Proteins
... Factors that must be supplied in the diet for the body to be able to synthesis PROTEİN include : 1 . all E.a.a consume simultaneously and in proper amount 2 . an adequate total amount of protein to supply amine groups to synthesis non – E.a.a 3 . adequate of CHO & FAT to spare protein being used to ...
... Factors that must be supplied in the diet for the body to be able to synthesis PROTEİN include : 1 . all E.a.a consume simultaneously and in proper amount 2 . an adequate total amount of protein to supply amine groups to synthesis non – E.a.a 3 . adequate of CHO & FAT to spare protein being used to ...
Proteins - Mr Waring`s Biology Blog
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 7 of 29 ...
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 7 of 29 ...
1-2 Biomolecules
... b. nitrogenous base c. phosphate d. all of these above 6. Vocabulary. Match the following words with its correct definition. _____ Amino acid _____ Polymer _____ Monomer ...
... b. nitrogenous base c. phosphate d. all of these above 6. Vocabulary. Match the following words with its correct definition. _____ Amino acid _____ Polymer _____ Monomer ...
Isolation of proteins
... phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anionic (-) one ...
... phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anionic (-) one ...
abstract form
... species. It is interesting to note, that the fraction of such proteins of halophilic archeae was decreased, and we did not notice similar patterns in bacterial proteomes. Next, we analyzed distribution of amyloidogeneic proteins among different functional classes. We have shown that amyloidogenic pr ...
... species. It is interesting to note, that the fraction of such proteins of halophilic archeae was decreased, and we did not notice similar patterns in bacterial proteomes. Next, we analyzed distribution of amyloidogeneic proteins among different functional classes. We have shown that amyloidogenic pr ...
Making Proteins
... • Fit together with its substrate like a “lock” and a I am now“key” a product. In addition I am a glucose now. to what – Not used in theI am reaction youup know. a – Work in asubstrate. very specific biological range – Usually end with “-ase” ...
... • Fit together with its substrate like a “lock” and a I am now“key” a product. In addition I am a glucose now. to what – Not used in theI am reaction youup know. a – Work in asubstrate. very specific biological range – Usually end with “-ase” ...
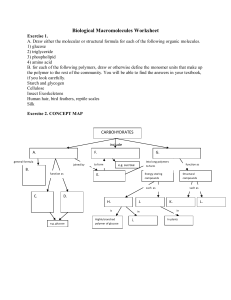
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
HonBio Chapter 3 notes
... This is done by means of an enzymemediated dehydration synthesis. A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids. The amino acid sequence causes the polypeptide to assume a particular shape The shape of a protein determines its specific function. ...
... This is done by means of an enzymemediated dehydration synthesis. A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids. The amino acid sequence causes the polypeptide to assume a particular shape The shape of a protein determines its specific function. ...
Amino acid sequence fingerprints in divergent evolution of
... are preserved, the resulting protein function and activity can remain without any observable modifications. The essential amino acid residues are mostly parts of the so-called conserved sequence regions that cover the isolated segments belonging to the active site of the protein. In the case the pro ...
... are preserved, the resulting protein function and activity can remain without any observable modifications. The essential amino acid residues are mostly parts of the so-called conserved sequence regions that cover the isolated segments belonging to the active site of the protein. In the case the pro ...
CH 460 Dr. Muccio What are the 4 levels of protein structure and
... What are the 4 levels of protein structure and describe each. Do proteins with similar structures usually have similar functions? Primary - amino acid sequence Secondary – helices, sheets, turns, loops Tertiary – 3d folding Quaternary – organization of 3d subunits Yes usually (not always), similar s ...
... What are the 4 levels of protein structure and describe each. Do proteins with similar structures usually have similar functions? Primary - amino acid sequence Secondary – helices, sheets, turns, loops Tertiary – 3d folding Quaternary – organization of 3d subunits Yes usually (not always), similar s ...
Sander van Riet 13 June Reviewer Gene co
... IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from the GEO database were used. First they linked with already known motile cilia proteins together w ...
... IvIiev et al. uses this concept together with Protein Atlas project in order to identify new genes associated with motile cilia. Data from 3 different regions known to harbour motile cilia obtained from the GEO database were used. First they linked with already known motile cilia proteins together w ...
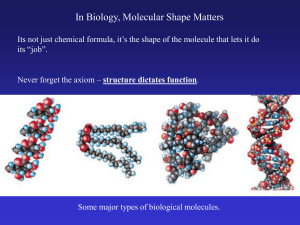
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
FROM TRAIT TO PROTEIN - CLASSROOM
... hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein. The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific funct ...
... hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein. The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific funct ...
AS Biology - Everything Protein
... A PROSTHETIC GROUP is a NON-POLYPEPTIDE that has been incorporated into a proteins structure. An example of this is Haem (iron group) in Haemoglobin. Not all proteins include prosthetic groups. The final 3D structure of a protein can be classified as either GLOBULAR or FIBROUS. GLOBULAR PROTEINS are ...
... A PROSTHETIC GROUP is a NON-POLYPEPTIDE that has been incorporated into a proteins structure. An example of this is Haem (iron group) in Haemoglobin. Not all proteins include prosthetic groups. The final 3D structure of a protein can be classified as either GLOBULAR or FIBROUS. GLOBULAR PROTEINS are ...
Proteins
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
Protein Folding and Quality Control
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
MTC25 - Intracellular Processing
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
Proteins
... • Levels of Protein structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary. • Protein structure • Classification of proteins. • Hydrolysis of proteins. • Denaturation of proteins. ...
... • Levels of Protein structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary. • Protein structure • Classification of proteins. • Hydrolysis of proteins. • Denaturation of proteins. ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
Peptide Bonds
... forces (not covalent bonds) Hemoglobin is tetrameric myglobin For example, Hemoglobin has four heme units, the protein globin surrounds the heme – Takes the shape of a giant tetrahedron – Two identical and globins. The and chains are very similar but distinguishable in both primary structure ...
... forces (not covalent bonds) Hemoglobin is tetrameric myglobin For example, Hemoglobin has four heme units, the protein globin surrounds the heme – Takes the shape of a giant tetrahedron – Two identical and globins. The and chains are very similar but distinguishable in both primary structure ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... Ballabio Gibson K, Mitchell G. The Online Metabolic andportion Molecular The release from BiP Valle allowsD,transport ATF6 to the Golgi apparatus. SubsequentSE, cleavage byA, the S1P and S2P proteases liberates an effector of Bases of Inherited Disease; ...
... Ballabio Gibson K, Mitchell G. The Online Metabolic andportion Molecular The release from BiP Valle allowsD,transport ATF6 to the Golgi apparatus. SubsequentSE, cleavage byA, the S1P and S2P proteases liberates an effector of Bases of Inherited Disease; ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.