Proteins
... #3 – Origin of SelfReplicating Molecules • Claim: RNA may have acted as an early catalyst for polymerization and/or molecule to store code. • Evidence: RNA (simpler than DNA) will: – Act as a catalyst for certain chemical reactions – Assemble itself (polymerization) – Replicate itself – make more c ...
... #3 – Origin of SelfReplicating Molecules • Claim: RNA may have acted as an early catalyst for polymerization and/or molecule to store code. • Evidence: RNA (simpler than DNA) will: – Act as a catalyst for certain chemical reactions – Assemble itself (polymerization) – Replicate itself – make more c ...
The World of Chemistry
... Episode 24 - The Genetic Code https://www.learner.org/vod/vod_window.html?pid=816 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
... Episode 24 - The Genetic Code https://www.learner.org/vod/vod_window.html?pid=816 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
Proteins
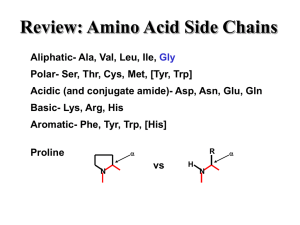
... whereas hydrophobic amino acids tend be located away from water, for example, in the hydrophobic core of a protein, or within the bilipid layer of a cell membrane. Hydrophibicity is strongly correlated with polarity; polar amino acids tend to be hydrophylic, nonpolar ones tend to be hydrophobic. ...
... whereas hydrophobic amino acids tend be located away from water, for example, in the hydrophobic core of a protein, or within the bilipid layer of a cell membrane. Hydrophibicity is strongly correlated with polarity; polar amino acids tend to be hydrophylic, nonpolar ones tend to be hydrophobic. ...
PROTEIN PROTEIN: Amino Acids PROTEIN: Complete Proteins
... PROTEIN: Incomplete Proteins Incomplete proteins contain some, but not all, of the amino acids. Incomplete proteins are from other plant sources Examples Include: grains, dried beans, nuts and seeds. Incomplete proteins can be combined to create a complementary protein. ...
... PROTEIN: Incomplete Proteins Incomplete proteins contain some, but not all, of the amino acids. Incomplete proteins are from other plant sources Examples Include: grains, dried beans, nuts and seeds. Incomplete proteins can be combined to create a complementary protein. ...
Characterization of head-hunter proteins for exchange of genetic information between cells.
... One graduate student position is available to further explore this exciting discovery. The details are as follows. Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasm ...
... One graduate student position is available to further explore this exciting discovery. The details are as follows. Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasm ...
Center for Structural Biology
... Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
... Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
Protein misfolding associated to mild modifications of local cellular pH
... mutants: Gly26Arg (a substitution mutant with a gain in a positive charge), and Lys1070 (showing a deletion of a Lisine residue). Structural analysis shows that acidic pH induces a strong conformational shift, decreasing the cooperative denaturation pattern, and the hydrophobic cavities present in t ...
... mutants: Gly26Arg (a substitution mutant with a gain in a positive charge), and Lys1070 (showing a deletion of a Lisine residue). Structural analysis shows that acidic pH induces a strong conformational shift, decreasing the cooperative denaturation pattern, and the hydrophobic cavities present in t ...
Study Guide
... 3. DNA contains the genetic code. It is a double stranded molecule that has a double helix structure. Deoxyribose is the sugar that makes up this molecule. DNA is contained in the nucleus of the cell. 4. The genetic code is the order of the nitrogen bases that form along a gene and directs what type ...
... 3. DNA contains the genetic code. It is a double stranded molecule that has a double helix structure. Deoxyribose is the sugar that makes up this molecule. DNA is contained in the nucleus of the cell. 4. The genetic code is the order of the nitrogen bases that form along a gene and directs what type ...
Conformational dynamics of signaling proteins and ion channels
... Radiolytic footprinting and mass spectrometry were used to probe the structure of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel KirBac 3.1 in its closed and open states. By subjecting protein solutions to focused synchrotron X-ray beams with millisecond timescale exposures we modified solvent accessible ...
... Radiolytic footprinting and mass spectrometry were used to probe the structure of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel KirBac 3.1 in its closed and open states. By subjecting protein solutions to focused synchrotron X-ray beams with millisecond timescale exposures we modified solvent accessible ...
charge-to-mass ratio. The electrophoretic mobility is defined as the
... Where "c" is a proportionality constant that depends on the gel properties. Each gel has a region where the above equation holds and a plot of log(MW) vs. Mobility will be linear. The determination of molecular weight requires the calibration of the SDS gel using proteins of known molecular weight. ...
... Where "c" is a proportionality constant that depends on the gel properties. Each gel has a region where the above equation holds and a plot of log(MW) vs. Mobility will be linear. The determination of molecular weight requires the calibration of the SDS gel using proteins of known molecular weight. ...
Supplementary Material
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
Ruth Stark (Distinguished Professor)
... Structural Biology of Fatty Acid Signalling Molecular recognition of fatty acid-binding proteins by ligands and peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptors (A) ...
... Structural Biology of Fatty Acid Signalling Molecular recognition of fatty acid-binding proteins by ligands and peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptors (A) ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in vegetarian diets? D. What ...
... 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in vegetarian diets? D. What ...
What are some other organic molecules?
... other quality of the environment can cause a protein to unravel and lose its normal shape Denatured proteins do not function properly! INCORRECT FORM….. NO FUNCTION! ...
... other quality of the environment can cause a protein to unravel and lose its normal shape Denatured proteins do not function properly! INCORRECT FORM….. NO FUNCTION! ...
Proteomics
... Uetz, et al., Nature 2000 403, 623-627. Schwikowski et al., 2000 Nature Biotech. 18, 1257-1261. ...
... Uetz, et al., Nature 2000 403, 623-627. Schwikowski et al., 2000 Nature Biotech. 18, 1257-1261. ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... proteins by bacteria is the investigator’s ability to identify, purify and quantify the proteins of interest. A wide variety of techniques are available providing the investigator with many possible outcomes of purity and concentration. ...
... proteins by bacteria is the investigator’s ability to identify, purify and quantify the proteins of interest. A wide variety of techniques are available providing the investigator with many possible outcomes of purity and concentration. ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... proteins by bacteria is the investigator’s ability to identify, purify and quantify the proteins of interest. A wide variety of techniques are available providing the investigator with many possible outcomes of purity and concentration. ...
... proteins by bacteria is the investigator’s ability to identify, purify and quantify the proteins of interest. A wide variety of techniques are available providing the investigator with many possible outcomes of purity and concentration. ...
Notes
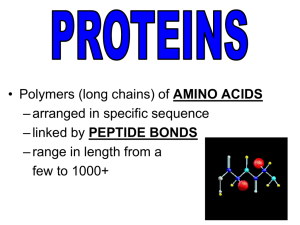
... – arranged in specific sequence – linked by PEPTIDE BONDS – range in length from a few to 1000+ ...
... – arranged in specific sequence – linked by PEPTIDE BONDS – range in length from a few to 1000+ ...
Announcements - Hiram College
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
Importance of Proteins Test
... 5. Foods that contain all eight essential amino acids are called _____________________ proteins. 6. Foods that are short of one or more of the essential amino acids are called ________________________ proteins. 7. _______________________is when the actual nature of the protein is changed. 8. When a ...
... 5. Foods that contain all eight essential amino acids are called _____________________ proteins. 6. Foods that are short of one or more of the essential amino acids are called ________________________ proteins. 7. _______________________is when the actual nature of the protein is changed. 8. When a ...
individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired
... individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
... individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
Day 2: Protein Sequence Analysis
... Can include the cleavage of the pro- region to release the active protein, the removal of the signal peptide and numerous covalent modifications such as, acetylations, glycosylations, hydroxylations, methylations and phosphorylations. Posttranslational modifications may alter the molecular weight of ...
... Can include the cleavage of the pro- region to release the active protein, the removal of the signal peptide and numerous covalent modifications such as, acetylations, glycosylations, hydroxylations, methylations and phosphorylations. Posttranslational modifications may alter the molecular weight of ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.