**** 1
... resistor, which entails power consumption. Conversion to higher levels cannot be done using resistors. • DC-DC converters are invented to accomplish voltage conversion to higher/lower levels without unnecessary power consumption. They utilize switches to change the voltage levels. • In this design p ...
... resistor, which entails power consumption. Conversion to higher levels cannot be done using resistors. • DC-DC converters are invented to accomplish voltage conversion to higher/lower levels without unnecessary power consumption. They utilize switches to change the voltage levels. • In this design p ...
Pocket Multi-channel Signal Analyzer
... Simple Operation Instructions for MCSA 2.0 The multi-channel signal analyzer software, MCSA Version 2.0, is used together with a MCSA-16000 Pocket Multi-Channel Signal Analyzer purchased. It is compatible with Window operation systems 98/2000/ME/NT/XP. The software has a built-in help and is easy t ...
... Simple Operation Instructions for MCSA 2.0 The multi-channel signal analyzer software, MCSA Version 2.0, is used together with a MCSA-16000 Pocket Multi-Channel Signal Analyzer purchased. It is compatible with Window operation systems 98/2000/ME/NT/XP. The software has a built-in help and is easy t ...
AN-536: Dimensional Gaging Measurements with Model
... of the object to be measured. The LVDTs are positioned such that there is a known maximum distance between them in the fully retracted position. When the object to be measured is placed between the two LVDTs, the displacement of both LVDTs are added together and then the computer or control system w ...
... of the object to be measured. The LVDTs are positioned such that there is a known maximum distance between them in the fully retracted position. When the object to be measured is placed between the two LVDTs, the displacement of both LVDTs are added together and then the computer or control system w ...
v O
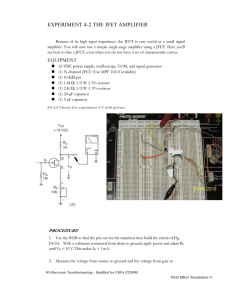
... the input coupling capacitor, as shown in Fig. E4-2C. Keep lead lengths short to minimize noise pick up. Keep all of the other circuit components as in step 6, and keep VS at 0.5 Vp-p. Now while watching vo with an oscilloscope, adjust potentiometer, until vo reads half the value obtained in step 6. ...
... the input coupling capacitor, as shown in Fig. E4-2C. Keep lead lengths short to minimize noise pick up. Keep all of the other circuit components as in step 6, and keep VS at 0.5 Vp-p. Now while watching vo with an oscilloscope, adjust potentiometer, until vo reads half the value obtained in step 6. ...
AN100 An overview of data converters
... again compared with the DAC output and the second bit cleared or many things; the accuracy required, the conversion speed left high, based on the same criteria as for the MSB. This process necessary, the necessary immunity to noise, and cost are some of continues until all bits have been determined. ...
... again compared with the DAC output and the second bit cleared or many things; the accuracy required, the conversion speed left high, based on the same criteria as for the MSB. This process necessary, the necessary immunity to noise, and cost are some of continues until all bits have been determined. ...
Simple Discrete SE-to-Differential Precision In
... advantage of the precise control that the in-amp has of its output voltage relative to the reference voltage. Although the dc performance and resistor matching of the op amp affect the dc common-mode output accuracy, these errors are likely to be rejected by the next device in the signal chain and, ...
... advantage of the precise control that the in-amp has of its output voltage relative to the reference voltage. Although the dc performance and resistor matching of the op amp affect the dc common-mode output accuracy, these errors are likely to be rejected by the next device in the signal chain and, ...
Pocket Multi-channel Signal Analyzer
... Simple Operation Instructions for MCSA 2.0 The multi-channel signal analyzer software, MCSA Version 2.0, is used together with a MCSA-16000 Pocket Multi-Channel Signal Analyzer purchased. It is compatible with Window operation systems 98/2000/ME/NT/XP. The software has a built-in help and is easy t ...
... Simple Operation Instructions for MCSA 2.0 The multi-channel signal analyzer software, MCSA Version 2.0, is used together with a MCSA-16000 Pocket Multi-Channel Signal Analyzer purchased. It is compatible with Window operation systems 98/2000/ME/NT/XP. The software has a built-in help and is easy t ...
the Enclosed DC Drives product datasheet.
... This compact unit allows for the safe reversal of DC Motors with armature currents up to 12 Amps. The card possesses all the necessary logic and unlike other available units, all the contactors for reversing and ...
... This compact unit allows for the safe reversal of DC Motors with armature currents up to 12 Amps. The card possesses all the necessary logic and unlike other available units, all the contactors for reversing and ...
Digital to Analog and Analog to Digital Conversion
... The negative reference voltage removes the charge stored in the integrator until the charge becomes zero. At this point, the comparator switches states producing a signal that disables the clock and freezes the counter ...
... The negative reference voltage removes the charge stored in the integrator until the charge becomes zero. At this point, the comparator switches states producing a signal that disables the clock and freezes the counter ...
AN-880 APPLICATION NOTE
... The measurements in temperature systems are typically low speed (up to 100 samples per seconds), so a low bandwidth ADC is suitable. However, the ADC must have high resolution. Their low bandwidth and high resolution make Σ-Δ ADCs ideal for these applications. With this architecture, the analog inpu ...
... The measurements in temperature systems are typically low speed (up to 100 samples per seconds), so a low bandwidth ADC is suitable. However, the ADC must have high resolution. Their low bandwidth and high resolution make Σ-Δ ADCs ideal for these applications. With this architecture, the analog inpu ...
DN308 - 100MHz Op Amp Features Low Noise Rail-to-Rail Performance While Consuming Only 2.5mA
... gain bandwidth of the LT6203, using this amplifier is not necessarily a case of overkill. A/D converters have sample apertures that are extremely narrow (infinitesimal as far as mathematicians are concerned) and make demands on upstream circuitry far in excess of what the innocent looking sample rat ...
... gain bandwidth of the LT6203, using this amplifier is not necessarily a case of overkill. A/D converters have sample apertures that are extremely narrow (infinitesimal as far as mathematicians are concerned) and make demands on upstream circuitry far in excess of what the innocent looking sample rat ...
- aes journals
... entire ADC. Two stage register offset averaging achieves ENOB of 3.71 bits. Hence no calibration is required. In this paper architecture of the proposed ADC is presented in section II. Comparator array is described in section III. Encoder design is discussed in section IV. Simulation results are giv ...
... entire ADC. Two stage register offset averaging achieves ENOB of 3.71 bits. Hence no calibration is required. In this paper architecture of the proposed ADC is presented in section II. Comparator array is described in section III. Encoder design is discussed in section IV. Simulation results are giv ...
Sheet 4
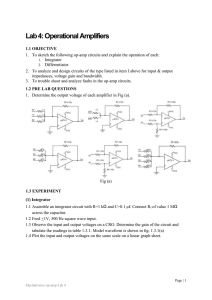
... 1.3 EXPERIMENT (1) Integrator 1.1 Assemble an integrator circuit with R=1 kΩ and C=0.1 µf. Connect Rf of value 1 MΩ across the capacitor. 1.2 Feed +1V, 500 Hz square wave input. 1.3 Observe the input and output voltages on a CRO. Determine the gain of the circuit and tabulate the readings in table 1 ...
... 1.3 EXPERIMENT (1) Integrator 1.1 Assemble an integrator circuit with R=1 kΩ and C=0.1 µf. Connect Rf of value 1 MΩ across the capacitor. 1.2 Feed +1V, 500 Hz square wave input. 1.3 Observe the input and output voltages on a CRO. Determine the gain of the circuit and tabulate the readings in table 1 ...
Analog signal chain design considerations
... © Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2007. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under ...
... © Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2007. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under ...
report
... subsequent circuitry digitizes it. Although an S/H refers to a device which spends an infinitesimal time acquiring signals and a T/H refers to a device which spends a finite time in this mode, common practice will be followed and the two terms will be used interchangeably throughout this discussion ...
... subsequent circuitry digitizes it. Although an S/H refers to a device which spends an infinitesimal time acquiring signals and a T/H refers to a device which spends a finite time in this mode, common practice will be followed and the two terms will be used interchangeably throughout this discussion ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).