What is Specific Phobia
... than there are men with this disorder. The gender ratio variable varies depending upon the type of specific phobia. Approximately 75%–90% of people with the animal, situational, and natural environment types are female. Approximately 55%–70% of people with the blood-injection-injury subtype are fema ...
... than there are men with this disorder. The gender ratio variable varies depending upon the type of specific phobia. Approximately 75%–90% of people with the animal, situational, and natural environment types are female. Approximately 55%–70% of people with the blood-injection-injury subtype are fema ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Acerophobia: fear of itching or the insects that cause itching Acrophobia: fear of heights Aerophobia: fear of flying Atelophobia: fear of imperfection Catagelophobia: fear of being ridiculed Claustrophobia: fear of closed spaces Entomophobia: fear of insects Felinophobia: fear of ca ...
... Acerophobia: fear of itching or the insects that cause itching Acrophobia: fear of heights Aerophobia: fear of flying Atelophobia: fear of imperfection Catagelophobia: fear of being ridiculed Claustrophobia: fear of closed spaces Entomophobia: fear of insects Felinophobia: fear of ca ...
Social phobia
... the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In children there must be evidence of the capacity for age-appropriate social relationships w ...
... the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In children there must be evidence of the capacity for age-appropriate social relationships w ...
here
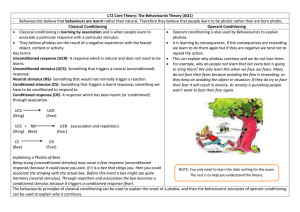
... They believe phobias are the result of a negative experience with the feared It is learning by consequences. If the consequences are rewarding object, context or activity. we learn to do them again but if they are negative we tend not to Key terms: repeat the action. Unconditioned response (UCR) ...
... They believe phobias are the result of a negative experience with the feared It is learning by consequences. If the consequences are rewarding object, context or activity. we learn to do them again but if they are negative we tend not to Key terms: repeat the action. Unconditioned response (UCR) ...
Functional neuroimaging of anxiety
... • Find common and disorder-specific functional neurobiological deficits in anxiety disorders. • Compare findings to systems engaged during anticipatory anxiety in healthy ...
... • Find common and disorder-specific functional neurobiological deficits in anxiety disorders. • Compare findings to systems engaged during anticipatory anxiety in healthy ...
Phobias - Honzoda
... Someone who experiences agoraphobia tends to have a number of fears of various places and situations both busy and quiet for example entering shops, public places, cinema, church or anywhere away from home. The underlying fear that causes this feeling of panic is the fear of being in a place where ...
... Someone who experiences agoraphobia tends to have a number of fears of various places and situations both busy and quiet for example entering shops, public places, cinema, church or anywhere away from home. The underlying fear that causes this feeling of panic is the fear of being in a place where ...
17.SpecificDisorders..
... Phobia are excessive, irrational fears of specific objects or situations, such as snakes or heights. ...
... Phobia are excessive, irrational fears of specific objects or situations, such as snakes or heights. ...
Specific Phobias
... The description and treatment of specific phobias, or fear of specific objects or situations, are embedded in the history of psychiatry and psychology. Indeed, Freud’s classic analytic case of “Little Hans” illustrated a common form of specific phobia (animal type).1 As opposed to psychodynamic theo ...
... The description and treatment of specific phobias, or fear of specific objects or situations, are embedded in the history of psychiatry and psychology. Indeed, Freud’s classic analytic case of “Little Hans” illustrated a common form of specific phobia (animal type).1 As opposed to psychodynamic theo ...
Phobias - Healthwise
... In severe cases, these symptoms can occur even when the person is thinking about being close to the feared object or simply seeing a picture of it. Causes We do not know what causes phobias. Psychologists who have studied phobias have suggested that they develop from an unpleasant experience in chil ...
... In severe cases, these symptoms can occur even when the person is thinking about being close to the feared object or simply seeing a picture of it. Causes We do not know what causes phobias. Psychologists who have studied phobias have suggested that they develop from an unpleasant experience in chil ...
Document
... that reduce anxiety Anxiety - diffuseمنتشر, vague feelings احساس مبهمof fear ...
... that reduce anxiety Anxiety - diffuseمنتشر, vague feelings احساس مبهمof fear ...
Anxiety Disorder
... can involve fear of an object (like an elevator) or a situation (like public speaking) that poses little or no danger. • Social Phobias can involve fear of being embarrassed, looked at, or made fun of in social or work situations • With both of these phobias, the fear is extreme and hard to control. ...
... can involve fear of an object (like an elevator) or a situation (like public speaking) that poses little or no danger. • Social Phobias can involve fear of being embarrassed, looked at, or made fun of in social or work situations • With both of these phobias, the fear is extreme and hard to control. ...
Phobias project example
... as an anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent of all adult mental disorders. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, DSM-IV, has classified anxiety disorders into a number of different categories according to symptomatology. One example is phobia ...
... as an anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent of all adult mental disorders. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, DSM-IV, has classified anxiety disorders into a number of different categories according to symptomatology. One example is phobia ...
Phobia

A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder, usually defined as a persistent fear of an object or situation in which the sufferer commits to great lengths in avoiding, typically disproportional to the actual danger posed, often being recognized as irrational. In the event the phobia cannot be avoided entirely, the sufferer will endure the situation or object with marked distress and significant interference in social or occupational activities.The terms distress and impairment as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV-TR) should also take into account the context of the sufferer's environment if attempting a diagnosis. The DSM-IV-TR states that if a phobic stimulus, whether it be an object or a social situation, is absent entirely in an environment — a diagnosis cannot be made. An example of this situation would be an individual who has a fear of mice but lives in an area devoid of mice. Even though the concept of mice causes marked distress and impairment within the individual, because the individual does not encounter mice in the environment no actual distress or impairment is ever experienced. Proximity and the degree to which escape from the phobic stimulus is impossible should also be considered. As the sufferer approaches a phobic stimulus, anxiety levels increase (e.g. as one gets closer to a snake, fear increases in ophidiophobia), and the degree to which escape of the phobic stimulus is limited has the effect of varying the intensity of fear in instances such as riding an elevator (e.g. anxiety increases at the midway point between floors and decreases when the floor is reached and the doors open).The term phobia is encompassing and usually discussed in the contexts of specific phobias and social phobias. Specific phobias are phobias to specific objects or environments, such as arachnophobia or acrophobia, and social phobias are phobias within social situations, such as public speaking and crowded areas. Some phobias, such as xenophobia, overlap with many other phobias.