(a) TL5501
... The TL5501 is a low-power ultra-high-speed video-band analog-to-digital converter that uses the Advanced Low-Power Schottky (ALS) process. It utilizes the full-parallel comparison (flash method) for high-speed conversion. It converts wide-band analog signals (such as a video signal) to a digital sig ...
... The TL5501 is a low-power ultra-high-speed video-band analog-to-digital converter that uses the Advanced Low-Power Schottky (ALS) process. It utilizes the full-parallel comparison (flash method) for high-speed conversion. It converts wide-band analog signals (such as a video signal) to a digital sig ...
ADC and DAC
... (Fmax/2) < 4.39KHz by Nyquist sampling theory. • Need to use a sample-and-hold circuit to freeze a fast changing input when using a low speed ADC to convert the signal. • For high speed conversion, use Direct-Memory-Access (DMA) to copy the data directly to P memory to reduce P to ADC delay. ...
... (Fmax/2) < 4.39KHz by Nyquist sampling theory. • Need to use a sample-and-hold circuit to freeze a fast changing input when using a low speed ADC to convert the signal. • For high speed conversion, use Direct-Memory-Access (DMA) to copy the data directly to P memory to reduce P to ADC delay. ...
AD633 Low Cost Analog Multiplier Data Sheet (REV. E)
... The AD633 is a functionally complete, four-quadrant, analog multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer th ...
... The AD633 is a functionally complete, four-quadrant, analog multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer th ...
MAX78700 Multichannel, Isolated, Precision ADC General Description Benefits and Features
... The MAX78700 is an isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for use with a compatible MAX78xxx energy measurement processor. The device provides current and voltage measurements to the host while the host provides control, command, and power to the MAX78700. A pulse transformer provides the isolat ...
... The MAX78700 is an isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for use with a compatible MAX78xxx energy measurement processor. The device provides current and voltage measurements to the host while the host provides control, command, and power to the MAX78700. A pulse transformer provides the isolat ...
2004 Mid-Term Exam and Solutions
... Auxochrome refers to a molecular substituent which itself is not optically active but nevertheless has an effect on a neighbouring group by shifting its absorptin position and intensity. 8. Both of these op amps are configured as integrators and are given the same time constants. The inputs both go ...
... Auxochrome refers to a molecular substituent which itself is not optically active but nevertheless has an effect on a neighbouring group by shifting its absorptin position and intensity. 8. Both of these op amps are configured as integrators and are given the same time constants. The inputs both go ...
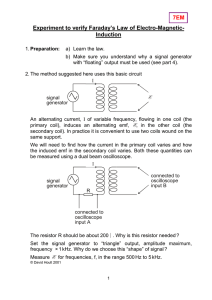
Experiment to verify Faraday’s Law of Electro-Magnetic- Induction 7EM
... - why the signal generator is set to “triangle” output and why you must maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The expe ...
... - why the signal generator is set to “triangle” output and why you must maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The expe ...
DAC and Diodes
... Sampling frequency is the number of data points sampled per unit time Sampling frequency must be twice the frequency of the sampled signal to avoid aliasing, per Nyquist criteria A higher sampling frequency decreases the sampling period, allowing more data to be transmitted in the same amount of tim ...
... Sampling frequency is the number of data points sampled per unit time Sampling frequency must be twice the frequency of the sampled signal to avoid aliasing, per Nyquist criteria A higher sampling frequency decreases the sampling period, allowing more data to be transmitted in the same amount of tim ...
E2518 Data Sheet - Endicott Research Group, Inc.
... This standard inverter is designed to satisfy the most common cold-cathode lighting requirements for the LQ10D131 displays. Custom units, providing different inputs, outputs or package refinements are available. ...
... This standard inverter is designed to satisfy the most common cold-cathode lighting requirements for the LQ10D131 displays. Custom units, providing different inputs, outputs or package refinements are available. ...
Digital Intro
... Frequency response limits • An ideal opamp has open-loop (no feedback) gain A= • More realistically, it is typically ~105-106 at DC, dropping to 1 at frequency, fT=1-10 MHz • The opamp also introduces a phase shift between input and output • At high frequencies, as the open-loop gain approaches 1, ...
... Frequency response limits • An ideal opamp has open-loop (no feedback) gain A= • More realistically, it is typically ~105-106 at DC, dropping to 1 at frequency, fT=1-10 MHz • The opamp also introduces a phase shift between input and output • At high frequencies, as the open-loop gain approaches 1, ...
ELAB-080 Specifications
... All clocks in share the same base clock. Because of this, ALL active clocks (DSO, AWG, user clocks) must be below 10KHz or above 10KHz. ...
... All clocks in share the same base clock. Because of this, ALL active clocks (DSO, AWG, user clocks) must be below 10KHz or above 10KHz. ...
Signal Conditioning
... Figure 6.2: Clamping a Signal Since the diode will conduct once it is forward biased, the output voltage will follow the input until the input goes below about −0.7V , and from then on the output will not decrease. (This slight negative voltage will not be a problem for most electronics.) The resist ...
... Figure 6.2: Clamping a Signal Since the diode will conduct once it is forward biased, the output voltage will follow the input until the input goes below about −0.7V , and from then on the output will not decrease. (This slight negative voltage will not be a problem for most electronics.) The resist ...
DN439 - Signal Chain Noise Analysis for RF-to-Digital Receivers
... example is N2 = 375μVRMS. The total theoretical SNR can be calculated as: ...
... example is N2 = 375μVRMS. The total theoretical SNR can be calculated as: ...
DN182 - The LT1167: Single Resistor Sets the Gain of the Best Instrumentation Amplifier
... of 1 to 100, gain error is less than 0.05%, making the gainset resistor tolerance the dominant source of gain error. The LT1167’s gain nonlinearity is unsurpassed when compared to other monolithic solutions. It is specified at less than 40ppm when operating at a gain of 1000 while driving a 2kΩ load ...
... of 1 to 100, gain error is less than 0.05%, making the gainset resistor tolerance the dominant source of gain error. The LT1167’s gain nonlinearity is unsurpassed when compared to other monolithic solutions. It is specified at less than 40ppm when operating at a gain of 1000 while driving a 2kΩ load ...
AD9357 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... channel filters, digitize the received signals and produce 12-bit output signals at a sample rate determined by the bandwidth mode. The transmit path takes 12-bit input data and interpolates before converting to the analog domain and upconverting to the carrier frequency. ...
... channel filters, digitize the received signals and produce 12-bit output signals at a sample rate determined by the bandwidth mode. The transmit path takes 12-bit input data and interpolates before converting to the analog domain and upconverting to the carrier frequency. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).