The Arabidopsis TRM1-TON1 interaction reveals a recruitment
... (Figure 2), plus a few isolated ones. Apart from the six motifs, no significant similarity is detectable between groups. TRMs are rather large (80 kD on average) and charged proteins, covering a large range of pI from 4.3 to 10.6. They often contain a large positively charged domain of 150 to 300 re ...
... (Figure 2), plus a few isolated ones. Apart from the six motifs, no significant similarity is detectable between groups. TRMs are rather large (80 kD on average) and charged proteins, covering a large range of pI from 4.3 to 10.6. They often contain a large positively charged domain of 150 to 300 re ...
Molecular Docking
... Lock-and-key, induced-fit and the conformation ensemble model are not contradictory. Each one focuses on a particular aspect of the recognition process. The lock-and-key model introduces the principle of 3D complementarity, the induced-fit model explains how complementarity is achieved, and the ense ...
... Lock-and-key, induced-fit and the conformation ensemble model are not contradictory. Each one focuses on a particular aspect of the recognition process. The lock-and-key model introduces the principle of 3D complementarity, the induced-fit model explains how complementarity is achieved, and the ense ...
Fast and simple purification of GST fusion proteins using prepacked
... capacity will vary depending on flow rate and sample properties. Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow is available in lab packs for scale-up. Table 1 lists the main characteristics of GSTrap and Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow. ...
... capacity will vary depending on flow rate and sample properties. Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow is available in lab packs for scale-up. Table 1 lists the main characteristics of GSTrap and Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow. ...
Redalyc.MOLECULAR CHARACTERIZATION OF CRUDE SEED
... been purified and the presence of other bands in the cr ude extract; interestingly, in this study a protein of ~30kDa is highlighted, which suggests that it was not possible to break the peptide bonds of protein by the effect of the salt and that it is necessary to improve the method by increasing ...
... been purified and the presence of other bands in the cr ude extract; interestingly, in this study a protein of ~30kDa is highlighted, which suggests that it was not possible to break the peptide bonds of protein by the effect of the salt and that it is necessary to improve the method by increasing ...
Selective Dimerization of a C2H2 Zinc Finger Subfamily
... 7A). Structures of several C2H2 domains bound to DNA have been solved by X-ray crystallography and NMR (Wolfe et al., 2000). The structures reveal that nucleotide base contacts are mediated primarily by residues near the N-terminal half of the ␣ helix. The four residues most commonly involved in spe ...
... 7A). Structures of several C2H2 domains bound to DNA have been solved by X-ray crystallography and NMR (Wolfe et al., 2000). The structures reveal that nucleotide base contacts are mediated primarily by residues near the N-terminal half of the ␣ helix. The four residues most commonly involved in spe ...
The nucleolus and herpesviral usurpation
... nucleus. The NLS motifs, which are well-characterized and moderately conserved, are usually abundant in basic amino acids or can be predicted by suitable algorithms (Cokol et al., 2000; la Cour et al., 2004). Dedicated transport systems interact with the NLS and carry the protein into the nucleus (B ...
... nucleus. The NLS motifs, which are well-characterized and moderately conserved, are usually abundant in basic amino acids or can be predicted by suitable algorithms (Cokol et al., 2000; la Cour et al., 2004). Dedicated transport systems interact with the NLS and carry the protein into the nucleus (B ...
A Cyanobacterial Chlorophyll Synthase-HliD
... maltoside, and the extract applied to an anti-FLAG affinity column. Following extensive washing, the eluted material was separated by SDS-PAGE (Figure 1A). The Coomassie blue– stained bands were digested with trypsin and identified by MS. In addition to the FLAG-ChlG protein used as bait, we identified ...
... maltoside, and the extract applied to an anti-FLAG affinity column. Following extensive washing, the eluted material was separated by SDS-PAGE (Figure 1A). The Coomassie blue– stained bands were digested with trypsin and identified by MS. In addition to the FLAG-ChlG protein used as bait, we identified ...
Stitching proteins into membranes, not sew simple
... an N-terminal domain consisting of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, approximately 200 amino acids) could be controlled by the addition of methotrexate (MTX). In the absence of MTX, ‘loosely folded’ DHFR could be efficiently transported into the ER lumen, driven by a hydrophobic domain; while in the pr ...
... an N-terminal domain consisting of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, approximately 200 amino acids) could be controlled by the addition of methotrexate (MTX). In the absence of MTX, ‘loosely folded’ DHFR could be efficiently transported into the ER lumen, driven by a hydrophobic domain; while in the pr ...
The Ubiquitin System for Protein Degradation and Some of Its Roles
... reproduces energy-dependent protein degradation in the test tube, essential for the biochemical analysis of this system. For this purpose, we tried different sources, such as liver homogenates and extracts from cultured cells, and even from bacteria. We did not have any success in any of these attem ...
... reproduces energy-dependent protein degradation in the test tube, essential for the biochemical analysis of this system. For this purpose, we tried different sources, such as liver homogenates and extracts from cultured cells, and even from bacteria. We did not have any success in any of these attem ...
Amino Acids
... 1. Location of nonpolar amino acids in proteins • Proteins found in aqueous solutions (a polar environment), the side chains of the nonpolar amino acids tend to cluster together in the interior of the protein. • This phenomenon, known as the hydrophobic effect, is the result of the hydrophobicity o ...
... 1. Location of nonpolar amino acids in proteins • Proteins found in aqueous solutions (a polar environment), the side chains of the nonpolar amino acids tend to cluster together in the interior of the protein. • This phenomenon, known as the hydrophobic effect, is the result of the hydrophobicity o ...
Question #1 - Jordan
... filaments relative to each other leads to the contraction and relaxation of whole muscles. The myosin heads on the thick filaments "hook" onto, and pull, the thin filaments towards the center of each sarcomere. The appearance of this action is transitioned from a "relaxed" to a "fully contracted" mu ...
... filaments relative to each other leads to the contraction and relaxation of whole muscles. The myosin heads on the thick filaments "hook" onto, and pull, the thin filaments towards the center of each sarcomere. The appearance of this action is transitioned from a "relaxed" to a "fully contracted" mu ...
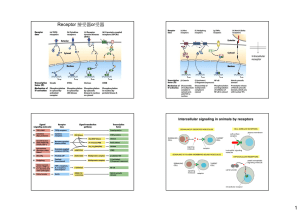
Receptor 接受器or受器
... All have a structure with seven transmembrane alpha helical Loops Orientation is always conserved with N terminus outside, C terminus inside the cell and cytosolic segments interacting with G proteins Sequences at C3, C4 and sometimes C2 determine which G protein is activated Genome sequencing has r ...
... All have a structure with seven transmembrane alpha helical Loops Orientation is always conserved with N terminus outside, C terminus inside the cell and cytosolic segments interacting with G proteins Sequences at C3, C4 and sometimes C2 determine which G protein is activated Genome sequencing has r ...
Case for support – Programme of work
... Fig. 3. (A) AtSufB/AtNAP1 can complement SufB deficiency in E. coli. (B) AtSufB/AtNAP1 is an ATPase. (C) AtSufB/AtNAP1 forms homodimers and interacts with AtSufC/AtNAP7 in yeast and in living chloroplast using BiMolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC). AtSufE To investigate sulfur acquisition ...
... Fig. 3. (A) AtSufB/AtNAP1 can complement SufB deficiency in E. coli. (B) AtSufB/AtNAP1 is an ATPase. (C) AtSufB/AtNAP1 forms homodimers and interacts with AtSufC/AtNAP7 in yeast and in living chloroplast using BiMolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC). AtSufE To investigate sulfur acquisition ...
A New Signal Sequence for Recombinant Protein Secretion in
... Pichia pastoris is one of the most widely used expression systems for the secretory expression of recombinant proteins. The secretory expression in P. pastoris usually makes use of the prepro MATα sequence from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which has a dibasic amino acid cleavage site at the end of the ...
... Pichia pastoris is one of the most widely used expression systems for the secretory expression of recombinant proteins. The secretory expression in P. pastoris usually makes use of the prepro MATα sequence from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which has a dibasic amino acid cleavage site at the end of the ...
Cell and Organelle Movement
... Cell and Organelle Movement I. Motor Proteins A. Myosin II, first identified in skeletal muscle, fig. 16-51 1. Responsible for generating force for muscle contraction and cytokenesis 2. Elongated protein composed of two heavy chains and two light chains a. Heavy chain composed of a globular head dom ...
... Cell and Organelle Movement I. Motor Proteins A. Myosin II, first identified in skeletal muscle, fig. 16-51 1. Responsible for generating force for muscle contraction and cytokenesis 2. Elongated protein composed of two heavy chains and two light chains a. Heavy chain composed of a globular head dom ...
Cardiac O-GlcNAc signaling is increased in hypertrophy and heart
... fashion to O-phosphorylation by kinases and phosphatases. The aim of our study was to determine if cardiac OGlcNAcylation, OGT, OGA, and GFAT levels were altered in human heart disease and in animal models of the three most common etiologies of heart failure; i.e., hypertension, myocardial infarctio ...
... fashion to O-phosphorylation by kinases and phosphatases. The aim of our study was to determine if cardiac OGlcNAcylation, OGT, OGA, and GFAT levels were altered in human heart disease and in animal models of the three most common etiologies of heart failure; i.e., hypertension, myocardial infarctio ...
Amyloid deposits - Lindquist Lab
... characteristics independent of the proteins’ primary amino acid sequences and may share a common mechanism of toxicity.5 Indeed even proteins completely unrelated to disease, such as PI3 kinase and the E. Coli protein HypF-N, can be induced to form such prefibrillar structures in vitro and, when the ...
... characteristics independent of the proteins’ primary amino acid sequences and may share a common mechanism of toxicity.5 Indeed even proteins completely unrelated to disease, such as PI3 kinase and the E. Coli protein HypF-N, can be induced to form such prefibrillar structures in vitro and, when the ...
Hydrophilic Linkers and Polar Contacts Affect Aggregation of FG
... (10). Interactions between FG domains are therefore unlikely to be controlled by hydrophobic FG motifs alone, but should also depend on the amino acid composition of the hydrophilic linkers connecting them. To study the influence of the hydrophilic linker sequences on aggregation, five different lin ...
... (10). Interactions between FG domains are therefore unlikely to be controlled by hydrophobic FG motifs alone, but should also depend on the amino acid composition of the hydrophilic linkers connecting them. To study the influence of the hydrophilic linker sequences on aggregation, five different lin ...
pGADT7 AD Vector Information
... • Suitable host strains: Y1HGold, Y2HGold, AH109(MATa), Y187(MATα), Y190(MATa), SFY526(MATa), CG1945(MATa), HF7c(MATa) • Selectable marker: LEU2 • S. cerevisiae origin: 2 μ Reference ...
... • Suitable host strains: Y1HGold, Y2HGold, AH109(MATa), Y187(MATα), Y190(MATa), SFY526(MATa), CG1945(MATa), HF7c(MATa) • Selectable marker: LEU2 • S. cerevisiae origin: 2 μ Reference ...
SAPS(1) USER COMMANDS SAPS(1) NAME saps
... SAPS evaluates by statistical criteria a wide variety of protein sequence properties. Properties considered include compositional biases; clusters and runs of charge and other amino acid types; different kinds and extents of repetitive structures; locally periodic motifs; and anomalous spacings betw ...
... SAPS evaluates by statistical criteria a wide variety of protein sequence properties. Properties considered include compositional biases; clusters and runs of charge and other amino acid types; different kinds and extents of repetitive structures; locally periodic motifs; and anomalous spacings betw ...
Auxin Action in a Cell
... the Aux/IAA Proteins and SCFTIR1 in Cell-Free Extracts Auxin treatment of Arabidopsis seedlings stimulates binding of Aux/IAA proteins by SCFTIR1 [2]. To further investigate this response, we tested the effects of auxin added directly to protein extracts prepared from seedlings expressing c-myc-tagg ...
... the Aux/IAA Proteins and SCFTIR1 in Cell-Free Extracts Auxin treatment of Arabidopsis seedlings stimulates binding of Aux/IAA proteins by SCFTIR1 [2]. To further investigate this response, we tested the effects of auxin added directly to protein extracts prepared from seedlings expressing c-myc-tagg ...
Alignment
... alignments by hand if the structure is available. • These alignments can then serve as a benchmark to train gap parameters so that the alignment program produces correct alignments. ...
... alignments by hand if the structure is available. • These alignments can then serve as a benchmark to train gap parameters so that the alignment program produces correct alignments. ...
Protein methylation at the surface and buried deep
... are central to the recognition of trimethyllysine residues by a novel histone H3 binding module [40]. The 56 members of the SET-domain family encoded by the human genome can be divided into ten classes by their amino acid sequences [4]. Nine of these classes, with 53 members in total, were initially ...
... are central to the recognition of trimethyllysine residues by a novel histone H3 binding module [40]. The 56 members of the SET-domain family encoded by the human genome can be divided into ten classes by their amino acid sequences [4]. Nine of these classes, with 53 members in total, were initially ...
The proteomics of plant cell membranes
... Arabidopsis. Chloroplasts perform vital biosynthetic functions, and many processes are located exclusively within these unique organelles including the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis, and the biosynthetic pathways for fatty acids, vitamins, and amino acids. The envelope, a two-membrane s ...
... Arabidopsis. Chloroplasts perform vital biosynthetic functions, and many processes are located exclusively within these unique organelles including the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis, and the biosynthetic pathways for fatty acids, vitamins, and amino acids. The envelope, a two-membrane s ...
Monoclonal Anti-human IL-18 BP Antibody Catalogue Number
... Specificity: human IL-18BPa & c Immunogen: E.coli-derived rhIL18BPc ...
... Specificity: human IL-18BPa & c Immunogen: E.coli-derived rhIL18BPc ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.