Lecture 5
... No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better accounted for by chronic Major Depressive Disorder, or Major Depressive Disorder, In Partial Remission. Note: There may have been previo ...
... No Major Depressive Episode has been present during the first 2 years of the disturbance (1 year for children and adolescents); i.e., the disturbance is not better accounted for by chronic Major Depressive Disorder, or Major Depressive Disorder, In Partial Remission. Note: There may have been previo ...
Chapter 7: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Posttraumatic s
... Chapter 7: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) 1. Posttraumatic stress disorder … a. … Is now considered an anxiety disorder in the DSM-5. b. … Is considered a disorder of nonrecovery from trauma. c. … Is more likely to occur after a natural disaster than in cases of sexual abuse. d. … Typically de ...
... Chapter 7: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) 1. Posttraumatic stress disorder … a. … Is now considered an anxiety disorder in the DSM-5. b. … Is considered a disorder of nonrecovery from trauma. c. … Is more likely to occur after a natural disaster than in cases of sexual abuse. d. … Typically de ...
Personality Disorder
... elimination of unwanted behaviors • Behaviorists believe that mental problems are caused by: • classical conditioning (for example, phobias), • operant conditioning (addictions, depression), and • observational learning (we watch our parents and friends suffer so we copy them). ...
... elimination of unwanted behaviors • Behaviorists believe that mental problems are caused by: • classical conditioning (for example, phobias), • operant conditioning (addictions, depression), and • observational learning (we watch our parents and friends suffer so we copy them). ...
Anxiety Disorders and Depression Dr H Grandy
... performance situation(s) interferes significantly with the person's normal routine, occupational (academic) functioning, or social activities or relationships, or there is marked distress about having the phobia. ...
... performance situation(s) interferes significantly with the person's normal routine, occupational (academic) functioning, or social activities or relationships, or there is marked distress about having the phobia. ...
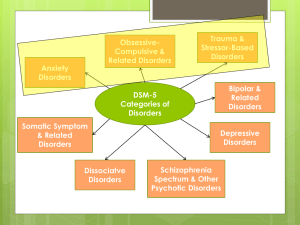
anxiety disorders in the dsm-5
... Avoidance of the event or situation must also be present and can include cognitive or behavioral aspects (APA, 2013). • Acute stress disorder and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder can ...
... Avoidance of the event or situation must also be present and can include cognitive or behavioral aspects (APA, 2013). • Acute stress disorder and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder can ...
Anxiety
... almost as if someone is stalking you and you never know when those arms are going to wrap around you and drag you away. • There’s more anxiety today, and that women, in particular, are feeling it ...
... almost as if someone is stalking you and you never know when those arms are going to wrap around you and drag you away. • There’s more anxiety today, and that women, in particular, are feeling it ...
New Vistas on Amygdala Networks in Conditioned Fear
... synapses conveying information about the CS to the LA (LeDoux 2000; Walker and Davis 2000). As a result, subsequent presentations of the CS alone evoke larger responses in the LA (Collins and Paré 2000; Quirk et al. 1995; Repa et al. 2001). The LA, in turn, evokes conditioned fear responses via its ...
... synapses conveying information about the CS to the LA (LeDoux 2000; Walker and Davis 2000). As a result, subsequent presentations of the CS alone evoke larger responses in the LA (Collins and Paré 2000; Quirk et al. 1995; Repa et al. 2001). The LA, in turn, evokes conditioned fear responses via its ...
Anxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sucheta Connolly M.D.
... Child imagines item or situation from Fear Ladder/Hierarchy in detail Begin with easy items to more challenging Child notes intensity on Fear Thermometer Bring anxiety to 2 or below before next item Ask: Did anything terrible happen? Praise often. Reward for efforts & successes Incorporate relaxatio ...
... Child imagines item or situation from Fear Ladder/Hierarchy in detail Begin with easy items to more challenging Child notes intensity on Fear Thermometer Bring anxiety to 2 or below before next item Ask: Did anything terrible happen? Praise often. Reward for efforts & successes Incorporate relaxatio ...
anxiety disorders (cont.)
... • Other problems and disorders: Axes II, III, IV, V – Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems • refers to psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders in Axes I and II – Axis V: global assessment of functioning scale • u ...
... • Other problems and disorders: Axes II, III, IV, V – Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems • refers to psychosocial and environmental problems that may affect the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of mental disorders in Axes I and II – Axis V: global assessment of functioning scale • u ...
4468 ANXIETY DISORDERS - PANIC DISORDER
... c. invariably leads to agoraphobia if not treated with medications 14. The behavior portion of cognitive-behavioral therapy for panic disorder may involve: a. analyzing one’s thought process b. psychodynamic approaches c. systematic training in relaxation techniques ...
... c. invariably leads to agoraphobia if not treated with medications 14. The behavior portion of cognitive-behavioral therapy for panic disorder may involve: a. analyzing one’s thought process b. psychodynamic approaches c. systematic training in relaxation techniques ...
Memory - Mrfarshtey.net
... Natural Selection has led our ancestors to learn to fear snakes, spiders, and other animals. Therefore, fear preserves the species. ...
... Natural Selection has led our ancestors to learn to fear snakes, spiders, and other animals. Therefore, fear preserves the species. ...
Depression
... supernatural forces. Ancient human skulls have been found with large holes in them, a process that has become known as trepanning. The accepted theory is that it was an attempt to let evil spirits out. We cannot be certain of this, but we do know that again and again human kind has returned to the i ...
... supernatural forces. Ancient human skulls have been found with large holes in them, a process that has become known as trepanning. The accepted theory is that it was an attempt to let evil spirits out. We cannot be certain of this, but we do know that again and again human kind has returned to the i ...
Childhood Anxiety Disorders
... It's natural for unfamiliar or challenging situations to prompt feelings of anxiety or nervousness in people of all ages. Kids feel it, too – when facing an important test or switching schools, for example. These experiences can trigger normal anxiety because they cause us to focus on the "what if's ...
... It's natural for unfamiliar or challenging situations to prompt feelings of anxiety or nervousness in people of all ages. Kids feel it, too – when facing an important test or switching schools, for example. These experiences can trigger normal anxiety because they cause us to focus on the "what if's ...
Personality disorders
... during distress. -Restructure their cognitions or information processing. (b) Thought stopping: Ask the patient to focus on one’s obsessive thoughtsSTOP! (c) Cognitive rehearsal: Cognitively rehearse adaptive approaches to problematic situations. (d) Worry exposure: Worst outcome? ...
... during distress. -Restructure their cognitions or information processing. (b) Thought stopping: Ask the patient to focus on one’s obsessive thoughtsSTOP! (c) Cognitive rehearsal: Cognitively rehearse adaptive approaches to problematic situations. (d) Worry exposure: Worst outcome? ...
Seniors / Books on anxiety
... Her program is built around four simple steps: Face-do not run, Accept-do not fight, Float past-do not listen in, Let time pass-do not be impatient with time. The author discusses many case studies, and writes with great compassion and understanding. Wilson, R. Reid, Ph.D., Don’t Panic, Taking Contr ...
... Her program is built around four simple steps: Face-do not run, Accept-do not fight, Float past-do not listen in, Let time pass-do not be impatient with time. The author discusses many case studies, and writes with great compassion and understanding. Wilson, R. Reid, Ph.D., Don’t Panic, Taking Contr ...
Mental Disorders - University of Alberta
... false belief that someone (usually someone in higher social strata) is in love with them Fregoli’s syndrome: someone known to you has changed identities, and is out to get you Folie a Deux: shared delusions; one person with genuine delusional disorder, and a second person (usually less intelligent) ...
... false belief that someone (usually someone in higher social strata) is in love with them Fregoli’s syndrome: someone known to you has changed identities, and is out to get you Folie a Deux: shared delusions; one person with genuine delusional disorder, and a second person (usually less intelligent) ...
Taking a look at the DSM V
... Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) Best current alternative, but APA is not recommending until there is more research to validate use ...
... Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) Best current alternative, but APA is not recommending until there is more research to validate use ...
PSychiatric NurSing - Think Link
... They spend there great deal of time and energy validating their ...
... They spend there great deal of time and energy validating their ...
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... – Hypersensitivity, including: inability to sleep, anxious feelings, hypervigilance, irritability and anger. ...
... – Hypersensitivity, including: inability to sleep, anxious feelings, hypervigilance, irritability and anger. ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Panic: a feeling of sudden, helpless terror, such as the overwhelming fright one might experience when cornered by a predator Panic Disorder: an extreme anxiety that manifests itself in the form of panic attacks Panic Attacks: sudden and unexplainable attacks or intense anxiety, leading the individu ...
... Panic: a feeling of sudden, helpless terror, such as the overwhelming fright one might experience when cornered by a predator Panic Disorder: an extreme anxiety that manifests itself in the form of panic attacks Panic Attacks: sudden and unexplainable attacks or intense anxiety, leading the individu ...
An Optogenetic Approach to Understanding the Neural Circuits of Fear
... simple features is used) require the medial geniculate (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar thalamic nuclei (PIN) (28 –31) (but see Campeau and Davis [30] and Boatman and Kim [32]), whereas fear conditioning to more complex CSs recruits both thalamic and auditory cortical pathways (31,33). Neurons i ...
... simple features is used) require the medial geniculate (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar thalamic nuclei (PIN) (28 –31) (but see Campeau and Davis [30] and Boatman and Kim [32]), whereas fear conditioning to more complex CSs recruits both thalamic and auditory cortical pathways (31,33). Neurons i ...
index for handouts
... 4. Use family history as a guide. Mental disorders run in families. Whether the mode of transmission is environmental or hereditary, the presence of a relative with disorder X suggests that your client may need to be assessed for similar disorders. 5. Try first to identify one or two general categor ...
... 4. Use family history as a guide. Mental disorders run in families. Whether the mode of transmission is environmental or hereditary, the presence of a relative with disorder X suggests that your client may need to be assessed for similar disorders. 5. Try first to identify one or two general categor ...
Date
... sleeping and vivid flashbacks of her assault. Brianna is most clearly showing signs of A) panic disorder. B) post-traumatic stress disorder. C) generalized anxiety disorder. D) conversion disorder. 17. Some people are more vulnerable to PTSD because they have a sensitive ________, which floods the b ...
... sleeping and vivid flashbacks of her assault. Brianna is most clearly showing signs of A) panic disorder. B) post-traumatic stress disorder. C) generalized anxiety disorder. D) conversion disorder. 17. Some people are more vulnerable to PTSD because they have a sensitive ________, which floods the b ...
Phobia

A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder, usually defined as a persistent fear of an object or situation in which the sufferer commits to great lengths in avoiding, typically disproportional to the actual danger posed, often being recognized as irrational. In the event the phobia cannot be avoided entirely, the sufferer will endure the situation or object with marked distress and significant interference in social or occupational activities.The terms distress and impairment as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV-TR) should also take into account the context of the sufferer's environment if attempting a diagnosis. The DSM-IV-TR states that if a phobic stimulus, whether it be an object or a social situation, is absent entirely in an environment — a diagnosis cannot be made. An example of this situation would be an individual who has a fear of mice but lives in an area devoid of mice. Even though the concept of mice causes marked distress and impairment within the individual, because the individual does not encounter mice in the environment no actual distress or impairment is ever experienced. Proximity and the degree to which escape from the phobic stimulus is impossible should also be considered. As the sufferer approaches a phobic stimulus, anxiety levels increase (e.g. as one gets closer to a snake, fear increases in ophidiophobia), and the degree to which escape of the phobic stimulus is limited has the effect of varying the intensity of fear in instances such as riding an elevator (e.g. anxiety increases at the midway point between floors and decreases when the floor is reached and the doors open).The term phobia is encompassing and usually discussed in the contexts of specific phobias and social phobias. Specific phobias are phobias to specific objects or environments, such as arachnophobia or acrophobia, and social phobias are phobias within social situations, such as public speaking and crowded areas. Some phobias, such as xenophobia, overlap with many other phobias.