Slide 1
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. wij ...
Towards an Empirically Grounded Predictive Coding Account of
... Friston, 2010), and thus mirror neurons that behave like error units are necessary for a predictive coding theory of action understanding. Unfortunately, the paradigm used by Maranesi and colleagues (2014) precluded the ability to definitively label any of their mirror neurons as error units because ...
... Friston, 2010), and thus mirror neurons that behave like error units are necessary for a predictive coding theory of action understanding. Unfortunately, the paradigm used by Maranesi and colleagues (2014) precluded the ability to definitively label any of their mirror neurons as error units because ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
... neurons was full after 2-3 days of MD. - The increase in the response to the closed eye in monocular neurons was only full after 4-7 days of MD, just like the general increase in binocular neurons (supporting prediction ‘c’). binocular ...
... neurons was full after 2-3 days of MD. - The increase in the response to the closed eye in monocular neurons was only full after 4-7 days of MD, just like the general increase in binocular neurons (supporting prediction ‘c’). binocular ...
Synaptic energy efficiency in retinal processing
... DC response. This describes responses to the level of illumination and is a key feature of ganglion cells (Enroth-Cugell & Robson, 1966; Linsenmeier et al., 1982). All filters calculated with a variety of energy budgets and convergence ratios had positive DC. This is of relevance to image coding beca ...
... DC response. This describes responses to the level of illumination and is a key feature of ganglion cells (Enroth-Cugell & Robson, 1966; Linsenmeier et al., 1982). All filters calculated with a variety of energy budgets and convergence ratios had positive DC. This is of relevance to image coding beca ...
Hailee Denson Biology 1090 Mark Radandt Taking Sides Analysis
... to the cortex. But still more goes into forming a perception of a scene. The activity of cortical neurons that receive visual input is influenced not only by those inputs but also by excitatory and inhibitory interactions between cortical neurons. Of particular importance for coordinating the many n ...
... to the cortex. But still more goes into forming a perception of a scene. The activity of cortical neurons that receive visual input is influenced not only by those inputs but also by excitatory and inhibitory interactions between cortical neurons. Of particular importance for coordinating the many n ...
Lecture 27 Powerpoint File
... fire when monkey sees a graspable object or a stimulus that could be interacted with ...
... fire when monkey sees a graspable object or a stimulus that could be interacted with ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
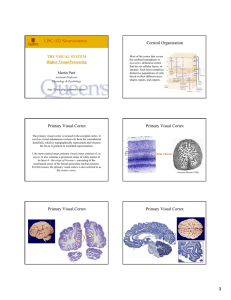
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
text
... longer present, and that single temporal neurons respond to objects located anywhere in the visual field. Thus, inferior temporal neurons respond to a viewed object even if the eyes are moved from one position to another, so long as its image remains on the retina. The neurons in the inferior tempor ...
... longer present, and that single temporal neurons respond to objects located anywhere in the visual field. Thus, inferior temporal neurons respond to a viewed object even if the eyes are moved from one position to another, so long as its image remains on the retina. The neurons in the inferior tempor ...
Processing of complex stimuli and natural scenes in the visual cortex
... exert an important influence on the overall response properties of these neurons. These results imply that the response properties of a neuron can only be fully characterized if the entire RF plus surround are stimulated with realistic natural stimuli. This is also supported by experiments that stud ...
... exert an important influence on the overall response properties of these neurons. These results imply that the response properties of a neuron can only be fully characterized if the entire RF plus surround are stimulated with realistic natural stimuli. This is also supported by experiments that stud ...
In cognitive neuroscience, the prefrontal cortex represents a kind of
... ‘where’ working memory. They recorded from 195 neurons in ‘lateral’ PFC, but unfortunately do not provide much more information regarding the specific location of recording sites. The monkey was instructed to fixate on a fixation spot while a pictorial stimulus was presented. After a delay, two obje ...
... ‘where’ working memory. They recorded from 195 neurons in ‘lateral’ PFC, but unfortunately do not provide much more information regarding the specific location of recording sites. The monkey was instructed to fixate on a fixation spot while a pictorial stimulus was presented. After a delay, two obje ...
Philosophy of the spike
... Spelling out the rate-based postulate 1) for each neuron, there exists a private quantity r(t) whose evolution only depends on the other quantities ri(t). 2) ri(t) is the expected firing probability of neuron i. 3) spike trains (realizations) depend on r(t) only, through a private stochastic proces ...
... Spelling out the rate-based postulate 1) for each neuron, there exists a private quantity r(t) whose evolution only depends on the other quantities ri(t). 2) ri(t) is the expected firing probability of neuron i. 3) spike trains (realizations) depend on r(t) only, through a private stochastic proces ...
Representation of naturalistic image structure in the primate visual
... response of a center-surround linear filter. V1 simple cell responses are commonly described as rectified (or rectified and squared) responses of oriented linear filters (Heeger, 1992). And V1 complex cell responses are described as an average over these simple cell responses, all having the same o ...
... response of a center-surround linear filter. V1 simple cell responses are commonly described as rectified (or rectified and squared) responses of oriented linear filters (Heeger, 1992). And V1 complex cell responses are described as an average over these simple cell responses, all having the same o ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... to 0 degrees, it was found9 that responses of cells preferring directions near 0 degrees are enhanced by about 10%, on average. As a result, two cells with direction preferences of –5 and 5 degrees would receive a common boost when the animal attends to 0 degrees. If this common boost varies slightl ...
... to 0 degrees, it was found9 that responses of cells preferring directions near 0 degrees are enhanced by about 10%, on average. As a result, two cells with direction preferences of –5 and 5 degrees would receive a common boost when the animal attends to 0 degrees. If this common boost varies slightl ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... to 0 degrees, it was found9 that responses of cells preferring directions near 0 degrees are enhanced by about 10%, on average. As a result, two cells with direction preferences of –5 and 5 degrees would receive a common boost when the animal attends to 0 degrees. If this common boost varies slight ...
... to 0 degrees, it was found9 that responses of cells preferring directions near 0 degrees are enhanced by about 10%, on average. As a result, two cells with direction preferences of –5 and 5 degrees would receive a common boost when the animal attends to 0 degrees. If this common boost varies slight ...
Information Optimization in Coupled Audio–Visual Cortical Maps Mehran Kardar A. Zee
... Ref. [7]. The essence of this approach is the assumption that neural connections act as linear filters of the incoming signals, and also introduce noise in the outputs. If the (correlated) input signals, and the random noise, are taken from Gaussian probability distributions, the outputs are also Ga ...
... Ref. [7]. The essence of this approach is the assumption that neural connections act as linear filters of the incoming signals, and also introduce noise in the outputs. If the (correlated) input signals, and the random noise, are taken from Gaussian probability distributions, the outputs are also Ga ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Document
... • a region of visual association cortex; receives fibers from the striate cortex and from the superior colliculi and projects to the inferior temporal cortex • Each region is specialized, containing neurons that respond to particular features of visual information, such as orientation, movement, spa ...
... • a region of visual association cortex; receives fibers from the striate cortex and from the superior colliculi and projects to the inferior temporal cortex • Each region is specialized, containing neurons that respond to particular features of visual information, such as orientation, movement, spa ...
Damien Lescal , Jean Rouat, and Stéphane Molotchnikoff
... overload the ears of the patient with wasteful sounds that carry useless characteristics of the image. Usually these systems encode the luminosity of all pixels from the image in the amplitude of modulated sounds. The vOICe and the Cronly-Dillon device use left-to-right time scanning to encode horiz ...
... overload the ears of the patient with wasteful sounds that carry useless characteristics of the image. Usually these systems encode the luminosity of all pixels from the image in the amplitude of modulated sounds. The vOICe and the Cronly-Dillon device use left-to-right time scanning to encode horiz ...
NeuralNets
... synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) built a first abstract model of a neuron. ...
... synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) built a first abstract model of a neuron. ...
P-retinal ganglion cells
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
Document
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
The relative advantages of sparse versus distributed encoding for
... firing rate of each output neuron is not linear, it is necessary to find a more appropriate criterion, to evaluate the capacity of the associative network, than the maximum number of independent associations which can be stored. In fact, the mapping from the axonal firing pattern in the input to the ...
... firing rate of each output neuron is not linear, it is necessary to find a more appropriate criterion, to evaluate the capacity of the associative network, than the maximum number of independent associations which can be stored. In fact, the mapping from the axonal firing pattern in the input to the ...
A quantitative theory of neural computation Cambridge, MA 02138
... uncover how the brain actually works if the brain is computationally so constrained that there are few solutions consistent with those constraints. We take this observation as our methodology. It appears that the brain is indeed highly constrained in how a neuron can have a purposeful effect on an a ...
... uncover how the brain actually works if the brain is computationally so constrained that there are few solutions consistent with those constraints. We take this observation as our methodology. It appears that the brain is indeed highly constrained in how a neuron can have a purposeful effect on an a ...
Efficient coding hypothesis

The efficient coding hypothesis was proposed by Horace Barlow in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the brain. Within the brain, neurons often communicate with one another by sending electrical impulses referred to as action potentials or spikes. One goal of sensory neuroscience is to decipher the meaning of these spikes in order to understand how the brain represents and processes information about the outside world. Barlow hypothesized that the spikes in the sensory system formed a neural code for efficiently representing sensory information. By efficient Barlow meant that the code minimized the number of spikes needed to transmit a given signal. This is somewhat analogous to transmitting information across the internet, where different file formats can be used to transmit a given image. Different file formats require different number of bits for representing the same image at given distortion level, and some are better suited for representing certain classes of images than others. According to this model, the brain is thought to use a code which is suited for representing visual and audio information representative of an organism's natural environment.