Test Procedure for the NCP1083WIRGEVB Evaluation Board
... to connector P1, pin 7, 8 for the positive node and pin 9, 10 for ground. 4) The DC/DC converter shall start working as soon as detection and classification is completed in PoE powered mode or as soon as power is applied on the auxiliary input. 5) Measure the output voltage to be 12V and that ripple ...
... to connector P1, pin 7, 8 for the positive node and pin 9, 10 for ground. 4) The DC/DC converter shall start working as soon as detection and classification is completed in PoE powered mode or as soon as power is applied on the auxiliary input. 5) Measure the output voltage to be 12V and that ripple ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... In the last few years, there has been a growing interest in the design of wireless sensing device for portable, wearable or implantable biomedical applications. These sensing devices are generally used for detecting and monitoring biomedical signals such as electrocardiographic (ECG), electroencepha ...
... In the last few years, there has been a growing interest in the design of wireless sensing device for portable, wearable or implantable biomedical applications. These sensing devices are generally used for detecting and monitoring biomedical signals such as electrocardiographic (ECG), electroencepha ...
Advanced Digital Post-Processing Techniques Enhance
... in their design, but space-saving was not its only benefit. Time interleaving of ADCs offers a conceptually simple method for multiplying the sample rate of existing high-performing ADCs, such as the 14-bit, 105-MSPS AD6645 and the 12-bit, 210-MSPS AD9430. In many different applications, this concep ...
... in their design, but space-saving was not its only benefit. Time interleaving of ADCs offers a conceptually simple method for multiplying the sample rate of existing high-performing ADCs, such as the 14-bit, 105-MSPS AD6645 and the 12-bit, 210-MSPS AD9430. In many different applications, this concep ...
View File
... • Digital Signal is Representation of the Analog Signal in Sequence of Numbers • Each Number Representing The Signal Magnitude at An Instant of Time • Let us Take the Analog Signal and Convert it To Digital Signal by SAMPLING • Sampling is a Process of Measuring The Magnitude of a Signal at an Inst ...
... • Digital Signal is Representation of the Analog Signal in Sequence of Numbers • Each Number Representing The Signal Magnitude at An Instant of Time • Let us Take the Analog Signal and Convert it To Digital Signal by SAMPLING • Sampling is a Process of Measuring The Magnitude of a Signal at an Inst ...
DAC
... • There will therefore be 2n steps in the mbed DAC output characteristic, i.e. 1024. • The step size, or resolution, is therefore be 3.3/1024, i.e. 3.2mV per bit. • The conversion speed is 200,000/s. The clock speed is 100 MHz so the conversion time is equivalent to 500 clock cycles. • There is anot ...
... • There will therefore be 2n steps in the mbed DAC output characteristic, i.e. 1024. • The step size, or resolution, is therefore be 3.3/1024, i.e. 3.2mV per bit. • The conversion speed is 200,000/s. The clock speed is 100 MHz so the conversion time is equivalent to 500 clock cycles. • There is anot ...
Test Circuit
... NON−INVERTING COMPARATOR: 1. In this example POT1 is used to set the reference voltage (Vref) and POT2 supplies the input voltage (Vin). 2. Use the DMM to measure Vref at TEST POINT A. Turn POT1 to set it. You can set it to whatever you need, but for now let’s set it to 3 volts. 3. Now measure Vin a ...
... NON−INVERTING COMPARATOR: 1. In this example POT1 is used to set the reference voltage (Vref) and POT2 supplies the input voltage (Vin). 2. Use the DMM to measure Vref at TEST POINT A. Turn POT1 to set it. You can set it to whatever you need, but for now let’s set it to 3 volts. 3. Now measure Vin a ...
lecture3 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Transmission: Communication of data by propagation and processing of signals Issue: signal distorted and attenuated over distance Analog Transmission - Use amplifiers to boost signal - Amplify both signal and distortion Digital Transmission - Use repeaters to boost signal • receives signal • extract ...
... Transmission: Communication of data by propagation and processing of signals Issue: signal distorted and attenuated over distance Analog Transmission - Use amplifiers to boost signal - Amplify both signal and distortion Digital Transmission - Use repeaters to boost signal • receives signal • extract ...
Coding digital signals Boolean algebra, Boolean functions
... • Digital-to-analog conversion is a process in which signals having a few defined levels or states are converted into signals having a theoretically infinite number of states. • A common example is the processing, by a modem, of computer data into audio-frequency (AF) tones that can be transmitted o ...
... • Digital-to-analog conversion is a process in which signals having a few defined levels or states are converted into signals having a theoretically infinite number of states. • A common example is the processing, by a modem, of computer data into audio-frequency (AF) tones that can be transmitted o ...
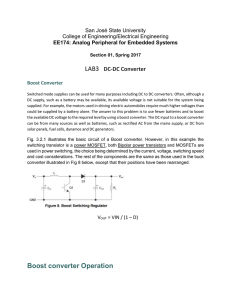
Lab3: DC-DC Boost Converter
... Switched mode supplies can be used for many purposes including DC to DC converters. Often, although a DC supply, such as a battery may be available, its available voltage is not suitable for the system being supplied. For example, the motors used in driving electric automobiles require much higher v ...
... Switched mode supplies can be used for many purposes including DC to DC converters. Often, although a DC supply, such as a battery may be available, its available voltage is not suitable for the system being supplied. For example, the motors used in driving electric automobiles require much higher v ...
- Krest Technology
... require the minimum indirect energy delivery and therefore have the minimum component stresses for a given voltage conversion ratio. Based on this observation, it is of interest to investigate buck-boost converter topologies with two independently controllable switches that can operate as boost (for ...
... require the minimum indirect energy delivery and therefore have the minimum component stresses for a given voltage conversion ratio. Based on this observation, it is of interest to investigate buck-boost converter topologies with two independently controllable switches that can operate as boost (for ...
- IEEE Projects IN MADURAI
... output load and battery storage, and several unidirectional input ports to get powers from different input dc sources. In fact, the proposed topology consists of two sets of parallel dc-dc boost converters, which are actively controlled to produce two independent output voltage components. Choosing ...
... output load and battery storage, and several unidirectional input ports to get powers from different input dc sources. In fact, the proposed topology consists of two sets of parallel dc-dc boost converters, which are actively controlled to produce two independent output voltage components. Choosing ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).