2. Intro to Proteins
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
Project-JP
... during correct mRNA product formation. Without these two RNA binding proteins, incorrect mRNA synthesis, and consequently incorrect protein products, may result. This research project attempts to characterize the interaction of Hrp1, Rna15, and their shared RNA to discover the exact mechanism of cor ...
... during correct mRNA product formation. Without these two RNA binding proteins, incorrect mRNA synthesis, and consequently incorrect protein products, may result. This research project attempts to characterize the interaction of Hrp1, Rna15, and their shared RNA to discover the exact mechanism of cor ...
ppt
... 1. Antibody columns - for specific antigens 2. Cellulose columns - for cellulases 3. Starch columns - for amylases 4. DNA columns - for DNA binding proteins 5. Ligand columns - for specific receptors 6. Metal columns - for proteins that bind metal ions IMAC, or Immobilized Metal ion Affinity Chromat ...
... 1. Antibody columns - for specific antigens 2. Cellulose columns - for cellulases 3. Starch columns - for amylases 4. DNA columns - for DNA binding proteins 5. Ligand columns - for specific receptors 6. Metal columns - for proteins that bind metal ions IMAC, or Immobilized Metal ion Affinity Chromat ...
Characterization of head-hunter proteins for exchange of genetic information between cells.
... One graduate student position is available to further explore this exciting discovery. The details are as follows. Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasm ...
... One graduate student position is available to further explore this exciting discovery. The details are as follows. Acquiring new genetic information is a critical way for a cell to adapt to the changing environment. This is particularly prevalent in bacteria as they exchange DNA molecules like plasm ...
Protein Synthesis
... • DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid • Composed of nucleotides • Each nucleotide contains – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group (PO4-1) – Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G) ...
... • DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid • Composed of nucleotides • Each nucleotide contains – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group (PO4-1) – Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G) ...
Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
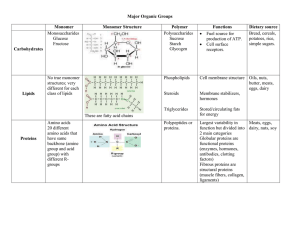
... structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
... structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
Paper background for Students
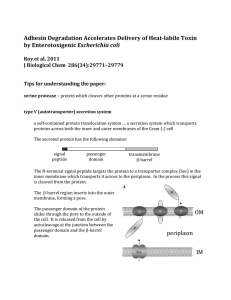
... serine protease – protein which cleaves other proteins at a serine residue type V (autotransporter) secretion system a self-contained protein translocation system … a secretion system which transports proteins across both the inner and outer membranes of the Gram (-) cell The secreted protein has th ...
... serine protease – protein which cleaves other proteins at a serine residue type V (autotransporter) secretion system a self-contained protein translocation system … a secretion system which transports proteins across both the inner and outer membranes of the Gram (-) cell The secreted protein has th ...
WSB2 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q01)
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
... http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: S ...
Data/hora: 18/04/2017 14:16:42 Provedor de dados: 189 País
... Resumo: In plants, a family of ubiquitous proteins named non-specific lipid-transfer proteins (ns-LTPs) facilitates the transfer of fatty acids, phospholipids and steroids between membranes. Recent data suggest that these secreted proteins play a key role in the formation of cuticular wax layers and ...
... Resumo: In plants, a family of ubiquitous proteins named non-specific lipid-transfer proteins (ns-LTPs) facilitates the transfer of fatty acids, phospholipids and steroids between membranes. Recent data suggest that these secreted proteins play a key role in the formation of cuticular wax layers and ...
Inside the nucleus of each human cell are 46 chromosomes. We
... made differently, which may mean it cannot work properly; for example, an enzyme may be the wrong shape. A mutation can cause a genetic disorder. ...
... made differently, which may mean it cannot work properly; for example, an enzyme may be the wrong shape. A mutation can cause a genetic disorder. ...
HOW GOOD DO WE HAVE TO BE TO SOLVE THE PROTEIN FOLDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND SCORING PROBLEMS?
... significant successes to show for several decades of effort. Nonetheless, several challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, ...
... significant successes to show for several decades of effort. Nonetheless, several challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, ...
Review For Final I - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... Molecule movement across lipid bilayer without proteins ...
... Molecule movement across lipid bilayer without proteins ...
the protein (or proteins)
... red dots = essential proteins (so knockout is lethal) green = non-lethal; orange = slow growth; yellow = unknown effect ...
... red dots = essential proteins (so knockout is lethal) green = non-lethal; orange = slow growth; yellow = unknown effect ...
Measurement of Protein Molecular Weight using MALDI MS
... To calculate the molecular weight of the protein, the measured m/z value of charge state, n, is multiplied by n and then n protons (n * 1.0079) are subtracted to give the measured molecular weight. ...
... To calculate the molecular weight of the protein, the measured m/z value of charge state, n, is multiplied by n and then n protons (n * 1.0079) are subtracted to give the measured molecular weight. ...
What is a Gene?
... • If your hair is brown, it’s because your DNA code is telling your cells to make a specific protein. That protein makes your hair brown. ...
... • If your hair is brown, it’s because your DNA code is telling your cells to make a specific protein. That protein makes your hair brown. ...
Proteomics
... • Approximately 35,000 genes. • Genes account for 2% of genome sequence. • Genes encode proteins. ...
... • Approximately 35,000 genes. • Genes account for 2% of genome sequence. • Genes encode proteins. ...
Naomi`s Nucleants - Molecular Dimensions
... material (CaO-P2O5-SiO2) and has a highly porous surface with cavities of similar sizes to proteins. It is hypothesised that the cavities entrap protein molecules, thereby encouraging nucleation and crystal formation. ...
... material (CaO-P2O5-SiO2) and has a highly porous surface with cavities of similar sizes to proteins. It is hypothesised that the cavities entrap protein molecules, thereby encouraging nucleation and crystal formation. ...
Protein Folding File
... What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what i ...
... What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what i ...
Supplementary data 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9 include N, Total (ProtScore)
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
REPSA-Directed Identification of DNA
... Proteins responsible for the majority of cellular activities Transcription Factors are proteins that bind to DNA to regulate expression ...
... Proteins responsible for the majority of cellular activities Transcription Factors are proteins that bind to DNA to regulate expression ...
Endosymbiosis and Evidence for Endosymbiosis
... • Allows mucus to slide freely on these linings • Mutation= no hypertonic condition is established on the exterior of the cell and water does not flow outward ...
... • Allows mucus to slide freely on these linings • Mutation= no hypertonic condition is established on the exterior of the cell and water does not flow outward ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.