* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Byzantine Empire - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
Emirate of Crete wikipedia , lookup
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Decline of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
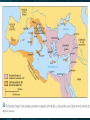
The Byzantine Empire Oh No!! Rome Has Fallen! • Eastern and Western halves were officially split into two distinct empires in 395 CE • 476 CE: Fall of Western Rome • Eastern Empire dates from 395 – 1453 CE • Capital is Constantinople (modern name: Istanbul) • Called the Byzantine Empire Characteristics of Byzantine Empire • Elegant buildings • Christian (Roman Catholic, then Eastern Orthodox) • Language: Greek • Strong Commercial Focus • Armies based on barbarian recruits • Emperor separate from society Emperor Justinian (r. 527- 565 CE) • Successes: – Law Code – Rebuilt Constantinople – Reclaims some Roman provinces: • North Africa, city of Rome (temporarily), parts of Spain • Failures: – Unable to retake Italy for good – Weakened empire through expansion Justinian Code • Created between 528-533 CE – Preserved and reformed/updated Roman law – Ultimate Goal: Create a single, uniform law code – Forms the basis of modern legal systems. • Covered all aspects of life: marriage, slavery, property, inheritance, women’s rights and crimes • Code is used for over 900 years Empress Theodora • Justinian’s wife • Very powerful in her own right: – Met with foreign leaders, passed laws, built churches • Theodora pushes for women’s rights: – Man couldn’t beat wife – Women could sue for divorce. – Women could own property Politics in the Byzantine Empire • Emperor head of church and state • Make religious and secular laws • Not uncommon for women to hold throne temporarily • Troops given land for service • Government keeps food prices low • Bureaucracy – Trained in Greek classics – From all classes – Spies – Emperor appointed local leaders to be sent throughout the empire Constantinople (Istanbul) • Founded by Constantine and established as the capital of the Byzantine Empire in 330 CE Constantinople • Naturally protected by waterways on either side – Controlled the water between the Aegean and Black Sea. • Only land border is protected by a moat and three other walls • Constantinople is in middle of trade routes. • City became rich from taxes on trade. • Revenue from trade funds governmentsupported building projects: – Hagia Sophia • (“Holy Wisdom”) – Palaces – Aqueducts – Schools – Hospitals Life in Constantinople • Great trade, shopping and cultural attractions in the city • Entertainment: – Hippodrome: chariot races; circus; held 60,000 people • Intellectual Life: – education highly prized, influenced by ancient Greek literature and historical writings – passed on Greco-Roman mathematics and geometry to the Arabs who adopted and improved it Problems in the Byzantine Empire • The Plague – – – – Originated in rats on an Indian trading ship 542: 10,000 die per day Outbreaks continued around every 8-10 years Smaller population caused empire to be an easy target for outside groups • Outside Attacks: – Several groups attempted to attack the empire: Slavs, Persians, Arab armies, Russians, Turks, knights from Western Europe – The Crusaders (sacked Constantinople in 1204 CE) – Battle of Manzikert (1071 CE) – army defeated and destroyed by Muslim Turkish invaders – Finally falls in 1453 to the Ottoman Turks