PTSD - Being Proactive
... -PTSD is a severe anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to any event that results in psychological trauma. (Wikipedia, ...
... -PTSD is a severe anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to any event that results in psychological trauma. (Wikipedia, ...
Blue and Red Gradient
... As a result Susan will show a reduction in avoidance and anxious arousal She will start to return to school for partial then full day by reduction of phone calls made to her parents Be able to stay at home with babysitter and increase social activities (peers); Girl Scouts ...
... As a result Susan will show a reduction in avoidance and anxious arousal She will start to return to school for partial then full day by reduction of phone calls made to her parents Be able to stay at home with babysitter and increase social activities (peers); Girl Scouts ...
Stop the Anxiety! Presentation Notes: Stop the Anxiety! Anxiety Disorders
... Persistent fear of one or more social or performance situations in which a person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others Fears he/she will act in a way (or show anxiety) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Fear of fainting, losing control of bowel or bladder function ...
... Persistent fear of one or more social or performance situations in which a person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others Fears he/she will act in a way (or show anxiety) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Fear of fainting, losing control of bowel or bladder function ...
Generalized anxiety disorder
... Psychoanalytical theory proposes that anxiety arises from intrapsychic conflict when the ego is overwhelmed by excitation from any of the following three sources : •the outside world (realistic anxiety) •the instinctual levels of the id, including love, anger, and sex (neurotic anxiety ) •the supere ...
... Psychoanalytical theory proposes that anxiety arises from intrapsychic conflict when the ego is overwhelmed by excitation from any of the following three sources : •the outside world (realistic anxiety) •the instinctual levels of the id, including love, anger, and sex (neurotic anxiety ) •the supere ...
Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
... Various talking therapies can be helpful in lessening anxiety problems, one example is Cognitive Therapy - this aims to change thinking patterns - negative thought patterns that trigger anxiety are substituted for positive ones. Psychodynamic Therapy seeks to find the underlying cause of the anxiety ...
... Various talking therapies can be helpful in lessening anxiety problems, one example is Cognitive Therapy - this aims to change thinking patterns - negative thought patterns that trigger anxiety are substituted for positive ones. Psychodynamic Therapy seeks to find the underlying cause of the anxiety ...
Psychological Disorders
... Causes of Anxiety Disorders The causes of anxiety disorders depend on the model of psychopathology: – biological: disorders are the result of organic causes; neurotransmitter imbalances (anxiety, mood and schizophrenic disorders) and hereditary genetics (schizophrenia) cause the disorder – behaviora ...
... Causes of Anxiety Disorders The causes of anxiety disorders depend on the model of psychopathology: – biological: disorders are the result of organic causes; neurotransmitter imbalances (anxiety, mood and schizophrenic disorders) and hereditary genetics (schizophrenia) cause the disorder – behaviora ...
Types of Psychological Disorders
... images or sounds that are not real, such as hearing voices; and delusions—false beliefs that the ill person accepts as true, despite evidence to the contrary. Schizophrenia is an example of a psychotic disorder. Eating Disorders: Eating disorders such as anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder ...
... images or sounds that are not real, such as hearing voices; and delusions—false beliefs that the ill person accepts as true, despite evidence to the contrary. Schizophrenia is an example of a psychotic disorder. Eating Disorders: Eating disorders such as anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder ...
A mood disorder - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety, • often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath. • Panic attacks may happen several times a day ...
... sudden bouts of intense, unexplained anxiety, • often associated with physical symptoms like choking sensations or shortness of breath. • Panic attacks may happen several times a day ...
Emotional Health
... Fear of dying/losing control, feelings of detachment Attacks not due to chemical substance ...
... Fear of dying/losing control, feelings of detachment Attacks not due to chemical substance ...
OL Chapter 12
... a person experiences terror and chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations • Panic attack symptoms often misread as a heart attack or similar • Smokers have at least doubled risk of panic attack ...
... a person experiences terror and chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations • Panic attack symptoms often misread as a heart attack or similar • Smokers have at least doubled risk of panic attack ...
Ch. 12,13 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. Match each term with its definition. (1) _____ agoraphobia (2) _____ specific phobia (3) _____ social anxiety disorder (4) _____ panic disorder (A) fear of a certain object or situation (B) persistent, irrational fear of open spaces (C) irrational fear of embarrassment (D) repeated episodes of ex ...
... 1. Match each term with its definition. (1) _____ agoraphobia (2) _____ specific phobia (3) _____ social anxiety disorder (4) _____ panic disorder (A) fear of a certain object or situation (B) persistent, irrational fear of open spaces (C) irrational fear of embarrassment (D) repeated episodes of ex ...
Humanistic Therapy - Solon City Schools
... spiders to show that they have no reason to fear them ...
... spiders to show that they have no reason to fear them ...
Perspectives on Psychological Disorders
... • cognitive distortions: An illogical and maladaptive response to early negative life events that leads to feelings of incompetence and unworthiness that are reactivated whenever a new situation arises that resembles the original events. ...
... • cognitive distortions: An illogical and maladaptive response to early negative life events that leads to feelings of incompetence and unworthiness that are reactivated whenever a new situation arises that resembles the original events. ...
Psychology
... • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
... • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
Psychosocial Risk Factors Interventions_2010
... This is best done by keeping track of the triggers on a daily basis for one week by using the obsessive fear monitoring form. Because obsessions can happen frequently, writing down 3 triggers per day (i.e., one in the morning, one in the afternoon, and one in the evening) will be enough to give them ...
... This is best done by keeping track of the triggers on a daily basis for one week by using the obsessive fear monitoring form. Because obsessions can happen frequently, writing down 3 triggers per day (i.e., one in the morning, one in the afternoon, and one in the evening) will be enough to give them ...
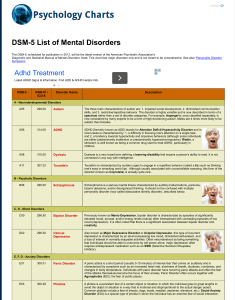
DSM-5 ICD-10 Disorder Name Description A
... Also known as Major Depressive Disorder or Unipolar Depression, this type of recurrent depression is characterized by an allencompassing low mood, diminished self-esteem, and a loss of interest in normally enjoyable activities. Often misunderstood as being something that individuals should be able t ...
... Also known as Major Depressive Disorder or Unipolar Depression, this type of recurrent depression is characterized by an allencompassing low mood, diminished self-esteem, and a loss of interest in normally enjoyable activities. Often misunderstood as being something that individuals should be able t ...
Panic Disorder - Schoolwires.net
... B. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way or show anxiety symptoms that will be negatively evaluated (i.e. will be humiliating or embarrassing; will lead to rejection or offend others). C. The social situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety. Note: In children, the fear of anxi ...
... B. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way or show anxiety symptoms that will be negatively evaluated (i.e. will be humiliating or embarrassing; will lead to rejection or offend others). C. The social situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety. Note: In children, the fear of anxi ...
DSM-5 - KVCC Docs
... OCD stands for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and is characterized by uncontrollable thoughts (obsessions) that lead to repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, ...
... OCD stands for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and is characterized by uncontrollable thoughts (obsessions) that lead to repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, ...
Trapped Within OCD
... The video made clear that medical science does not know what causes OCD, although many patients describe life events or stressors like childhood abuse, a divorce, or other disruption. Some patients acquire the disorder very young, even at age two, and one boy at the age of nine was frightened by im ...
... The video made clear that medical science does not know what causes OCD, although many patients describe life events or stressors like childhood abuse, a divorce, or other disruption. Some patients acquire the disorder very young, even at age two, and one boy at the age of nine was frightened by im ...
Anxiety and Education: Impact, Recognition and Management
... – High anxious children in grade 1 are 10x more likely to be in bottom 1/3 of class by grade 5 – High anxious students score lower than peers on measures of IQ and achievement tests (eg basic skills) • Anxiety leads to poor engagement in class – High anxious students often avoid tasks that require c ...
... – High anxious children in grade 1 are 10x more likely to be in bottom 1/3 of class by grade 5 – High anxious students score lower than peers on measures of IQ and achievement tests (eg basic skills) • Anxiety leads to poor engagement in class – High anxious students often avoid tasks that require c ...
Mood Disorders for MRCPsych Part I
... • Common residual symptoms may include anxiety, somatic symptoms, sleep disturbances, fatigue, apathy, and/or cognitive and executive dysfunction. • For many patients it is often difficult to assess whether side effects are residual or part of antidepressant treatment. • 10% to 20% of patients treat ...
... • Common residual symptoms may include anxiety, somatic symptoms, sleep disturbances, fatigue, apathy, and/or cognitive and executive dysfunction. • For many patients it is often difficult to assess whether side effects are residual or part of antidepressant treatment. • 10% to 20% of patients treat ...
Niamh - Inspire
... there is no easy exit. But they all stem from one underlying fear. That is, a fear of being in a place where help will not be available, or where you feel it may be difficult to escape to a safe place (usually to your home). When you are in a feared place you become very anxious and distressed, an ...
... there is no easy exit. But they all stem from one underlying fear. That is, a fear of being in a place where help will not be available, or where you feel it may be difficult to escape to a safe place (usually to your home). When you are in a feared place you become very anxious and distressed, an ...
15 - Chapter 14 - Psychological Disorders
... • Other: Rates are higher among the rich, nonreligious and those who are single, widowed or divorced. In the last 60 years, the global rate of annual suicide rose from 10 to 18 per 100,000. In 2006 in the US, suicide per 100,000: 11.1 (or 33,300 people). ...
... • Other: Rates are higher among the rich, nonreligious and those who are single, widowed or divorced. In the last 60 years, the global rate of annual suicide rose from 10 to 18 per 100,000. In 2006 in the US, suicide per 100,000: 11.1 (or 33,300 people). ...
Phobia

A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder, usually defined as a persistent fear of an object or situation in which the sufferer commits to great lengths in avoiding, typically disproportional to the actual danger posed, often being recognized as irrational. In the event the phobia cannot be avoided entirely, the sufferer will endure the situation or object with marked distress and significant interference in social or occupational activities.The terms distress and impairment as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV-TR) should also take into account the context of the sufferer's environment if attempting a diagnosis. The DSM-IV-TR states that if a phobic stimulus, whether it be an object or a social situation, is absent entirely in an environment — a diagnosis cannot be made. An example of this situation would be an individual who has a fear of mice but lives in an area devoid of mice. Even though the concept of mice causes marked distress and impairment within the individual, because the individual does not encounter mice in the environment no actual distress or impairment is ever experienced. Proximity and the degree to which escape from the phobic stimulus is impossible should also be considered. As the sufferer approaches a phobic stimulus, anxiety levels increase (e.g. as one gets closer to a snake, fear increases in ophidiophobia), and the degree to which escape of the phobic stimulus is limited has the effect of varying the intensity of fear in instances such as riding an elevator (e.g. anxiety increases at the midway point between floors and decreases when the floor is reached and the doors open).The term phobia is encompassing and usually discussed in the contexts of specific phobias and social phobias. Specific phobias are phobias to specific objects or environments, such as arachnophobia or acrophobia, and social phobias are phobias within social situations, such as public speaking and crowded areas. Some phobias, such as xenophobia, overlap with many other phobias.