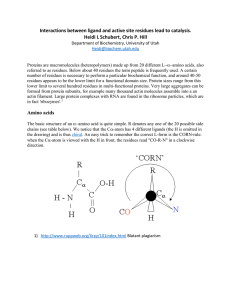
Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides)
... A typical tetrasaccharide linker (blue) connects a glycosamino-glycan—in this case chondroitin 4-sulfate (orange)—to a Ser residue (pink) in the core protein. The xylose residue at the reducing end of the linker is joined by its anomeric carbon to the hydroxyl of the Ser residue. ...
... A typical tetrasaccharide linker (blue) connects a glycosamino-glycan—in this case chondroitin 4-sulfate (orange)—to a Ser residue (pink) in the core protein. The xylose residue at the reducing end of the linker is joined by its anomeric carbon to the hydroxyl of the Ser residue. ...
Proteins pages 8 and 9
... type of protein. The body can make eleven amino acids. The remaining nine have to be obtained from protein in the diet. These are known as essential amino acids. ...
... type of protein. The body can make eleven amino acids. The remaining nine have to be obtained from protein in the diet. These are known as essential amino acids. ...
On the Origin of Language
... • Precursor-product pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
... • Precursor-product pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
Protein and Amino Acid
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
... Proteins are complex molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. All proteins also contain approximately 16% nitrogen. This nitrogen consistency is the basis for the nitrogen balance test which is used to estimate an animal’s body protein status. Amino acids are the basis units of proteins a ...
(size, shape, surface charge, roughness and
... 1. The effect of surface properties (size, shape, surface charge, roughness and porosity) on protein adsorption 2. How the protein adsorption affects the particle properties. Approach • Spectroscopy & computer simulation technique to understand fundamentals of protein adsorption and conformation of ...
... 1. The effect of surface properties (size, shape, surface charge, roughness and porosity) on protein adsorption 2. How the protein adsorption affects the particle properties. Approach • Spectroscopy & computer simulation technique to understand fundamentals of protein adsorption and conformation of ...
Proteins Behaving badly - The University of Oklahoma
... diseases. These aggregates, called amyloid, are believed to be the root cause of disease pathology. Although it was once believed that the insoluble aggregates were the biologically active species, a growing body of data suggests that intermediates along the aggregation pathway, rather than the fina ...
... diseases. These aggregates, called amyloid, are believed to be the root cause of disease pathology. Although it was once believed that the insoluble aggregates were the biologically active species, a growing body of data suggests that intermediates along the aggregation pathway, rather than the fina ...
Word Doc - Biochemistry
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
... Proteins are macromolecules (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different Lamino acids, also referred to as residues. Below about 40 residues the term peptide is frequently used. A certain number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears ...
THE PROTEOME RESPONSE OF LARVAL STAGES OF
... analysis of the eye-spot larvae of statistically similar size at the time of settlement, displayed protein expression pattern and/or phosphorylation levels decreased with increasing OA stress. The differential expressed proteins that are identified in this study are related to energy metabolism, cal ...
... analysis of the eye-spot larvae of statistically similar size at the time of settlement, displayed protein expression pattern and/or phosphorylation levels decreased with increasing OA stress. The differential expressed proteins that are identified in this study are related to energy metabolism, cal ...
The Protein Interaction Prediction Engine (PIPE)
... specific protein-protein interaction prediction profiles. Given a set of target proteins and a set of non-target proteins, InSiPS can generate a protein sequence that is predicted to interact with the target proteins and predicted not to interact with the non-targets. ...
... specific protein-protein interaction prediction profiles. Given a set of target proteins and a set of non-target proteins, InSiPS can generate a protein sequence that is predicted to interact with the target proteins and predicted not to interact with the non-targets. ...
ppt - Scientific Data Analysis Lab
... which lack a fixed tertiary structure, essentially being partially or fully unfolded. Such disordered regions have been shown to be involved in a variety of functions, including DNA recognition, modulation of specificity/affinity of protein binding, molecular threading, activation by cleavage, and c ...
... which lack a fixed tertiary structure, essentially being partially or fully unfolded. Such disordered regions have been shown to be involved in a variety of functions, including DNA recognition, modulation of specificity/affinity of protein binding, molecular threading, activation by cleavage, and c ...
Purified Sp1 protein
... Background: Sp1 (specificity protein 1) is a human transcription factor involved in gene expression in the early development of an organism. The protein is 785 amino acids long, with a molecular weight of 81 kDa. The SP1 transcription factor contains a zinc finger protein motif, by which it binds di ...
... Background: Sp1 (specificity protein 1) is a human transcription factor involved in gene expression in the early development of an organism. The protein is 785 amino acids long, with a molecular weight of 81 kDa. The SP1 transcription factor contains a zinc finger protein motif, by which it binds di ...
The Human Proteome
... proteins along two axis using two physical properties In addition to mass, the isoelectric point can be used (the pH at which a molecule has no charge) ...
... proteins along two axis using two physical properties In addition to mass, the isoelectric point can be used (the pH at which a molecule has no charge) ...
martakmalina proteins
... are formed by hydrogen bonding. Secondary structures are locally defined, meaning that there can be many different secondary motifs present in one single protein molecule. ...
... are formed by hydrogen bonding. Secondary structures are locally defined, meaning that there can be many different secondary motifs present in one single protein molecule. ...
The Essential Need for Protein Chemists
... protein was stored at room temperature and formed detectable aggregates. Consequently, both the formation of aggregates and immunogenicity were reduced upon storage at 4 °C (6). Persistent antibodies were generated in patients treated with natural human growth hormone with formulations containing 50 ...
... protein was stored at room temperature and formed detectable aggregates. Consequently, both the formation of aggregates and immunogenicity were reduced upon storage at 4 °C (6). Persistent antibodies were generated in patients treated with natural human growth hormone with formulations containing 50 ...
PLANT PROTEINS FOR THE FUTURE-English
... Soybean, peanut, common bean, pea, lupins, chickpea, faba bean, lentil grass pea, cowpea, pigeon pea, etc. are currently the most important legumes for human consumption and animal feed. Amaranth and quinoa are considered “pseudocereals” and are also good sources of proteins. Amaranth seeds contain ...
... Soybean, peanut, common bean, pea, lupins, chickpea, faba bean, lentil grass pea, cowpea, pigeon pea, etc. are currently the most important legumes for human consumption and animal feed. Amaranth and quinoa are considered “pseudocereals” and are also good sources of proteins. Amaranth seeds contain ...
Importance of Proteins Test
... 3. Protein molecules are made up of a chain of acids that contain carbon molecules called amino acids. 4. Amino acids can be classified into two groups: Essential and Non-Essential. 5. Foods that contain all eight essential amino acids are called Complete proteins. 6. Foods that are short of one or ...
... 3. Protein molecules are made up of a chain of acids that contain carbon molecules called amino acids. 4. Amino acids can be classified into two groups: Essential and Non-Essential. 5. Foods that contain all eight essential amino acids are called Complete proteins. 6. Foods that are short of one or ...
GenLysate, Mouse Liver Mitochondria Cell Fraction
... 3. Western Re-Probe™ (Cat # 786-119): Western Re-Probe (5X) kit provides buffer for stripping and re-probing western blot membranes. ...
... 3. Western Re-Probe™ (Cat # 786-119): Western Re-Probe (5X) kit provides buffer for stripping and re-probing western blot membranes. ...
Proteins = polymers of 20 amino acids, connected by peptide bonds
... mechanisms of macromolecular structures in biology. You will learn about the physical basis for these structures, their folding, stability, and interactions with other molecules, as well as the structural basis of catalytic mechanisms. You will gain a working knowledge of computer programs for manip ...
... mechanisms of macromolecular structures in biology. You will learn about the physical basis for these structures, their folding, stability, and interactions with other molecules, as well as the structural basis of catalytic mechanisms. You will gain a working knowledge of computer programs for manip ...
Gene Ontology (GO)
... – Protein-DNA/RNA binding (e.g. histones, transcription factors) – Protein-protein interactions (e.g. antibody-lysozyme) (experimentally determined by yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) or bacterial two-hybrid (B2H) screening ) – Protein-fatty acid binding (e.g. apolipoproteins) – Protein – small molecules (dru ...
... – Protein-DNA/RNA binding (e.g. histones, transcription factors) – Protein-protein interactions (e.g. antibody-lysozyme) (experimentally determined by yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) or bacterial two-hybrid (B2H) screening ) – Protein-fatty acid binding (e.g. apolipoproteins) – Protein – small molecules (dru ...
CMSE 520 BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND
... biology is to “decipher” information contained in biological sequences Since the nucleotide sequence of a genome contains all information necessary to produce a functional organism, we should in theory be able to duplicate this decoding using ...
... biology is to “decipher” information contained in biological sequences Since the nucleotide sequence of a genome contains all information necessary to produce a functional organism, we should in theory be able to duplicate this decoding using ...
presentation
... Proteins are first separated across a gel according to their isoelectric point, then separated in a perpendicular direction on the basis of their molecular weight. Electrophoresis in which a second perpendicular electrophoretic transport is performed on the separate components resulting from the fir ...
... Proteins are first separated across a gel according to their isoelectric point, then separated in a perpendicular direction on the basis of their molecular weight. Electrophoresis in which a second perpendicular electrophoretic transport is performed on the separate components resulting from the fir ...
The presentation part I
... Computational methods • Mentioned in this seminar, mainly for understanding proteins’ Functions and using to detect interactions ...
... Computational methods • Mentioned in this seminar, mainly for understanding proteins’ Functions and using to detect interactions ...
Proceedings of a meeting held at Allerton House, Monticello, Illinois
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
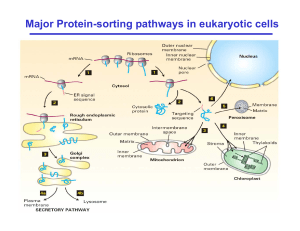
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
Cellular compartmentalization
... SIGNAL SEQUENCES - Proteins are tagged with special sequences (signal sequences - 12 to 60 amino acids long) that are like barcodes. These are read by special courier protein systems within the cytoplasm and then targeted to their destinations. ...
... SIGNAL SEQUENCES - Proteins are tagged with special sequences (signal sequences - 12 to 60 amino acids long) that are like barcodes. These are read by special courier protein systems within the cytoplasm and then targeted to their destinations. ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.