Anxiety in Teenagers
... episodes of intense fear, physiological arousal, and escape behaviors. Common symptoms: heart palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness and anxiety and these symptoms are often confused with those of a heart attack. ...
... episodes of intense fear, physiological arousal, and escape behaviors. Common symptoms: heart palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness and anxiety and these symptoms are often confused with those of a heart attack. ...
Psychology
... feelings of apprehension and tenseness – Until pharmaceutical companies began a hardsell TV ad campaign for drugs to combat it, many people had never heard of it. – Most of us have the symptoms they identify – Effexor and Paxil, Prozac and Zolof are all used to treat GAD and major depression; also s ...
... feelings of apprehension and tenseness – Until pharmaceutical companies began a hardsell TV ad campaign for drugs to combat it, many people had never heard of it. – Most of us have the symptoms they identify – Effexor and Paxil, Prozac and Zolof are all used to treat GAD and major depression; also s ...
Memory
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder Generalized anxiety disorder is a disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic arousal. People with this condition are often jittery, agitated, and sleep-deprived. It is often, but not always, accompanied by depressed mood. ...
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder Generalized anxiety disorder is a disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic arousal. People with this condition are often jittery, agitated, and sleep-deprived. It is often, but not always, accompanied by depressed mood. ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
... fight with or bully others, and are at a real risk of getting into trouble at school or with the police. violate the basic rights of other people, are aggressive toward people and/or animals, destroy property, break into people’s homes, commit thefts, carry or use weapons, or engage in vanda ...
... fight with or bully others, and are at a real risk of getting into trouble at school or with the police. violate the basic rights of other people, are aggressive toward people and/or animals, destroy property, break into people’s homes, commit thefts, carry or use weapons, or engage in vanda ...
Childhood Anxiety in the Classroom
... Prevalence of anxiety disorders in children and adolescents Who is the anxious child Developmental factors to consider Overview of common childhood anxiety disorders The impact of anxiety in the classroom How to talk to parents about it Classroom support strategies ...
... Prevalence of anxiety disorders in children and adolescents Who is the anxious child Developmental factors to consider Overview of common childhood anxiety disorders The impact of anxiety in the classroom How to talk to parents about it Classroom support strategies ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS Sharon Crews, RN
... Criteria noted in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ...
... Criteria noted in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ...
Slide 1
... 1) Social Phobia: severe fear and avoidance of other people in a variety of social settings. 2) Agoraphobia: an intense fear of open or public places with or without the presence of other people. ...
... 1) Social Phobia: severe fear and avoidance of other people in a variety of social settings. 2) Agoraphobia: an intense fear of open or public places with or without the presence of other people. ...
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
... F. In individuals under age 18 years, the duration is at least 6 months. G. The fear or avoidance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance or a general medical condition and is not better accounted for by another mental disorder. H. If a general medical condition or another ment ...
... F. In individuals under age 18 years, the duration is at least 6 months. G. The fear or avoidance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance or a general medical condition and is not better accounted for by another mental disorder. H. If a general medical condition or another ment ...
Postnatal Anxiety
... which can occur after a person experiences, or sees, a traumatic event, or series of traumatic events. A traumatic event is one that makes a person feel that their own life, or the lives of other people, is in serious danger. In some cases, this can include a traumatic birth experience. Features of ...
... which can occur after a person experiences, or sees, a traumatic event, or series of traumatic events. A traumatic event is one that makes a person feel that their own life, or the lives of other people, is in serious danger. In some cases, this can include a traumatic birth experience. Features of ...
Mental Disorders
... A) engage in ritualized behaviors in an effort to ward off their fears. B) interpret heightened physiological arousal as the prelude to disaster. C) underreact to normal physiological stimulants such as caffeine and lactic acid injections. D) vividly relive traumatic events. 13. An example of a nega ...
... A) engage in ritualized behaviors in an effort to ward off their fears. B) interpret heightened physiological arousal as the prelude to disaster. C) underreact to normal physiological stimulants such as caffeine and lactic acid injections. D) vividly relive traumatic events. 13. An example of a nega ...
Anxiety Disorders
... D. If another Axis I disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted to it (e.g., preoccupation with food in the presence of an Eating Disorder; hair pulling in the presence of Trichotillomania; concern with appearance in the presence of Body Dysmorphic Disorder; ...
... D. If another Axis I disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted to it (e.g., preoccupation with food in the presence of an Eating Disorder; hair pulling in the presence of Trichotillomania; concern with appearance in the presence of Body Dysmorphic Disorder; ...
Anxiety
... losing control in a very extreme way. My heart pounds hard, I feel I can't get my breath, and that things are crashing in on me.” Find the autonomic, cognitive, behavioral and emotional feeling components. ...
... losing control in a very extreme way. My heart pounds hard, I feel I can't get my breath, and that things are crashing in on me.” Find the autonomic, cognitive, behavioral and emotional feeling components. ...
Coping with Anxiety Disorder
... controlled. People with OCD often constantly have unwelcome thoughts or images, or have the urgent need to perform certain rituals, such as hand washing or locking doors. • Panic disorder: unexpected and repeated episodes of intense fear with physical symptoms. These symptoms may include chest pain ...
... controlled. People with OCD often constantly have unwelcome thoughts or images, or have the urgent need to perform certain rituals, such as hand washing or locking doors. • Panic disorder: unexpected and repeated episodes of intense fear with physical symptoms. These symptoms may include chest pain ...
Epidemiology of Anxiety
... attacks followed by at least 1 month of persistent concern about having another attack worry about the possible implications of the panic attacks significant behavioral change related to the attacks. ...
... attacks followed by at least 1 month of persistent concern about having another attack worry about the possible implications of the panic attacks significant behavioral change related to the attacks. ...
Psychological Disorders
... anxiety reactions. The major types are: phobias, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessivecompulsive disorder. Phobias are irrational or excessive fears of particular objects or situations. The three types are: social phobia, specific phobia, and agoraphobia. Persons with social ...
... anxiety reactions. The major types are: phobias, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessivecompulsive disorder. Phobias are irrational or excessive fears of particular objects or situations. The three types are: social phobia, specific phobia, and agoraphobia. Persons with social ...
Treating Early Life Developmental Trauma: A Science Based
... Ability to tune into others including the experience of empathy Emotional balance including the ability to inhibit impulses Self-Knowing Awareness thru autobiographical narrative – Horizontal Integration ...
... Ability to tune into others including the experience of empathy Emotional balance including the ability to inhibit impulses Self-Knowing Awareness thru autobiographical narrative – Horizontal Integration ...
Slide 1
... Simple – fear of specific situation or thing Agoraphobia - fear of wide open spaces, crowds, or uncontrolled social conditions - Both marked by panic attacks when confronted with phobic situation - 2/3 of all phobias are agoraphobics ...
... Simple – fear of specific situation or thing Agoraphobia - fear of wide open spaces, crowds, or uncontrolled social conditions - Both marked by panic attacks when confronted with phobic situation - 2/3 of all phobias are agoraphobics ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS I-Lecture 10 Anxiety disorder is the most
... 2-To be unwilling to participate in a new game for fear that you won’t be the absolute best player is irrational. Dog lovers, when approached by a dog, might perceive the dog in any of several ways — in terms of attractiveness, breed, grooming, or posture. But people with a dog phobia (an excessive ...
... 2-To be unwilling to participate in a new game for fear that you won’t be the absolute best player is irrational. Dog lovers, when approached by a dog, might perceive the dog in any of several ways — in terms of attractiveness, breed, grooming, or posture. But people with a dog phobia (an excessive ...
Chapter 1 - CCRI Faculty Web
... Very frightening—sufferers live in fear of having them Agoraphobia often develops as a result ...
... Very frightening—sufferers live in fear of having them Agoraphobia often develops as a result ...
Psychopharmacology in pediatric OCD
... • Excessive fear in social situations where child is exposed to unfamiliar people/evaluation by others • Excessively self conscious/shy • Tremendous concern about social failure/embarrassment/humiliation ...
... • Excessive fear in social situations where child is exposed to unfamiliar people/evaluation by others • Excessively self conscious/shy • Tremendous concern about social failure/embarrassment/humiliation ...
Anxiety Disorders
... presence of (or anticipation of) a specific object or situation Examples: y ...
... presence of (or anticipation of) a specific object or situation Examples: y ...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders * 5th
... Feeding and eating disorders Sleep–wake disorders Sexual dysfunctions ...
... Feeding and eating disorders Sleep–wake disorders Sexual dysfunctions ...
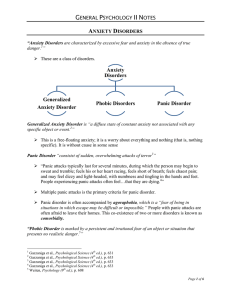
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... Gazzaniga et al6 point out several contributing factors to the development of anxiety disorders: o Temperment o Biased thinking (e.g., interpreting neutral events as threatening) o Excessive focus on threats o Learning (this is particularly true with phobias, but can be seen in other disorders) Qu ...
... Gazzaniga et al6 point out several contributing factors to the development of anxiety disorders: o Temperment o Biased thinking (e.g., interpreting neutral events as threatening) o Excessive focus on threats o Learning (this is particularly true with phobias, but can be seen in other disorders) Qu ...
Phobia

A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder, usually defined as a persistent fear of an object or situation in which the sufferer commits to great lengths in avoiding, typically disproportional to the actual danger posed, often being recognized as irrational. In the event the phobia cannot be avoided entirely, the sufferer will endure the situation or object with marked distress and significant interference in social or occupational activities.The terms distress and impairment as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV-TR) should also take into account the context of the sufferer's environment if attempting a diagnosis. The DSM-IV-TR states that if a phobic stimulus, whether it be an object or a social situation, is absent entirely in an environment — a diagnosis cannot be made. An example of this situation would be an individual who has a fear of mice but lives in an area devoid of mice. Even though the concept of mice causes marked distress and impairment within the individual, because the individual does not encounter mice in the environment no actual distress or impairment is ever experienced. Proximity and the degree to which escape from the phobic stimulus is impossible should also be considered. As the sufferer approaches a phobic stimulus, anxiety levels increase (e.g. as one gets closer to a snake, fear increases in ophidiophobia), and the degree to which escape of the phobic stimulus is limited has the effect of varying the intensity of fear in instances such as riding an elevator (e.g. anxiety increases at the midway point between floors and decreases when the floor is reached and the doors open).The term phobia is encompassing and usually discussed in the contexts of specific phobias and social phobias. Specific phobias are phobias to specific objects or environments, such as arachnophobia or acrophobia, and social phobias are phobias within social situations, such as public speaking and crowded areas. Some phobias, such as xenophobia, overlap with many other phobias.