1. Overview
... • Coordinates can be extracted and viewed • Comparisons of structures allows identification of structural motifs • Proteins with similar functions and sequences = homologs ...
... • Coordinates can be extracted and viewed • Comparisons of structures allows identification of structural motifs • Proteins with similar functions and sequences = homologs ...
Power Point
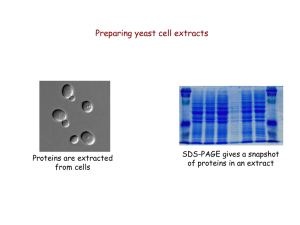
... “Quick and dirty” protein extraction from yeast 1. Collect cells by centrifugation 2. Wash cells with deionized water ...
... “Quick and dirty” protein extraction from yeast 1. Collect cells by centrifugation 2. Wash cells with deionized water ...
Project
... potential of a battery of recombinant aegerolysins from selected bacteria and fungi, alone and in combination with their MACPF-protein partners, to act as potential bio-pesticides against some of the currently most damaging insects, and other selected invertebrates. Aegerolysin interactions with mem ...
... potential of a battery of recombinant aegerolysins from selected bacteria and fungi, alone and in combination with their MACPF-protein partners, to act as potential bio-pesticides against some of the currently most damaging insects, and other selected invertebrates. Aegerolysin interactions with mem ...
THE PROTEOME RESPONSE OF LARVAL STAGES OF
... Oysters are one of the most important commercially exploited species cultured in the molluskan hatcheries around the world. Due to rising CO 2 and subsequent decrease in seawater pH, their survival and shell forming processes are threatened globally. Our large-scale CO 2 perturbation experiments at ...
... Oysters are one of the most important commercially exploited species cultured in the molluskan hatcheries around the world. Due to rising CO 2 and subsequent decrease in seawater pH, their survival and shell forming processes are threatened globally. Our large-scale CO 2 perturbation experiments at ...
Interactive Software for the study of membrane biology: lipid
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
The instructions for how to create and run a living organism are
... To make proteins—the large, complex molecules necessary for structure and function—a cell must first make a copy of its DNA. The cell does that through transcription, which uses the DNA as a template to produce a corresponding strand of messenger RNA (mRNA). That mRNA then undergoes translation. In ...
... To make proteins—the large, complex molecules necessary for structure and function—a cell must first make a copy of its DNA. The cell does that through transcription, which uses the DNA as a template to produce a corresponding strand of messenger RNA (mRNA). That mRNA then undergoes translation. In ...
Determination of Proteins
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
Auxiliary proteins of photosystem II: tuning the enzyme for optimal
... has revealed that the cap of the OEC is composed of three polypeptides: PsbO, PsbU and PsbV, and two large loops from CP43 and CP47. In green algae and plants, PsbU and PsbV are absent but two different proteins, PsbP and PsbQ, are present. However, biochemical and genomic studies have now establish ...
... has revealed that the cap of the OEC is composed of three polypeptides: PsbO, PsbU and PsbV, and two large loops from CP43 and CP47. In green algae and plants, PsbU and PsbV are absent but two different proteins, PsbP and PsbQ, are present. However, biochemical and genomic studies have now establish ...
PDF - Available Technologies
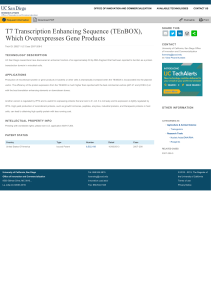
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
Nuclease Digestion
... to form the primary structure of a protein • H-bonding and folding lead to secondary and tertiary structure ...
... to form the primary structure of a protein • H-bonding and folding lead to secondary and tertiary structure ...
Using light as a superglue for proteins and their binding partners
... and their binding partners Most of what happens in a cell involves fleeting interactions between proteins. Molecules briefly dock onto each other, change each other's chemistry, and then separate again. While these encounters are crucial to the health of cells, they often happen so quickly that they ...
... and their binding partners Most of what happens in a cell involves fleeting interactions between proteins. Molecules briefly dock onto each other, change each other's chemistry, and then separate again. While these encounters are crucial to the health of cells, they often happen so quickly that they ...
Proteins and DNA
... the proteins that should be made. Like proteins DNA is similar to a string of pearls, but in this case, there are only four kinds of pearls. The letters A, C, G and T represents the four kinds. Their order in the string describes the proteins to be made. The DNA sequence is translated into proteins ...
... the proteins that should be made. Like proteins DNA is similar to a string of pearls, but in this case, there are only four kinds of pearls. The letters A, C, G and T represents the four kinds. Their order in the string describes the proteins to be made. The DNA sequence is translated into proteins ...
Protein Aggregation in High-Protein Caramel
... protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form into small (10 – 30 nm) micelles in milk in order to protect the hydrophobic components f ...
... protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form into small (10 – 30 nm) micelles in milk in order to protect the hydrophobic components f ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
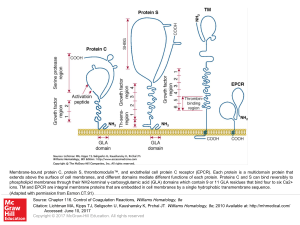
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... make specific proteins • Many diseases are caused by the bodies inability to make specific proteins properly ...
... make specific proteins • Many diseases are caused by the bodies inability to make specific proteins properly ...
Proteins
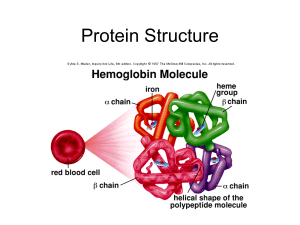
... – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
... – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
File
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins are
... an amino group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH) on each end. • 20 different amino groups are found in nature • Proteins control rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissue like bone and muscle. Some proteins transport materials or help to ...
... an amino group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH) on each end. • 20 different amino groups are found in nature • Proteins control rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissue like bone and muscle. Some proteins transport materials or help to ...
Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins
... Identification of regulatory proteins from human cells using 2D-GE and LC-MS/MS Victor Paromov Christian Muenyi William L. Stone ...
... Identification of regulatory proteins from human cells using 2D-GE and LC-MS/MS Victor Paromov Christian Muenyi William L. Stone ...
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
Proteins pages 8 and 9
... Proteins Protein is required in the body for growth and repair. Too much protein is used by the body for energy or stored as fat. ...
... Proteins Protein is required in the body for growth and repair. Too much protein is used by the body for energy or stored as fat. ...
distinct format
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.