Expanding small UAV capabilities with ANN : a case - HAL-ENAC
... with higher security and much lower cost than other traditional means could provide, for example, the use crewed helicopters. With factors like fatigue and tiredness due to extensive hours of work the human eye can often fail on the mission of detect a change in the terrain. An autonomous helicopter ...
... with higher security and much lower cost than other traditional means could provide, for example, the use crewed helicopters. With factors like fatigue and tiredness due to extensive hours of work the human eye can often fail on the mission of detect a change in the terrain. An autonomous helicopter ...
Impact of Correlated inputs on Simple Neural Models
... Conclusions The pair wise correlation in the spike trains has a fundamental effect on the firing rate of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation ...
... Conclusions The pair wise correlation in the spike trains has a fundamental effect on the firing rate of the recipient neuron The effect is qualitatively independent of the neural model The neurons have specific preferences to certain levels of correlations in input trains The temporal correlation ...
PY460: Physiological Psychology
... coding of visual information in the brain does not duplicate the stimulus being viewed ...
... coding of visual information in the brain does not duplicate the stimulus being viewed ...
On-center off surround ganglion cells
... low spatial resolution, high sensitivity to contrast, rapid signal transfer, without information about color. The small-celled pathway has 4 small-grained layers in the LGN, high spatial resolution, color, slower information transfer, low sensitivity ...
... low spatial resolution, high sensitivity to contrast, rapid signal transfer, without information about color. The small-celled pathway has 4 small-grained layers in the LGN, high spatial resolution, color, slower information transfer, low sensitivity ...
Natural signal statistics and sensory gain control
... it in a wide variety of natural images and sounds. It occurs even when the filters are chosen to be orthogonal, non-overlapping or from a set that is optimized for statistical independence5. The strength of the dependency varies depending on the specific pair of filters chosen (Fig. 3). Nevertheless ...
... it in a wide variety of natural images and sounds. It occurs even when the filters are chosen to be orthogonal, non-overlapping or from a set that is optimized for statistical independence5. The strength of the dependency varies depending on the specific pair of filters chosen (Fig. 3). Nevertheless ...
cogsci200
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
November 2000 Volume 3 Number Supp p 1168
... that the response, unlike a speedometer, should not increase continuously with increasing velocity; instead, going beyond an optimum velocity should decrease the response. The model also predicted that the optimum velocity should vary with the pattern's spatial wavelength so that their ratio remains ...
... that the response, unlike a speedometer, should not increase continuously with increasing velocity; instead, going beyond an optimum velocity should decrease the response. The model also predicted that the optimum velocity should vary with the pattern's spatial wavelength so that their ratio remains ...
Learning receptive fields using predictive feedback
... and the next neuron is chosen by again determining which of the remaining V1 basis vectors best predicts this residual input. In a neural network, the subtractive process is carried out using feedback connections, so that at each iteration of the algorithm the residual input is described by the acti ...
... and the next neuron is chosen by again determining which of the remaining V1 basis vectors best predicts this residual input. In a neural network, the subtractive process is carried out using feedback connections, so that at each iteration of the algorithm the residual input is described by the acti ...
Chapter Summary Visual Stimulus Light is part of the
... The visual system has two kinds of crossovers: (a) visual material is reversed by the lens onto the retina and (b) at the optic chiasm, half of the fibers in each optic nerve cross over. As a result of these crossovers, everything from the left side of the visual field ends up on the right-hand side ...
... The visual system has two kinds of crossovers: (a) visual material is reversed by the lens onto the retina and (b) at the optic chiasm, half of the fibers in each optic nerve cross over. As a result of these crossovers, everything from the left side of the visual field ends up on the right-hand side ...
Optical Illusion - CS 229: Machine Learning
... and dark borders. We were expecting to be able to demonstrate brightness and watercolor illusion by this smoothening. The same test has been performed on brightness illusion and a group of watercolor illusions. Figure 3 shows brightness illusion image reconstructed by the sparse coding before and af ...
... and dark borders. We were expecting to be able to demonstrate brightness and watercolor illusion by this smoothening. The same test has been performed on brightness illusion and a group of watercolor illusions. Figure 3 shows brightness illusion image reconstructed by the sparse coding before and af ...
P312Ch04C_BeyondV1
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...
... 3) May be a separate area in the inferotemporal lobe containing neurons which respond to face-like stimuli. The fusiform face area has been identified in humans. It’s under the temporal lobe. 4) Ramachandran has suggested that there may be as many as 30 different processing modules. Each one contain ...
How fast is the speed of thought?
... still be only about 20-30 ms processing time per synapse. How fast can you see? Another way of looking at processing times is to examine the responses of individual neurons, and to determine at what point in their responses it is possible to discriminate between stimuli. For example, Thorpe and Imbe ...
... still be only about 20-30 ms processing time per synapse. How fast can you see? Another way of looking at processing times is to examine the responses of individual neurons, and to determine at what point in their responses it is possible to discriminate between stimuli. For example, Thorpe and Imbe ...
What are Computational Neuroscience and Neuroinformatics
... Computational Neuroscience1 is an interdisciplinary science that links the diverse fields of neuroscience, computer science, physics and applied mathematics together. It serves as the primary theoretical method for investigating the function and mechanism of the nervous system. Computational neurosc ...
... Computational Neuroscience1 is an interdisciplinary science that links the diverse fields of neuroscience, computer science, physics and applied mathematics together. It serves as the primary theoretical method for investigating the function and mechanism of the nervous system. Computational neurosc ...
Stimulus Response Time Lab
... Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the CNS. Signals from the brain are carried to motor neurons (PNS), which carry out responses by muscles. In this lab, you will be comparing the rate at which sensory neurons, working through the brain, can elicit responses via motor neurons. Purpose: ...
... Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the CNS. Signals from the brain are carried to motor neurons (PNS), which carry out responses by muscles. In this lab, you will be comparing the rate at which sensory neurons, working through the brain, can elicit responses via motor neurons. Purpose: ...
Attending to Contrast
... study. Stimuli consisted of patches of sinusoidal gratings (rows of alternating bright and dark bars), which were presented at various levels of contrast. With this experimental design, the authors could compare the firing rates of neurons across a range of contrasts, and thus compute the neuron’s c ...
... study. Stimuli consisted of patches of sinusoidal gratings (rows of alternating bright and dark bars), which were presented at various levels of contrast. With this experimental design, the authors could compare the firing rates of neurons across a range of contrasts, and thus compute the neuron’s c ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produced by distinct functional and transient neural ensembles, has been named the degeneracy ...
... spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produced by distinct functional and transient neural ensembles, has been named the degeneracy ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 26.11 Optical imaging of functional architecture in the primate visual cortex. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for optical imaging. Digitized images of a region of visual cortex (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual ...
... FIGURE 26.11 Optical imaging of functional architecture in the primate visual cortex. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for optical imaging. Digitized images of a region of visual cortex (as in B) are taken with a CCD camera while the anesthetized, paralyzed animal is viewing a visual ...
SOLARcief2003
... Through learning, one pair of function and threshold will be chosen and solidified. ...
... Through learning, one pair of function and threshold will be chosen and solidified. ...
Neurons and Networks. An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, Second Edition Brochure
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
overview imagenet neural networks alexnet meta-network
... Previous winner of ImageNet, the large, deep convolutional neural network trained by Alex Krizhevsky et al to classify the 1.2 million high-resolution images in the ImageNet LSVRC-2012 contest into the 1000 different classes. AlexNet was constructed similarly to L E N ET, but was expanded in every d ...
... Previous winner of ImageNet, the large, deep convolutional neural network trained by Alex Krizhevsky et al to classify the 1.2 million high-resolution images in the ImageNet LSVRC-2012 contest into the 1000 different classes. AlexNet was constructed similarly to L E N ET, but was expanded in every d ...
It takes all kinds to make a brain
... good match for that movie. Similarly, the ability of mitral cells to encode an odor stimulus may depend on how well their filters match the properties of ORN input. Nevertheless, the fundamental conclusion of this study is likely to be relevant to other circuits. Indeed, there is evidence for a simi ...
... good match for that movie. Similarly, the ability of mitral cells to encode an odor stimulus may depend on how well their filters match the properties of ORN input. Nevertheless, the fundamental conclusion of this study is likely to be relevant to other circuits. Indeed, there is evidence for a simi ...
Sparse but not `Grandmother-cell` coding in the medial temporal lobe
... the case when using single electrode recordings with movable probes that tend to miss sparsely firing cells – which might be quiet when the electrode passes in their vicinity unless their ‘trigger’ stimulus is shown – and are more likely to report neurons with high spontaneous rates and broadly tune ...
... the case when using single electrode recordings with movable probes that tend to miss sparsely firing cells – which might be quiet when the electrode passes in their vicinity unless their ‘trigger’ stimulus is shown – and are more likely to report neurons with high spontaneous rates and broadly tune ...
Principles of Sensory Coding
... cortical neurons). If it is activated it may increase its rate to 50 spikes/s; its target cells will have to wait for at least 1/2 second to figure out (reliably decode) that there has been a significant increase in firing rate. Our ability to detect novel input is far faster than this suggesting th ...
... cortical neurons). If it is activated it may increase its rate to 50 spikes/s; its target cells will have to wait for at least 1/2 second to figure out (reliably decode) that there has been a significant increase in firing rate. Our ability to detect novel input is far faster than this suggesting th ...
Slide ()
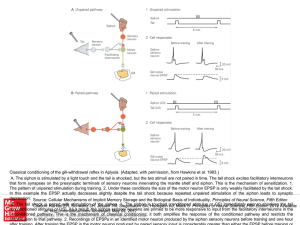
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
BrainMechanismsofUnconsciousInference2011
... inhibitory signals obtained from other neurons. • They signal to other neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
... inhibitory signals obtained from other neurons. • They signal to other neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
Efficient coding hypothesis

The efficient coding hypothesis was proposed by Horace Barlow in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the brain. Within the brain, neurons often communicate with one another by sending electrical impulses referred to as action potentials or spikes. One goal of sensory neuroscience is to decipher the meaning of these spikes in order to understand how the brain represents and processes information about the outside world. Barlow hypothesized that the spikes in the sensory system formed a neural code for efficiently representing sensory information. By efficient Barlow meant that the code minimized the number of spikes needed to transmit a given signal. This is somewhat analogous to transmitting information across the internet, where different file formats can be used to transmit a given image. Different file formats require different number of bits for representing the same image at given distortion level, and some are better suited for representing certain classes of images than others. According to this model, the brain is thought to use a code which is suited for representing visual and audio information representative of an organism's natural environment.