Byzantine Empire
... site of the Greek city Byzantium. The Byzantine empire arose from this site. ...
... site of the Greek city Byzantium. The Byzantine empire arose from this site. ...
Hagia Sophia - cloudfront.net
... heads represent the dual sovereignty of the Emperor (secular and religious) and/or dominance of the Byzantine Emperors over both East and West. ...
... heads represent the dual sovereignty of the Emperor (secular and religious) and/or dominance of the Byzantine Emperors over both East and West. ...
Byzantine empire - Ms. Mcatee`s Site
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
Chapter 13 - resources
... The general Belisarius’s conquests reconstructed most of the Roman Empire. ...
... The general Belisarius’s conquests reconstructed most of the Roman Empire. ...
Byzantine Empire Vocabulary Dowry
... Byzantium - was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 657 BC and named after their king Byzas . The city was later renamed Nova Roma by Constantine the Great, but popularly called Constantinople and briefly became the imperial residence of the classical Roman Empire. Then ...
... Byzantium - was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 657 BC and named after their king Byzas . The city was later renamed Nova Roma by Constantine the Great, but popularly called Constantinople and briefly became the imperial residence of the classical Roman Empire. Then ...
What means “Holy Wisdom” - MyClass at TheInspiredInstructor.com
... What was a circus performer that became Justinian’s wife and helped him fight the rioters? What means “hatred of sacred pictures and statues”? What are pictures made by setting small stones or pieces of glass in mortar? What Byzantium general conquered Egypt, Carthage, northern Africa, and Italy? Wh ...
... What was a circus performer that became Justinian’s wife and helped him fight the rioters? What means “hatred of sacred pictures and statues”? What are pictures made by setting small stones or pieces of glass in mortar? What Byzantium general conquered Egypt, Carthage, northern Africa, and Italy? Wh ...
DAY 44: PowerPoint on the Byzantines File
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
The Byzantine Empire
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
The Byzantine Empire
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
... from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. ...
UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE
... 5. What was the main message of Jesus’ teachings? What factors helped Christianity spread throughout the Roman Empire? 6. How did the Christian church change as it grew and as time passed? Why? 7. What reforms did Diocletian and Constantine attempt? How successful were they? Why? 8. What problems di ...
... 5. What was the main message of Jesus’ teachings? What factors helped Christianity spread throughout the Roman Empire? 6. How did the Christian church change as it grew and as time passed? Why? 7. What reforms did Diocletian and Constantine attempt? How successful were they? Why? 8. What problems di ...
Unit 2 ppt Byzantium - Fulton County Schools
... Eastern Orthodox built on the early works of church fathers, such as St Basil and St John Chrysostom (KRIHSuh-stuhm) who later became the patriarch or leading bishop of the east even patriarchs bowed to emperor’s authority which led to controversy the use of icons (religious images used by eas ...
... Eastern Orthodox built on the early works of church fathers, such as St Basil and St John Chrysostom (KRIHSuh-stuhm) who later became the patriarch or leading bishop of the east even patriarchs bowed to emperor’s authority which led to controversy the use of icons (religious images used by eas ...
CHAPTER 14 : THE GREAT SCHISM AND THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
... Besides, the Popes had begun to think themselves universal Bishops, heads over all other Patriarchs; and to this the Patriarch of Constantinople would not submit. The Patriarch asserted that from the old times all Patriarchs had been equal, and had no right to take authority over one another. At las ...
... Besides, the Popes had begun to think themselves universal Bishops, heads over all other Patriarchs; and to this the Patriarch of Constantinople would not submit. The Patriarch asserted that from the old times all Patriarchs had been equal, and had no right to take authority over one another. At las ...
The Byzantine Empire and the Crusades
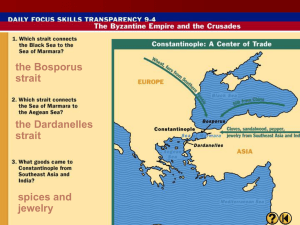
... Center of trade btw the E. and W. Hippodrome (like coliseum), many churches ...
... Center of trade btw the E. and W. Hippodrome (like coliseum), many churches ...
The Byzantine Empire
... As Rome was falling to invaders, strong fortifications and an excellent army protected Constantinople. The Byzantine Empire had also many excellent rulers who were wise as popular, who encouraged education and made reforms to laws and government contributing to the strength of their empire. ...
... As Rome was falling to invaders, strong fortifications and an excellent army protected Constantinople. The Byzantine Empire had also many excellent rulers who were wise as popular, who encouraged education and made reforms to laws and government contributing to the strength of their empire. ...
The Byzantine Empire & the Eastern Orthodox Church
... Eastern Orthodox Church came into conflict with Christian churches of West Iconoclasm – orders by Byzantine emperor to destroy icons after seeing people were worshipping symbols and images instead of God Crowning of Empress Irene in 800 led the Pope of the West to “defend” the church against the r ...
... Eastern Orthodox Church came into conflict with Christian churches of West Iconoclasm – orders by Byzantine emperor to destroy icons after seeing people were worshipping symbols and images instead of God Crowning of Empress Irene in 800 led the Pope of the West to “defend” the church against the r ...
The Byzantine Empire - White Plains Public Schools
... Germanic tribes. By this time, however, the once great empire had already undergone significant changes. It had been divided into western and eastern empires, and its capital had moved east from Rome to the Greek city of Byzantium. The city would become known as Constantinople after the emperor Cons ...
... Germanic tribes. By this time, however, the once great empire had already undergone significant changes. It had been divided into western and eastern empires, and its capital had moved east from Rome to the Greek city of Byzantium. The city would become known as Constantinople after the emperor Cons ...
Byzantine Empire Notes
... Empire, though, grew in wealth and power and ended up being known as the _____________________ Empire. The Classical culture of ___________ and ___________ survived in this empire. Watch the video on the Byzantine Empire and answer the following questions. 1. What did the Eastern Roman Empire come t ...
... Empire, though, grew in wealth and power and ended up being known as the _____________________ Empire. The Classical culture of ___________ and ___________ survived in this empire. Watch the video on the Byzantine Empire and answer the following questions. 1. What did the Eastern Roman Empire come t ...
The Byzantine Empire
... – Priests may not marry; this is called celibacy – Divorce is not permitted – Church is centered in Rome; it is far from the capital of Constantinople ...
... – Priests may not marry; this is called celibacy – Divorce is not permitted – Church is centered in Rome; it is far from the capital of Constantinople ...
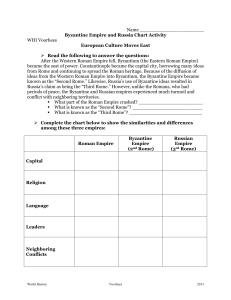
Byzantine Empire and Russia Chart Activity
... After the Western Roman Empire fell, Byzantium (the Eastern Roman Empire) became the seat of power. Constantinople became the capital city, borrowing many ideas from Rome and continuing to spread the Roman heritage. Because of the diffusion of ideas from the Western Roman Empire into Byzantium, the ...
... After the Western Roman Empire fell, Byzantium (the Eastern Roman Empire) became the seat of power. Constantinople became the capital city, borrowing many ideas from Rome and continuing to spread the Roman heritage. Because of the diffusion of ideas from the Western Roman Empire into Byzantium, the ...
Name: Date - Mr. Dowling
... and the Romans. Renaissance scholars referred to the era of the Greeks and Romans as “the classical age,” a term we still use today. Roman literature, law and language have been studied and adopted by many cultures. Our form of government, many of our laws, and our public architecture are based on R ...
... and the Romans. Renaissance scholars referred to the era of the Greeks and Romans as “the classical age,” a term we still use today. Roman literature, law and language have been studied and adopted by many cultures. Our form of government, many of our laws, and our public architecture are based on R ...
DOC - Mr. Dowling
... and the Romans. Renaissance scholars referred to the era of the Greeks and Romans as “the classical age,” a term we still use today. Roman literature, law and language have been studied and adopted by many cultures. Our form of government, many of our laws, and our public architecture are based on R ...
... and the Romans. Renaissance scholars referred to the era of the Greeks and Romans as “the classical age,” a term we still use today. Roman literature, law and language have been studied and adopted by many cultures. Our form of government, many of our laws, and our public architecture are based on R ...
Byzantine Papacy

The Byzantine Papacy was a period of Byzantine domination of the papacy from 537 to 752, when popes required the approval of the Byzantine Emperor for episcopal consecration, and many popes were chosen from the apocrisiarii (liaisons from the pope to the emperor) or the inhabitants of Byzantine Greece, Byzantine Syria, or Byzantine Sicily. Justinian I conquered the Italian peninsula in the Gothic War (535–554) and appointed the next three popes, a practice that would be continued by his successors and later be delegated to the Exarchate of Ravenna.With the exception of Pope Martin I, no pope during this period questioned the authority of the Byzantine monarch to confirm the election of the bishop of Rome before consecration could occur; however, theological conflicts were common between pope and emperor in the areas such as monotheletism and iconoclasm.Greek speakers from Greece, Syria, and Byzantine Sicily replaced members of the powerful Roman nobles in the papal chair during this period. Rome under the Greek popes constituted a ""melting pot"" of Western and Eastern Christian traditions, reflected in art as well as liturgy.