Lecture 7A
... • In the first stream, the information flows from the primary visual cortex to the inferior temporal cortex. • This stream includes the departments that deal with object recognition • Due to the stream’s direction from the back of the brain towards the front of the brain (along “the brain’s belly”), ...
... • In the first stream, the information flows from the primary visual cortex to the inferior temporal cortex. • This stream includes the departments that deal with object recognition • Due to the stream’s direction from the back of the brain towards the front of the brain (along “the brain’s belly”), ...
10-21-09
... multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC. This experiment will be compared to monkeys damaged in the lOFC from previous experiments. The experiments involved selecting from three stimuli on a screen, e ...
... multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC. This experiment will be compared to monkeys damaged in the lOFC from previous experiments. The experiments involved selecting from three stimuli on a screen, e ...
Visual vs. Language-based Thinking
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
Group Redundancy Measures Reveals Redundancy Reduction in the Auditory Pathway
... Interactions and high order correlations between neurons were mostly investigated within single brain areas on the level of pairs of cells, showing both synergistic and redundant interactions [5, 6, 4]. The current study focuses on developing redundancy measures for larger groups of neurons and comp ...
... Interactions and high order correlations between neurons were mostly investigated within single brain areas on the level of pairs of cells, showing both synergistic and redundant interactions [5, 6, 4]. The current study focuses on developing redundancy measures for larger groups of neurons and comp ...
Autobiography for 2016 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience Carla J. Shatz
... because they are relatively accessible and highly stereotyped: in adult, retinal ganglion cells from each eye are connected to LGN neurons in separate but adjacent eye-specific layers. However, as with the OD columns in visual cortex, it was assumed that the segregation of RGC axons originating from ...
... because they are relatively accessible and highly stereotyped: in adult, retinal ganglion cells from each eye are connected to LGN neurons in separate but adjacent eye-specific layers. However, as with the OD columns in visual cortex, it was assumed that the segregation of RGC axons originating from ...
Basic Architecture of the Visual Cortex
... • Standard wisdom: “smart animals have dumb retinas and dumb animals have smart retinas.” • This is questioned by M. Meister (handout). He argues that human/monkey retinas are more complex than current models suggest. That current models of retinal neurons are based on experimental findings using si ...
... • Standard wisdom: “smart animals have dumb retinas and dumb animals have smart retinas.” • This is questioned by M. Meister (handout). He argues that human/monkey retinas are more complex than current models suggest. That current models of retinal neurons are based on experimental findings using si ...
PDF
... Neural circuit building During development, sensory neurons form neural circuits with motoneurons. Although the anatomical details of these circuits are well described, less is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory n ...
... Neural circuit building During development, sensory neurons form neural circuits with motoneurons. Although the anatomical details of these circuits are well described, less is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory n ...
Ch 2 Cognition & the Brain
... (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? • Single cell recording ...
... (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? • Single cell recording ...
Lecture notes
... Mutual information is defined as the amount by which the received signal actually decreases uncertainty about the source. Mutual information depends on ...
... Mutual information is defined as the amount by which the received signal actually decreases uncertainty about the source. Mutual information depends on ...
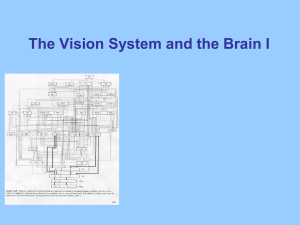
Lectures for 5th week: Visual System I
... occurs within brain regions (retina, LGN, V1) occurs between brain regions (V4, IT, MT, PPC) occurs between brain circuits (ventral, dorsal) Visual system also exemplifies concurrent processing ...
... occurs within brain regions (retina, LGN, V1) occurs between brain regions (V4, IT, MT, PPC) occurs between brain circuits (ventral, dorsal) Visual system also exemplifies concurrent processing ...
The language of the brain
... for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is said to be strengthened when the firing of a neuron on one side of a synapse leads the neuron on the other side of the synapse to register a stronger response. In 1997 Henry Markram and Bert Sak ...
... for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is said to be strengthened when the firing of a neuron on one side of a synapse leads the neuron on the other side of the synapse to register a stronger response. In 1997 Henry Markram and Bert Sak ...
MCB105 QUIZ 5 2016 wA
... - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these findings in previous investigations? Explain the methods in detail. [2] they pharmacologically block ga ...
... - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these findings in previous investigations? Explain the methods in detail. [2] they pharmacologically block ga ...
here - WPI
... Since the mid-1990s, however, the expanse and pace of BCI research has been increasing at a tremendous rate. In the past 20 years, scientists have been exploring BCIs in relation to a wide variety of fields, ranging from applied neuroscience to materials engineering. In this time, many studies and b ...
... Since the mid-1990s, however, the expanse and pace of BCI research has been increasing at a tremendous rate. In the past 20 years, scientists have been exploring BCIs in relation to a wide variety of fields, ranging from applied neuroscience to materials engineering. In this time, many studies and b ...
The relationship between the activity of neurons recorded
... information content of spike trains recorded from trials where movement was towards a target near the preferred direction would differ from the information content of spike trains recorded from trials where movement was in the opposite direction. Approximate entropy (Pincus, 1991) was used to charac ...
... information content of spike trains recorded from trials where movement was towards a target near the preferred direction would differ from the information content of spike trains recorded from trials where movement was in the opposite direction. Approximate entropy (Pincus, 1991) was used to charac ...
Information Integration and Decision Making in Humans and
... Short Interval of Time • If p(spike per 10 msec) = p(H|E) then having a single neuron to represent a hypothesis would make it difficult to get a clear estimate of P(H|E) within, say, 100 msec. • However, suppose many (say, 10,000) neurons each encode the same hypothesis, and suppose that they produc ...
... Short Interval of Time • If p(spike per 10 msec) = p(H|E) then having a single neuron to represent a hypothesis would make it difficult to get a clear estimate of P(H|E) within, say, 100 msec. • However, suppose many (say, 10,000) neurons each encode the same hypothesis, and suppose that they produc ...
Two Point Discrimination Lab
... fingers are very large and the arms and back are small. This type of picture is called a homunculus, literally, "little man" or person. All sensory systems feed information into the cerebral cortex in orderly maps, even though the other peripheral sensory receptors, unlike those of the touch or tact ...
... fingers are very large and the arms and back are small. This type of picture is called a homunculus, literally, "little man" or person. All sensory systems feed information into the cerebral cortex in orderly maps, even though the other peripheral sensory receptors, unlike those of the touch or tact ...
PPT2
... The complex cells, which are not sensitive to the polarity of the luminance contrast at edge, would be particularly suitable for representing borders or boundaries of regions. The Hypercomplex cells could serve as derivative operators which act on complex cells’ responses to detect texture boundarie ...
... The complex cells, which are not sensitive to the polarity of the luminance contrast at edge, would be particularly suitable for representing borders or boundaries of regions. The Hypercomplex cells could serve as derivative operators which act on complex cells’ responses to detect texture boundarie ...
salinas-banbury-2004.
... • wij - connection from GM neuron j to output neuron i • Encoded target location is center of mass of output units • wij set to minimize difference between desired and driven output ...
... • wij - connection from GM neuron j to output neuron i • Encoded target location is center of mass of output units • wij set to minimize difference between desired and driven output ...
Neuron highlight
... For example, two neural responses may be very similar in overall spike count, yet exhibit crucial differences in their temporal discharge pattern (Schnupp et al., 2006). To achieve a measure of redundancy which is largely independent of assumptions about the relevant response metric, Chechik and col ...
... For example, two neural responses may be very similar in overall spike count, yet exhibit crucial differences in their temporal discharge pattern (Schnupp et al., 2006). To achieve a measure of redundancy which is largely independent of assumptions about the relevant response metric, Chechik and col ...
... The continued development of computational tools offers the possibility to execute processes with the ability to carry out activities more efficiently, exact-ness and precision. Between these tools there is the neural architecture, Deep Belief Network (DBN), designed to collaborate in the developmen ...
The virtue of simplicity
... However, models that work well to explain perceptual phenomena are often difficult to instantiate in ‘wetware.’ For these reasons, a simple model that explains such a complex perceptual problem in neuronally realistic terms provides considerable cause for rejoicing. The model of Rust et al. in this ...
... However, models that work well to explain perceptual phenomena are often difficult to instantiate in ‘wetware.’ For these reasons, a simple model that explains such a complex perceptual problem in neuronally realistic terms provides considerable cause for rejoicing. The model of Rust et al. in this ...
Barlow, Horace (2001) - Cambridge Neuroscience
... There has been one major change in my viewpoint. Initially I thought that economy was the main benefit to be derived from exploiting redundancy, as it is for AT&T and British Telecom. But, as explained in greater detail below, the physiological and anatomical facts do not fit the idea that the brain ...
... There has been one major change in my viewpoint. Initially I thought that economy was the main benefit to be derived from exploiting redundancy, as it is for AT&T and British Telecom. But, as explained in greater detail below, the physiological and anatomical facts do not fit the idea that the brain ...
Efficient coding hypothesis

The efficient coding hypothesis was proposed by Horace Barlow in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the brain. Within the brain, neurons often communicate with one another by sending electrical impulses referred to as action potentials or spikes. One goal of sensory neuroscience is to decipher the meaning of these spikes in order to understand how the brain represents and processes information about the outside world. Barlow hypothesized that the spikes in the sensory system formed a neural code for efficiently representing sensory information. By efficient Barlow meant that the code minimized the number of spikes needed to transmit a given signal. This is somewhat analogous to transmitting information across the internet, where different file formats can be used to transmit a given image. Different file formats require different number of bits for representing the same image at given distortion level, and some are better suited for representing certain classes of images than others. According to this model, the brain is thought to use a code which is suited for representing visual and audio information representative of an organism's natural environment.