Byzantine Empire
... • The Byzantine empire had its influence in the development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as we ...
... • The Byzantine empire had its influence in the development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as we ...
Chapter 11 - SeymourSocialStudiesDepartment
... Institutes—Told law students how to use the laws ...
... Institutes—Told law students how to use the laws ...
Constantinople
... According to this map, how many continents was the Byzantine Empire located on? A. B. C. ...
... According to this map, how many continents was the Byzantine Empire located on? A. B. C. ...
Byzantium
... Eastern Church • Eastern Orthodox Christianity • Centered in Constantinople • Close to seat of power after Constantinople became capital • Use of Greek language in the liturgy ...
... Eastern Church • Eastern Orthodox Christianity • Centered in Constantinople • Close to seat of power after Constantinople became capital • Use of Greek language in the liturgy ...
Byzantine Empire
... Empire continued flourishing for 1000 years after the fall of Rome. •The empire continued many Greco-Roman life style patterns and spread its Orthodox Christian civilization through most of eastern Europe ( Kievian Russia) by using its missionaries. ...
... Empire continued flourishing for 1000 years after the fall of Rome. •The empire continued many Greco-Roman life style patterns and spread its Orthodox Christian civilization through most of eastern Europe ( Kievian Russia) by using its missionaries. ...
WH 12.1 Red Flag Questions
... By the end of this section, you will be able to answer these questions: 1. How did Byzantine emperors rule their empire from Constantinople? 2. What were some important features of Byzantine culture? 3. What led to the decline of the Byzantine Empire? ...
... By the end of this section, you will be able to answer these questions: 1. How did Byzantine emperors rule their empire from Constantinople? 2. What were some important features of Byzantine culture? 3. What led to the decline of the Byzantine Empire? ...
File
... Crusades decision to sack Constantinople. This occurred due to the loss of most of the Christian populace for that had caused the Byzantine Empire’s permanent degradation on a political stand point. ...
... Crusades decision to sack Constantinople. This occurred due to the loss of most of the Christian populace for that had caused the Byzantine Empire’s permanent degradation on a political stand point. ...
The Byzantine Empire - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 3. Institutes: textbook for law students; handbook on how to use laws 4. Novellae (New Laws): any legislation (laws) created after 534 ...
... 3. Institutes: textbook for law students; handbook on how to use laws 4. Novellae (New Laws): any legislation (laws) created after 534 ...
The Byzantine Empire
... But only the Western Empire crumbles! The Eastern Empire exists for 1,000 more years. • Capital is Constantinople • Called the Byzantine Empire ...
... But only the Western Empire crumbles! The Eastern Empire exists for 1,000 more years. • Capital is Constantinople • Called the Byzantine Empire ...
Name:
... icons, Leo III, patriarch, prayer, Roman Catholic Church, schism, western worshiping) ____________ are religious art used in religious services and ___________ Emperor __________believed that people were wrongly ________________ the icons themselves. Leo II ordered icons to be destroyed. Pope Gregor ...
... icons, Leo III, patriarch, prayer, Roman Catholic Church, schism, western worshiping) ____________ are religious art used in religious services and ___________ Emperor __________believed that people were wrongly ________________ the icons themselves. Leo II ordered icons to be destroyed. Pope Gregor ...
11.1 The Byzantine Empire
... different groups. • Empire survives through bribery, diplomacy, and military power. • Constantinople falls in 1453; brings an end to the Byzantine Empire. ...
... different groups. • Empire survives through bribery, diplomacy, and military power. • Constantinople falls in 1453; brings an end to the Byzantine Empire. ...
Introduction to the Byzantine Empire
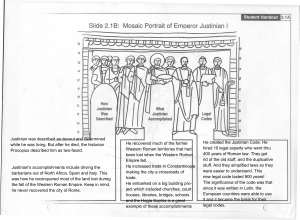
... The Emperor was the most powerful person in the Empire. Justinian ruled the Byzantine empire from 527 to 565. During his reign, he: recovered provinces that had been previously overrun by invaders. The Byzantine empire reached its greatest size under Justinian. launched a program to beautify Constan ...
... The Emperor was the most powerful person in the Empire. Justinian ruled the Byzantine empire from 527 to 565. During his reign, he: recovered provinces that had been previously overrun by invaders. The Byzantine empire reached its greatest size under Justinian. launched a program to beautify Constan ...
What is the name given to someone who digs up and studies
... convinced Justinian not to flee Constantinople, but to fight against the Nika rebellion. Theodora ...
... convinced Justinian not to flee Constantinople, but to fight against the Nika rebellion. Theodora ...
He created the Justinian Code. He hired 10 legal experts who went
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
... the Western Roman Empire and those in the Eastern Roman Empire. Eventually, they began to develop different rituals and ceremonies. The Pope (WEST) and the Patriarch (EAST) both disagreed on whether ICONS could be used in churches. These two excommunicated one another in 1054. This is when the two c ...
Byzantine Empire Study Guide
... Justinian’s Code – popular name for a massive collection of laws (Corpus Juris Civilis, or “Body of Civil Law”); Justinian set up a commission to collect, revise, and organize all the laws of ancient Rome; influenced many Western legal codes Theodora – wife of Justinian; shrewd politician, served as ...
... Justinian’s Code – popular name for a massive collection of laws (Corpus Juris Civilis, or “Body of Civil Law”); Justinian set up a commission to collect, revise, and organize all the laws of ancient Rome; influenced many Western legal codes Theodora – wife of Justinian; shrewd politician, served as ...
Byzantine Empire
... century A.D., the western half of the Roman Empire had been weakened by barbarian invasions. At the same time, Christianity was a growing force and Constantine the Great became the first Christian emperor of Rome. ...
... century A.D., the western half of the Roman Empire had been weakened by barbarian invasions. At the same time, Christianity was a growing force and Constantine the Great became the first Christian emperor of Rome. ...
The Byzantine Empire - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Theodora pushes for women’s rights: – Man couldn’t beat wife – Women could sue for divorce. – Women could own property ...
... • Theodora pushes for women’s rights: – Man couldn’t beat wife – Women could sue for divorce. – Women could own property ...
Byzantine Empire and Russia
... Roman Empire By 554— reclaimed Italy, North Africa, & Spain from Germanic tribes – Chemical weapon “Greek fire” – After Justinian’s death, Germanic tribes reclaimed lands ...
... Roman Empire By 554— reclaimed Italy, North Africa, & Spain from Germanic tribes – Chemical weapon “Greek fire” – After Justinian’s death, Germanic tribes reclaimed lands ...
The Commonwealth of Byzantium
... • Power centralized in figure of emperor. • Christian leader cannot claim divinity, rather divine authority. • Political rule. • Involved in Religious rule as well. • Authority absolute. ...
... • Power centralized in figure of emperor. • Christian leader cannot claim divinity, rather divine authority. • Political rule. • Involved in Religious rule as well. • Authority absolute. ...
Byzantine Empire
... Justinian wanted strength of old Roman Empire By 554— reclaimed Italy, North Africa, & Spain from Germanic tribes – Chemical weapon “Greek fire” – After Justinian’s death, Germanic tribes reclaimed lands ...
... Justinian wanted strength of old Roman Empire By 554— reclaimed Italy, North Africa, & Spain from Germanic tribes – Chemical weapon “Greek fire” – After Justinian’s death, Germanic tribes reclaimed lands ...
Byzantine Papacy

The Byzantine Papacy was a period of Byzantine domination of the papacy from 537 to 752, when popes required the approval of the Byzantine Emperor for episcopal consecration, and many popes were chosen from the apocrisiarii (liaisons from the pope to the emperor) or the inhabitants of Byzantine Greece, Byzantine Syria, or Byzantine Sicily. Justinian I conquered the Italian peninsula in the Gothic War (535–554) and appointed the next three popes, a practice that would be continued by his successors and later be delegated to the Exarchate of Ravenna.With the exception of Pope Martin I, no pope during this period questioned the authority of the Byzantine monarch to confirm the election of the bishop of Rome before consecration could occur; however, theological conflicts were common between pope and emperor in the areas such as monotheletism and iconoclasm.Greek speakers from Greece, Syria, and Byzantine Sicily replaced members of the powerful Roman nobles in the papal chair during this period. Rome under the Greek popes constituted a ""melting pot"" of Western and Eastern Christian traditions, reflected in art as well as liturgy.