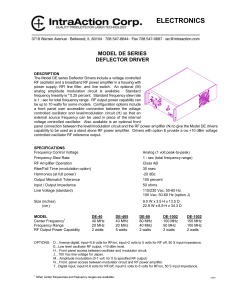
DE-70BM
... DEFLECTOR DRIVER DESCRIPTION The Model DE series Deflector Drivers include a voltage controlled RF oscillator and a broadband RF power amplifier in a housing with power supply, RFI line filter, and line switch. An optional (M) analog amplitude modulation circuit is available. Standard frequency line ...
... DEFLECTOR DRIVER DESCRIPTION The Model DE series Deflector Drivers include a voltage controlled RF oscillator and a broadband RF power amplifier in a housing with power supply, RFI line filter, and line switch. An optional (M) analog amplitude modulation circuit is available. Standard frequency line ...
03-DataTransmission
... strong enough to be detected sufficiently higher than noise to receive without error ...
... strong enough to be detected sufficiently higher than noise to receive without error ...
Abstract - 1000kv technologies
... Pulse width modulation is implemented using a microcontroller, dependent on an input value for generating variable pulse widths, for driving motor at variable speed. Therefore, the input value used is given with the help of potentiometer. ...
... Pulse width modulation is implemented using a microcontroller, dependent on an input value for generating variable pulse widths, for driving motor at variable speed. Therefore, the input value used is given with the help of potentiometer. ...
Measuring Temperature and Testing BASIC Stamp
... stage and should be the same value as at the previous testpoint (assuming the temperature hasn’t changed). 6. The output of the amplifier is the next test point to measure. What do you expect to see with the multimeter? This level should be the voltage at the input of the amplifier multiplied by the ...
... stage and should be the same value as at the previous testpoint (assuming the temperature hasn’t changed). 6. The output of the amplifier is the next test point to measure. What do you expect to see with the multimeter? This level should be the voltage at the input of the amplifier multiplied by the ...
AT84AS008
... ADC, the analog input can be indifferently driven single-ended or differential. On the contrary to the differential input clock buffer, the analog input buffer is not on-chip terminated by two 50Ω resistors connected to the die ground plane but it is terminated inside the cavity, in which case the 5 ...
... ADC, the analog input can be indifferently driven single-ended or differential. On the contrary to the differential input clock buffer, the analog input buffer is not on-chip terminated by two 50Ω resistors connected to the die ground plane but it is terminated inside the cavity, in which case the 5 ...
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... (Continued from first page) Circuits from the Lab circuits are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the Circuits from the Lab circuits in the design of your product, no other license is granted by i ...
... (Continued from first page) Circuits from the Lab circuits are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the Circuits from the Lab circuits in the design of your product, no other license is granted by i ...
Digital Representation of Audio Information
... Intervals between quantization levels are proportional to the resulting quantization noise since they limit the maximum rounding or truncation error. ...
... Intervals between quantization levels are proportional to the resulting quantization noise since they limit the maximum rounding or truncation error. ...
How the voltage reference affects performance
... 3 will appear in future issues of the Analog Applications Journal. Part 1 looks at the fundamental operation of an ADC independently, exactly as many designers do, and then at the performance characteristics that have an impact on the accuracy and repeatability of the system. Part 2 will delve into ...
... 3 will appear in future issues of the Analog Applications Journal. Part 1 looks at the fundamental operation of an ADC independently, exactly as many designers do, and then at the performance characteristics that have an impact on the accuracy and repeatability of the system. Part 2 will delve into ...
Capacitor Self
... control "digital" voltage. VCO are very easy to build and are composed of a transistor (or highfrequency op-amp) with a variable capacitor (actually a varactor diode) in the feedback circuit. The digital voltage controls the bias on the diode and hence the oscillation frequency. The VCO output is ge ...
... control "digital" voltage. VCO are very easy to build and are composed of a transistor (or highfrequency op-amp) with a variable capacitor (actually a varactor diode) in the feedback circuit. The digital voltage controls the bias on the diode and hence the oscillation frequency. The VCO output is ge ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).