Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
CHAPTER 3-Protein-In Class Activity
... Name some of the protein functions in the body with their examples. Define Primary structure of a protein with example Define Secondary structure of a protein with example Define Tertiary structure of a protein with example Define Quaternary structure of a protein with example Secondary structure, f ...
... Name some of the protein functions in the body with their examples. Define Primary structure of a protein with example Define Secondary structure of a protein with example Define Tertiary structure of a protein with example Define Quaternary structure of a protein with example Secondary structure, f ...
Protein Structure and Folding
... 1. Use SCOP (Structural Classification Of Proteins) http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/ to classify PDB entry 1tml. 2. Name the fold of central domain of 1m6h and draw the corresponding topology diagram. 3. Classify the two domains of a metabolic regulator protein 1d66 from Baker’s yeast. 4. Use DAL ...
... 1. Use SCOP (Structural Classification Of Proteins) http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/ to classify PDB entry 1tml. 2. Name the fold of central domain of 1m6h and draw the corresponding topology diagram. 3. Classify the two domains of a metabolic regulator protein 1d66 from Baker’s yeast. 4. Use DAL ...
Proteins POSTER ppt
... Currently available structural comparison methods are both computationally expensive and fail to detect biologically significant local structural features. Developing better methods to generate highly representative and compact signatures is a crucial step in designing scalable and accurate data min ...
... Currently available structural comparison methods are both computationally expensive and fail to detect biologically significant local structural features. Developing better methods to generate highly representative and compact signatures is a crucial step in designing scalable and accurate data min ...
Protein Stability - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. the backbone folds adopts teh appropriate secondary structure. 2. 2 structure elements fold into common structural motifs. 3. these domains interact to form the globular core of a protein. 4. The complex domains interact through surface contacts. ...
... 1. the backbone folds adopts teh appropriate secondary structure. 2. 2 structure elements fold into common structural motifs. 3. these domains interact to form the globular core of a protein. 4. The complex domains interact through surface contacts. ...
... (who, unknown to me, was also considering such a machine) took up the suggestion and after a day of intense discussion we had a clear idea of how a protein sequencing machine would work. We started with a simple glass chromatographic column, tilted, so that the protein would not simply fall out. Onl ...
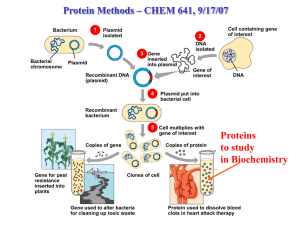
Recombinant human ADRB2 + GsalphaL fusion protein
... catecholamine epinephrine and couples to the G protein Gs to mediate adenylate cyclase activation. ADRB2 binds epinephrine with an approximately 30-fold greater affinity than it does norepinephrine. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various ...
... catecholamine epinephrine and couples to the G protein Gs to mediate adenylate cyclase activation. ADRB2 binds epinephrine with an approximately 30-fold greater affinity than it does norepinephrine. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various ...
1 Introduction - Computer Science Department
... supplement material available on individual virus type 1 (HTLV-1), which is responsible for causing researchers’ web sites. The major challenges in a type of leukemia and associated diseases in adults. A realizing our architecture are: viral protein called Tax plays a central role in the development ...
... supplement material available on individual virus type 1 (HTLV-1), which is responsible for causing researchers’ web sites. The major challenges in a type of leukemia and associated diseases in adults. A realizing our architecture are: viral protein called Tax plays a central role in the development ...
Interactive Software for the study of membrane biology: lipid
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
... Biological membranes define cellular boundaries, divide cells into discrete compartments, organize complex reaction sequences, and act in signal reception and energy transformations. This topic is studied in all undergraduate biochemistry courses. Visualization of structures generally facilitates th ...
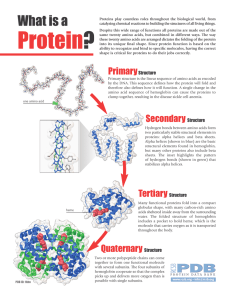
Protein?
... Alpha helices (shown in blue) are the basic structural elements found in hemoglobin, but many other proteins also include beta sheets. The inset highlights the pattern of hydrogen bonds (shown in green) that stabilizes alpha helices. ...
... Alpha helices (shown in blue) are the basic structural elements found in hemoglobin, but many other proteins also include beta sheets. The inset highlights the pattern of hydrogen bonds (shown in green) that stabilizes alpha helices. ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... of all attending colleagues including the Professors. So, everybody learns from the others, kind of a multiplication effect. One of the powers of molecular modelling resides in its informative value in displaying molecules, in total or in portions thereof, in different formats such as wireframe, pro ...
... of all attending colleagues including the Professors. So, everybody learns from the others, kind of a multiplication effect. One of the powers of molecular modelling resides in its informative value in displaying molecules, in total or in portions thereof, in different formats such as wireframe, pro ...
Puredown Protein A/G-Agarose Conjugate
... Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular protein. This process can be used to isolate and concentrate a particular protein from a sample containing many thousands of different proteins. I ...
... Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular protein. This process can be used to isolate and concentrate a particular protein from a sample containing many thousands of different proteins. I ...
from_Bi_150_molbiol
... a molecule on the cell surface or in the cell interior that has an affinity for a specific molecule (the ligand). Latin, “to tie” ...
... a molecule on the cell surface or in the cell interior that has an affinity for a specific molecule (the ligand). Latin, “to tie” ...
Symmetry
... these arrangements are actually precluded. In fact, proteins may only adopt 65 of the 230 possible 3D space groups. Many of these are observed when we crystallize proteins. In the case of naturally occurring multimers of proteins, other constraints occur which limit the possible arrangements. We are ...
... these arrangements are actually precluded. In fact, proteins may only adopt 65 of the 230 possible 3D space groups. Many of these are observed when we crystallize proteins. In the case of naturally occurring multimers of proteins, other constraints occur which limit the possible arrangements. We are ...
(1) Identify the secondary structure described in each of the
... (2) Below, you can find the structure of the C-terminal domain of protein L7/12. It is ...
... (2) Below, you can find the structure of the C-terminal domain of protein L7/12. It is ...
A non-conventional nuclear import pathway Sandra Korge1, Bert
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
docx - BeanBeetles.org
... Proteins are one of the fundamental types of macromolecules essential to the workings of individual cells and thus multicellular organisms. The information for building proteins expressed in a cell is coded for in the DNA of the cell. This relationship between proteins and DNA is well understood and ...
... Proteins are one of the fundamental types of macromolecules essential to the workings of individual cells and thus multicellular organisms. The information for building proteins expressed in a cell is coded for in the DNA of the cell. This relationship between proteins and DNA is well understood and ...
Homework Exercise 6 1(a). Name the “building blocks” of a protein
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
Designer enzymes Donald Hilvert ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
Biosynthesis and degradation of proteins
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
... Protein degradation systems Ubiquitin and proteasome Activation of proteases Protease inhibitors ...
Table S5. Proteins specifically induced or repressed during A
... (A) Genomic organization of JR1. Exons are indicated as rectangles. The triangle marks the region of T-DNA insertion. (B) qPCR analysis of JR1 expression in Col-0 or in the JR1 mutant line described in (A). Accumulation of the JR1 transcripts is expressed as fold change values related to the control ...
... (A) Genomic organization of JR1. Exons are indicated as rectangles. The triangle marks the region of T-DNA insertion. (B) qPCR analysis of JR1 expression in Col-0 or in the JR1 mutant line described in (A). Accumulation of the JR1 transcripts is expressed as fold change values related to the control ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.