired the modern concept and the very spelling of "justice". Politics & Military Political • Good people running civil service. • Good negotiators with foreigners. • Arranged marriages with foreign princes. Military • Soldiers trained, given medical aid, and updated weapons. • Used “Greek Fire” at sea. After Justinian… • Empire shrinks in size due to foreign invasions. • Seljuk Turks invade in 1000s AD. • Series of Crusades take place to drive out Turks. • Byzantines recapture Constantinople. The End of the Byzantines • The Byzantine Empire drew to a close in 1453 when forces from the Muslim Ottoman Empire surrounded and conquered Constantinople. • The ancient Christian city was renamed Istanbul and became the capital of the Ottoman Empire. THE BIG IDEA The Byzantine Empire: • had a strong government and a uniform code of laws under Justinian • was closely tied to the Orthodox Christian Church • Made contributions in architecture, engineering, and art • Affected the later development of Russia and other nations of Eastern Europe