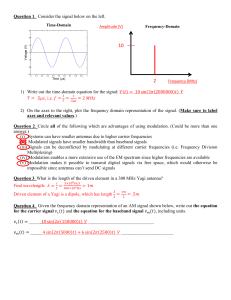
You only need to know the filter type (minimum-delay or zero
... • A variety of signals - sinewaves, pulses, pseudo-random signals - can be used for seismometer calibration. However, it is risky to rely on the precision of a waveform generator. Preferably, the input signal should be recorded together with the output signal. • The transfer function is defined as t ...
... • A variety of signals - sinewaves, pulses, pseudo-random signals - can be used for seismometer calibration. However, it is risky to rely on the precision of a waveform generator. Preferably, the input signal should be recorded together with the output signal. • The transfer function is defined as t ...
AN-781 APPLICATION NOTE
... broken down to two smaller selectable ranges for better resolution. The VP1 to VP3 pins can monitor from 0.573 V to 6 V. This range is broken down to three smaller selectable ranges for better resolution, which is especially important for accuracy at low voltages. The VX1 to VX4 pins are dual-purpos ...
... broken down to two smaller selectable ranges for better resolution. The VP1 to VP3 pins can monitor from 0.573 V to 6 V. This range is broken down to three smaller selectable ranges for better resolution, which is especially important for accuracy at low voltages. The VX1 to VX4 pins are dual-purpos ...
(minimum-delay or zero
... • A variety of signals - sinewaves, pulses, pseudo-random signals - can be used for seismometer calibration. However, it is risky to rely on the precision of a waveform generator. Preferably, the input signal should be recorded together with the output signal. • The transfer function is defined as t ...
... • A variety of signals - sinewaves, pulses, pseudo-random signals - can be used for seismometer calibration. However, it is risky to rely on the precision of a waveform generator. Preferably, the input signal should be recorded together with the output signal. • The transfer function is defined as t ...
A 40GS/s Track-and-Hold Amplifier with ... SOl Himanshu Aggrawal and Aydin Babakhani
... amplifier in the hold mode decreases, which reduces the effective number of bits. This is because the isolation of a CMOS switch degrades at high frequencies. In a series switch, the gate-source (CGs) and gate-drain (CGD) parasitic capacitors provides an alternate path for the signal to pass. This p ...
... amplifier in the hold mode decreases, which reduces the effective number of bits. This is because the isolation of a CMOS switch degrades at high frequencies. In a series switch, the gate-source (CGs) and gate-drain (CGD) parasitic capacitors provides an alternate path for the signal to pass. This p ...
Is 24-bit better than 16-bit for Data Acquisition Applications
... Developed for the high‐volume and cost‐conscious digital audio marketplace, 24‐bit Sigma‐Delta converters offer the potential for high resolution at a very low cost compared to traditional Successive Approximation Register (SAR) type A/D converters…often 1/10th the component cost for similar frequ ...
... Developed for the high‐volume and cost‐conscious digital audio marketplace, 24‐bit Sigma‐Delta converters offer the potential for high resolution at a very low cost compared to traditional Successive Approximation Register (SAR) type A/D converters…often 1/10th the component cost for similar frequ ...
Introduction to multimedia. Analog/digital representation of
... Analog signal - continuous signal for which the time varying feature (variable) of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. ex.: in sound recording, fluctuations in air pressure representing the actual sound “is analogus” to ...
... Analog signal - continuous signal for which the time varying feature (variable) of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. ex.: in sound recording, fluctuations in air pressure representing the actual sound “is analogus” to ...
Lecture 3
... If f s 2f o, then an aliasing occurs, and an alias frequency results, f a f s f o f s/ 2 But, if f s is very small this may not be the case, hence we must repeat the process to get the alias frequency. As before let f o 2 Hz but let f s 0.8 Hz (Ts 1.25 sec.) then f a f s f o 0.8 ...
... If f s 2f o, then an aliasing occurs, and an alias frequency results, f a f s f o f s/ 2 But, if f s is very small this may not be the case, hence we must repeat the process to get the alias frequency. As before let f o 2 Hz but let f s 0.8 Hz (Ts 1.25 sec.) then f a f s f o 0.8 ...
DIGITAL DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM
... Here, the transducer translates physical parameters to electrical signals acceptable by the acquisition system. The physical parameters include temperature, pressure, acceleration, weight, displacement, velocity etc. ...
... Here, the transducer translates physical parameters to electrical signals acceptable by the acquisition system. The physical parameters include temperature, pressure, acceleration, weight, displacement, velocity etc. ...
AVC63-12 and AVC125-10 Voltage Regulators
... • Single- or three-phase average sensing (jumper selectable) • Paralleling input from 1 or 5A CT secondaries • Nominal sensing inputs of 120, 240, 50/60 Hz or 400 Hz • Power input from shunt connections or PMGs operating at 50 to 400 Hz • Accessory input ...
... • Single- or three-phase average sensing (jumper selectable) • Paralleling input from 1 or 5A CT secondaries • Nominal sensing inputs of 120, 240, 50/60 Hz or 400 Hz • Power input from shunt connections or PMGs operating at 50 to 400 Hz • Accessory input ...
8 Data Conversion Methods I
... analogue voltage is known as Digital-to-Analogue Conversion. This will be treated first as it is normally used within the converse process of Analogue-to-Digital Conversion. It involves reproducing a quantised analogue voltage level from an input binary code. Ideally the output voltage should have a ...
... analogue voltage is known as Digital-to-Analogue Conversion. This will be treated first as it is normally used within the converse process of Analogue-to-Digital Conversion. It involves reproducing a quantised analogue voltage level from an input binary code. Ideally the output voltage should have a ...
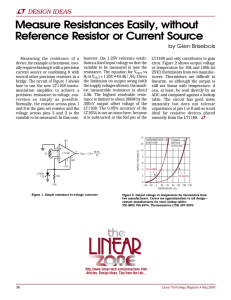
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... four resistors (RG1, RG2, RF 1, and RF 2) should be the same as shown in Figure 1. If the source has a 50 Ω impedance and a 50 Ω termination, for example, the value of RG 2 should be increased by 25 Ω to balance this parallel impedance on the input and thus ensure that both the positive and negative ...
... four resistors (RG1, RG2, RF 1, and RF 2) should be the same as shown in Figure 1. If the source has a 50 Ω impedance and a 50 Ω termination, for example, the value of RG 2 should be increased by 25 Ω to balance this parallel impedance on the input and thus ensure that both the positive and negative ...
Press release: Acquisition of inductive displacement - ADDI-DATA
... Acquisition of inductive displacement transducers with PCI Express length measurement board APCIe-3701 Rheinmuenster, 10th June 2016 - The PCI Express length measurement board APCIe-3701 has 8 or 16 inputs for the acquisition of inductive displacement transducers (Half-Bridge or LVDT) with 16bit res ...
... Acquisition of inductive displacement transducers with PCI Express length measurement board APCIe-3701 Rheinmuenster, 10th June 2016 - The PCI Express length measurement board APCIe-3701 has 8 or 16 inputs for the acquisition of inductive displacement transducers (Half-Bridge or LVDT) with 16bit res ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).