Heaven On - History of Christian Art
... dome and the apse. The visual and emotional effect was as if heaven had descended and enveloped the worshipper. Russian ambassadors, in the 6th century, were spellbound when they experienced the Byzantine liturgy celebrated in Hagia Sophia: “…we knew not whether we were in heaven or on earth. For on ...
... dome and the apse. The visual and emotional effect was as if heaven had descended and enveloped the worshipper. Russian ambassadors, in the 6th century, were spellbound when they experienced the Byzantine liturgy celebrated in Hagia Sophia: “…we knew not whether we were in heaven or on earth. For on ...
Orthodox Christianity in the East
... Hagia Sophia - 'Church of Holy Wisdom'. To women, Theodora may well be considered a noble pioneer of the women's liberation movement. She passed on rights that granted women more rights in divorce cases and established laws allowing women to own and ...
... Hagia Sophia - 'Church of Holy Wisdom'. To women, Theodora may well be considered a noble pioneer of the women's liberation movement. She passed on rights that granted women more rights in divorce cases and established laws allowing women to own and ...
The Byzantine Empire and the Crusades
... bureaucracies –Diplomacy –Most famous Byzantine emperor: Justinian ...
... bureaucracies –Diplomacy –Most famous Byzantine emperor: Justinian ...
Byzantine Empire Notes
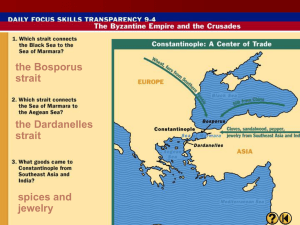
... the fourth side. Constantinople was one of the greatest centers of trade (on the silk route) Multi-ethnic city - Greeks, Persians, Romans, Turks, Slavs, Armenians, and Jews lived in the city The citizens spoke Greek, but Latin was the official ...
... the fourth side. Constantinople was one of the greatest centers of trade (on the silk route) Multi-ethnic city - Greeks, Persians, Romans, Turks, Slavs, Armenians, and Jews lived in the city The citizens spoke Greek, but Latin was the official ...
hw ch 10 sec 1 # 2
... Byzantine Christian Church it was Easter///Christmas. 36. In the masses of Byzantine Christianity Latin///Greek was the official language while the western Christian clergy spoke in Latin///Greek. 37. ___ What time period did the two branches of Christianity split apart? A. Roman empire B. Byzantine ...
... Byzantine Christian Church it was Easter///Christmas. 36. In the masses of Byzantine Christianity Latin///Greek was the official language while the western Christian clergy spoke in Latin///Greek. 37. ___ What time period did the two branches of Christianity split apart? A. Roman empire B. Byzantine ...
Slide 1
... Christianity develops differently in Eastern and Western Roman Empires. Two churches disagree over many issues, including the use of icons. Icons are two-dimensional religious images used to aid in prayer. Leading bishop of Eastern Christianity is known as a Patriarch. In the West, the pope exc ...
... Christianity develops differently in Eastern and Western Roman Empires. Two churches disagree over many issues, including the use of icons. Icons are two-dimensional religious images used to aid in prayer. Leading bishop of Eastern Christianity is known as a Patriarch. In the West, the pope exc ...
A Short History of the Byzantine Empire
... • Unable to take back Rome from the Germans, they established a western capital in Ravenna, Italy known for Christian mosaics • However, gains were short lived as Persians and Slavs(Bulgars) were taking Byzantine land • All these wars put more tax pressure on the Byzantine population ...
... • Unable to take back Rome from the Germans, they established a western capital in Ravenna, Italy known for Christian mosaics • However, gains were short lived as Persians and Slavs(Bulgars) were taking Byzantine land • All these wars put more tax pressure on the Byzantine population ...
chapter_10_rev_handout
... A) Reunification was still conceivable. B) Most of the ties between the two empires were still intact. C) The two halves were distinct and not capable of reunification. D) Justinian was successful in temporarily joining the two under his rule. 17) Which of the following statements about Empress The ...
... A) Reunification was still conceivable. B) Most of the ties between the two empires were still intact. C) The two halves were distinct and not capable of reunification. D) Justinian was successful in temporarily joining the two under his rule. 17) Which of the following statements about Empress The ...
10.2 The Byzantine Empire
... decrepit Rome, but not until over two hundred years later would a Byzantine emperor come even close to making this vision a reality. In founding his new city, Constantine tapped into an ideal within the Christian Scriptures of the New Jerusalem. Byzantine civilization was permeated with a belief in ...
... decrepit Rome, but not until over two hundred years later would a Byzantine emperor come even close to making this vision a reality. In founding his new city, Constantine tapped into an ideal within the Christian Scriptures of the New Jerusalem. Byzantine civilization was permeated with a belief in ...
leonin and perotin go to school
... Leonin's successor was Perotin. Perotin wrote polyphonic music in three and four parts. Toward the end of Perotin's life, composers began writing new words to be used by the additional voices. While the original Gregorian chant melody was sung with the original Gregorian chant text or words, new wor ...
... Leonin's successor was Perotin. Perotin wrote polyphonic music in three and four parts. Toward the end of Perotin's life, composers began writing new words to be used by the additional voices. While the original Gregorian chant melody was sung with the original Gregorian chant text or words, new wor ...
Review Sheet for Middle Ages
... Music in the Middle Ages was divided into two types. Sacred music was the music of the church, secular music was the music of the people. Pope Gregory established the liturgy of the Catholic Church. The Mass, or worship service, included the following five parts: Kyrie, Gloria, Agnus Dei, Credo, San ...
... Music in the Middle Ages was divided into two types. Sacred music was the music of the church, secular music was the music of the people. Pope Gregory established the liturgy of the Catholic Church. The Mass, or worship service, included the following five parts: Kyrie, Gloria, Agnus Dei, Credo, San ...
Unit 2 ppt Byzantium - Fulton County Schools
... and East (Byzantine) to split on doctrines and rituals outcome: Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic Churches Eastern Orthodox built on the early works of church fathers, such as St Basil and St John Chrysostom (KRIHSuh-stuhm) who later became the patriarch or leading bishop of the east even pa ...
... and East (Byzantine) to split on doctrines and rituals outcome: Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic Churches Eastern Orthodox built on the early works of church fathers, such as St Basil and St John Chrysostom (KRIHSuh-stuhm) who later became the patriarch or leading bishop of the east even pa ...
Byzanine Empire (dcarlile v1)
... The Ottoman forces surrounded the city. After two months the Ottoman Turks entered into the city. The City was renamed Istanbul and the Hogia Sophia (a Christian Church) now becomes the Islamic house of worship. The Great Byzantine Empire is now under the rule of the Turks and now becomes the Ottoma ...
... The Ottoman forces surrounded the city. After two months the Ottoman Turks entered into the city. The City was renamed Istanbul and the Hogia Sophia (a Christian Church) now becomes the Islamic house of worship. The Great Byzantine Empire is now under the rule of the Turks and now becomes the Ottoma ...
Rise of the Byzantines - Fall13-OR-01
... Describe Byzantine culture, which was based on Roman, Greek, and Christian ideas ...
... Describe Byzantine culture, which was based on Roman, Greek, and Christian ideas ...
PART III - Cengage Learning
... 1. Religious rituals are more a component of day-to-day secular activities in Islamic culture than in Western culture. 2. The pilgrimage to Mecca, (the haj) to be accomplished once in a lifetime, spiritually and corporally unites Muslims throughout the world. 3. The affirmation of faith, frequent pr ...
... 1. Religious rituals are more a component of day-to-day secular activities in Islamic culture than in Western culture. 2. The pilgrimage to Mecca, (the haj) to be accomplished once in a lifetime, spiritually and corporally unites Muslims throughout the world. 3. The affirmation of faith, frequent pr ...
Slide 1
... Perhaps the most significant event during Empress Theodora's rule was the Nika revolt in which she proved herself a worthy and able leader. Two rival political groups started a riot at the Hippodrome. They set many public buildings on fire and proclaimed a new emperor. Justinian and his officials, u ...
... Perhaps the most significant event during Empress Theodora's rule was the Nika revolt in which she proved herself a worthy and able leader. Two rival political groups started a riot at the Hippodrome. They set many public buildings on fire and proclaimed a new emperor. Justinian and his officials, u ...
Byzantine Empire Notes
... The Byzantine Empire and Justinian’s Rule After Rome got too big and had all those problems, Rome began to decline. One result was emperor _________________ (Die-o-clee-shun) decided to split the empire into two parts. The capitol of the Roman Empire moved from the West to the East...now the capitol ...
... The Byzantine Empire and Justinian’s Rule After Rome got too big and had all those problems, Rome began to decline. One result was emperor _________________ (Die-o-clee-shun) decided to split the empire into two parts. The capitol of the Roman Empire moved from the West to the East...now the capitol ...
The Byzantine Empire - White Plains Public Schools
... “The Western Roman Empire crumbled in the fifth century as it was overrun by invading Germanic tribes. By this time, however, the once great empire had already undergone significant changes. It had been divided into western and eastern empires, and its capital had moved east from Rome to the Greek c ...
... “The Western Roman Empire crumbled in the fifth century as it was overrun by invading Germanic tribes. By this time, however, the once great empire had already undergone significant changes. It had been divided into western and eastern empires, and its capital had moved east from Rome to the Greek c ...
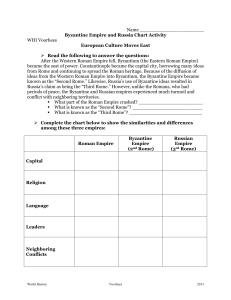
Byzantine Empire and Russia Chart Activity
... What part of the Roman Empire crashed? ______________________ What is known as the “Second Rome”? ________________________ What is known as the “Third Rome”? _________________________ Complete the chart below to show the similarities and differences among these three empires: Roman Empire ...
... What part of the Roman Empire crashed? ______________________ What is known as the “Second Rome”? ________________________ What is known as the “Third Rome”? _________________________ Complete the chart below to show the similarities and differences among these three empires: Roman Empire ...