Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... How do IT neurons encode objects/categories? e.g., • local versus distributed representations/coding • temporal versus rate coding at the neuronal level Can we recruit ANNs to answer such questions? Can ANNs perform classification as well given similar data? Recently, Elizabeth Thomas and colleagues ...
... How do IT neurons encode objects/categories? e.g., • local versus distributed representations/coding • temporal versus rate coding at the neuronal level Can we recruit ANNs to answer such questions? Can ANNs perform classification as well given similar data? Recently, Elizabeth Thomas and colleagues ...
Efficient Coding Hypothesis and an Introduction to
... their sensory pathways must have mechanisms for detecting such stimuli and discriminating between them. On the other hand, there was no evidence that frogs use visual system to locate themselves in surroundings [Yerkes 1903], contradictory to the "passwords" hypothesis. This hypothesis is based on e ...
... their sensory pathways must have mechanisms for detecting such stimuli and discriminating between them. On the other hand, there was no evidence that frogs use visual system to locate themselves in surroundings [Yerkes 1903], contradictory to the "passwords" hypothesis. This hypothesis is based on e ...
Lecture 2 - Computer Science
... •When you move your eyes, the image moves. How do you know the world is not moving? ...
... •When you move your eyes, the image moves. How do you know the world is not moving? ...
KC Kajander GJ Giesler, Jr. KJ Gingrich JH Byrne YS Chan J
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
Meart: 1000 word catalogue essay:
... images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technology. The simplified process follows. Video images (generated at the exhibition site) are sent to ...
... images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technology. The simplified process follows. Video images (generated at the exhibition site) are sent to ...
Positive sparse coding of natural images: a theory for simple cell
... a dark edge with bright flanks. We ask, what is the function of this polarity tuning, if any, and how does it arise from the underlying neural circuitry? Perhaps the most influential functional theory of simple cell tuning is sparse coding [2]. According to this theory, the function of simple cells ...
... a dark edge with bright flanks. We ask, what is the function of this polarity tuning, if any, and how does it arise from the underlying neural circuitry? Perhaps the most influential functional theory of simple cell tuning is sparse coding [2]. According to this theory, the function of simple cells ...
Neuron Powerpoint
... • The rods in the eye sensitive to light • The cons in the eye color-sensitive • These convert the light into the neural impulses, which are coded by the retina before going to the optic nerve. ...
... • The rods in the eye sensitive to light • The cons in the eye color-sensitive • These convert the light into the neural impulses, which are coded by the retina before going to the optic nerve. ...
Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
Key - Cornell
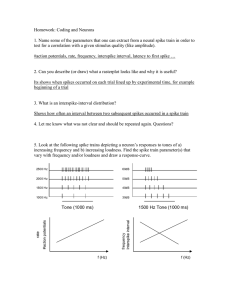
... Homework: Coding and Neurons 1. Name some of the parameters that one can extract from a neural spike train in order to test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
... Homework: Coding and Neurons 1. Name some of the parameters that one can extract from a neural spike train in order to test for a correlation with a given stimulus quality (like amplitude). #action potentials, rate, frequency, interspike interval, latency to first spike … ...
Nerve Cells Images
... Scanning electron micrograph of an isolated retinal ganglion cell. This is a type of neuron, typically located near the inner surface of the eye’s retina, that receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit visual infor ...
... Scanning electron micrograph of an isolated retinal ganglion cell. This is a type of neuron, typically located near the inner surface of the eye’s retina, that receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit visual infor ...
Slide ()
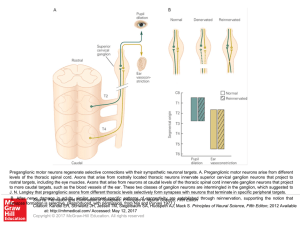
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
Lecture 5 - TeachLine
... Introduction to Sensory Systems Mapping the receptive field of visual system neurons using small spots of light or dark. Very effective in RGC & LGN. Very problematic for Visual Cortex. ...
... Introduction to Sensory Systems Mapping the receptive field of visual system neurons using small spots of light or dark. Very effective in RGC & LGN. Very problematic for Visual Cortex. ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
Accumulative evidence indicates that microglial cells influence the
... Representation of Visual Scenery How is our visual environment represented and processed in the brain? In my lab, we seek answers to this fundamental question with a multi-scale approach combining two-photon imaging with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive ...
... Representation of Visual Scenery How is our visual environment represented and processed in the brain? In my lab, we seek answers to this fundamental question with a multi-scale approach combining two-photon imaging with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive ...
Chapter 2 figures 2.7 to 2.12
... laterally). The output at the next layer of neurons (bottom in figure) has a slightly brighter "hairline" on the brighter side of the image(88 vs 80 units); and a slightly darker "hairline" on the darker side (8 vs 16 units). The units of brightness were selected as an example. Stimulus image ...
... laterally). The output at the next layer of neurons (bottom in figure) has a slightly brighter "hairline" on the brighter side of the image(88 vs 80 units); and a slightly darker "hairline" on the darker side (8 vs 16 units). The units of brightness were selected as an example. Stimulus image ...
Slide ()
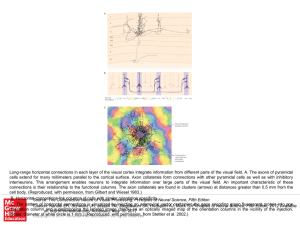
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
Nádasdy Zoltán Cal Tech
... (Encoding and decoding information by the phase of action potentials) Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO ...
... (Encoding and decoding information by the phase of action potentials) Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO ...
Sensory Physiology
... Action Potential Firing Rate • The steady state rate of action potential firing can increase or decrease in frequency known as “On” pathway and “Off” pathway. • Secondary neurons can receive inputs from both “on” and “off” neurons and that leads to more sensitivity. ...
... Action Potential Firing Rate • The steady state rate of action potential firing can increase or decrease in frequency known as “On” pathway and “Off” pathway. • Secondary neurons can receive inputs from both “on” and “off” neurons and that leads to more sensitivity. ...
Exam 2-SG suggested answers (2010)
... C. Visual information from the two eyes is kept separate up to the visual cortex, i.e. there are no binocular neurons below the level of the cortex, while auditory pathways from from the two ears are extensively crossed, so cells at all levels above the cochlear nuclei are binaural, i.e. they receiv ...
... C. Visual information from the two eyes is kept separate up to the visual cortex, i.e. there are no binocular neurons below the level of the cortex, while auditory pathways from from the two ears are extensively crossed, so cells at all levels above the cochlear nuclei are binaural, i.e. they receiv ...
Researchers find that neurons in the primary visual cortex listen to
... researchers were able to get a better look at what happens when neurons in the visual cortex send messages to one another by combing the two techniques. That allowed them to create receptive field maps for the neurons, which showed how much attention was paid to each input (as demonstrated by measur ...
... researchers were able to get a better look at what happens when neurons in the visual cortex send messages to one another by combing the two techniques. That allowed them to create receptive field maps for the neurons, which showed how much attention was paid to each input (as demonstrated by measur ...
Efficient coding hypothesis

The efficient coding hypothesis was proposed by Horace Barlow in 1961 as a theoretical model of sensory coding in the brain. Within the brain, neurons often communicate with one another by sending electrical impulses referred to as action potentials or spikes. One goal of sensory neuroscience is to decipher the meaning of these spikes in order to understand how the brain represents and processes information about the outside world. Barlow hypothesized that the spikes in the sensory system formed a neural code for efficiently representing sensory information. By efficient Barlow meant that the code minimized the number of spikes needed to transmit a given signal. This is somewhat analogous to transmitting information across the internet, where different file formats can be used to transmit a given image. Different file formats require different number of bits for representing the same image at given distortion level, and some are better suited for representing certain classes of images than others. According to this model, the brain is thought to use a code which is suited for representing visual and audio information representative of an organism's natural environment.