Byzantine Empire
... Empire (West) & Byzantine Empire (East) Greeks=most of Byzantine Empire’s population Wealthy families moved to Constantinople when barbarians invaded Rome ...
... Empire (West) & Byzantine Empire (East) Greeks=most of Byzantine Empire’s population Wealthy families moved to Constantinople when barbarians invaded Rome ...
Byzantine Empire
... They also differ in their belief of purgatory. Byzantine missionaries carried Orthodox Christianity to Russia and other Eastern European nations. The Greek Orthodox Church has nearly 250 million members today, third largest to Catholicism and Protestantism. ...
... They also differ in their belief of purgatory. Byzantine missionaries carried Orthodox Christianity to Russia and other Eastern European nations. The Greek Orthodox Church has nearly 250 million members today, third largest to Catholicism and Protestantism. ...
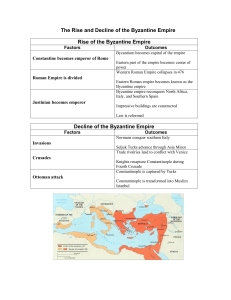
The Byzantine Empire
... plagued with problems (internal invasions, civil wars and poor economy) and began declining by the 300s AD ...
... plagued with problems (internal invasions, civil wars and poor economy) and began declining by the 300s AD ...
Byzantium
... • 1. Slaves are in the power of masters, a power derived from the law of nations: for among all nations it may be remarked that masters have the power of life and death over their slaves, and that everything acquired by the slave is acquired for the master. ...
... • 1. Slaves are in the power of masters, a power derived from the law of nations: for among all nations it may be remarked that masters have the power of life and death over their slaves, and that everything acquired by the slave is acquired for the master. ...
Byzantine Empire
... • The ancient city of Byzantium was originally founded by the Greeks. At its height the Byzantine Empire controlled most of the territory around the Mediterranean Sea. •Due to being strategically located on an Isthmus called the Bosporus Straits, Constantinople became very prosperous by controlling ...
... • The ancient city of Byzantium was originally founded by the Greeks. At its height the Byzantine Empire controlled most of the territory around the Mediterranean Sea. •Due to being strategically located on an Isthmus called the Bosporus Straits, Constantinople became very prosperous by controlling ...
Byzantine Empire Study Guide
... Terms, People, and Places Constantine – emperor of the Byzantine empire; established Constantinople (named for himself) as the capital of the eastern Roman empire; converted to Christianity; stopped persecution of Christians Constantinople – capital of the eastern Roman empire; Byzantium later renam ...
... Terms, People, and Places Constantine – emperor of the Byzantine empire; established Constantinople (named for himself) as the capital of the eastern Roman empire; converted to Christianity; stopped persecution of Christians Constantinople – capital of the eastern Roman empire; Byzantium later renam ...
What Teachers Need to Know - Core Knowledge Foundation
... The rise of Russia is closely related to the history of the Byzantine Empire, which students in Core Knowledge schools should have encountered in Grades 3 and 4. For a thousand years after the fall of the Roman Empire in the west, the Eastern or Byzantine Empire continued to build on ancient Greek a ...
... The rise of Russia is closely related to the history of the Byzantine Empire, which students in Core Knowledge schools should have encountered in Grades 3 and 4. For a thousand years after the fall of the Roman Empire in the west, the Eastern or Byzantine Empire continued to build on ancient Greek a ...
Byzantine Empire
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
document
... • Liturgy: the collection of prayers, chants, readings, and ritual acts by which the theology of the church, or any organized religion, is practiced • Chant: the monophic religious music that is sung in a house of worship. • Jerusalem: the birthplace of Christianity and Christian liturgy ...
... • Liturgy: the collection of prayers, chants, readings, and ritual acts by which the theology of the church, or any organized religion, is practiced • Chant: the monophic religious music that is sung in a house of worship. • Jerusalem: the birthplace of Christianity and Christian liturgy ...
DAY 44: PowerPoint on the Byzantines File
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
The Byzantine Empire
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
The Byzantine Empire
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
Byzantine Empire
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
... development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and E ...
Byzantine Empire Vocabulary Dowry
... renamed Nova Roma by Constantine the Great, but popularly called Constantinople and briefly became the imperial residence of the classical Roman Empire. Then subsequently the city was, for more than a thousand years, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, the Greek-speaking Roman Empire of late Antiqu ...
... renamed Nova Roma by Constantine the Great, but popularly called Constantinople and briefly became the imperial residence of the classical Roman Empire. Then subsequently the city was, for more than a thousand years, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, the Greek-speaking Roman Empire of late Antiqu ...
The Byzantine Empire - bdooleyworldhistory
... So Emperor Constantine decided to create a new capital at the former Greek city of Byzantium, which he renamed Constantinople (present-day Istanbul). When the western half of the Roman Empire fell in 476, the Eastern half survived and thrived. This Eastern half of the Roman Empire later became known ...
... So Emperor Constantine decided to create a new capital at the former Greek city of Byzantium, which he renamed Constantinople (present-day Istanbul). When the western half of the Roman Empire fell in 476, the Eastern half survived and thrived. This Eastern half of the Roman Empire later became known ...
The Commonwealth of Byzantium
... Byzantium and Rome’s Legacy 1. What does Rome mean? 2. Is the ideal of Rome greater than the reality of Rome? 3. In what way was Byzantium a different place than Rome politically, intellectually, culturally, and religiously? ...
... Byzantium and Rome’s Legacy 1. What does Rome mean? 2. Is the ideal of Rome greater than the reality of Rome? 3. In what way was Byzantium a different place than Rome politically, intellectually, culturally, and religiously? ...
The Byzantine Empire - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... – The Crusaders (sacked Constantinople in 1204 CE) – Battle of Manzikert (1071 CE) – army defeated and ...
... – The Crusaders (sacked Constantinople in 1204 CE) – Battle of Manzikert (1071 CE) – army defeated and ...
Introduction to the Byzantine Empire
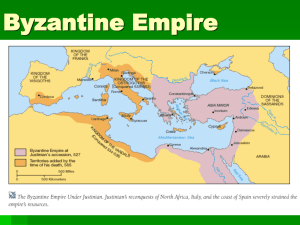
... The Emperor was the most powerful person in the Empire. Justinian ruled the Byzantine empire from 527 to 565. During his reign, he: recovered provinces that had been previously overrun by invaders. The Byzantine empire reached its greatest size under Justinian. launched a program to beautify Constan ...
... The Emperor was the most powerful person in the Empire. Justinian ruled the Byzantine empire from 527 to 565. During his reign, he: recovered provinces that had been previously overrun by invaders. The Byzantine empire reached its greatest size under Justinian. launched a program to beautify Constan ...
WH 12.1 Red Flag Questions
... How did Emperor Heraclitus bring an end to Roman traditions in the Eastern Empire? ...
... How did Emperor Heraclitus bring an end to Roman traditions in the Eastern Empire? ...