AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... Concept 48.4 Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses ...
... Concept 48.4 Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses ...
Identification of chemical probes for ionotropic glutamate receptors
... Ligand-gated ion channels are cell surface proteins that play an important role in fast synaptic transmission and in the modulation of cellular activity. Glutamate receptor ion channels, in particular, mediate excitatory responses at the majority of CNS synapses and transduce the binding of a glutam ...
... Ligand-gated ion channels are cell surface proteins that play an important role in fast synaptic transmission and in the modulation of cellular activity. Glutamate receptor ion channels, in particular, mediate excitatory responses at the majority of CNS synapses and transduce the binding of a glutam ...
neurons
... (GAT) GABA also found in glia receptor subtypes: ◦ GABA A – ionotropic – clinically important ◦ GABA B - metabotropic ...
... (GAT) GABA also found in glia receptor subtypes: ◦ GABA A – ionotropic – clinically important ◦ GABA B - metabotropic ...
Week 2 Lecture Notes
... Typical LTP experiment: record from cell in hippocampus area CA1 (receives Schaffer collaterals from area CA3). In addition, stimulate two sets of input fibers. ...
... Typical LTP experiment: record from cell in hippocampus area CA1 (receives Schaffer collaterals from area CA3). In addition, stimulate two sets of input fibers. ...
Academic Half-Day Neurophysiology 101
... Metabotropic/G-protein coupled receptors: ligand binds, activates GTP-binding protein which in term activates a channel via phosphorylation. Slower synaptic potentials lasting seconds or minutes Involved in strengthening synaptic connections of basic neural circuitry Role in modulating synapti ...
... Metabotropic/G-protein coupled receptors: ligand binds, activates GTP-binding protein which in term activates a channel via phosphorylation. Slower synaptic potentials lasting seconds or minutes Involved in strengthening synaptic connections of basic neural circuitry Role in modulating synapti ...
Neuroplasticity - University of Michigan–Flint
... • Long-term learning occurs by the reduction or formation of new synapses or structural changes on neurons, e.g. – Habituation: decrease in synapses (C) – Sensitization: increase in synapses (D) ...
... • Long-term learning occurs by the reduction or formation of new synapses or structural changes on neurons, e.g. – Habituation: decrease in synapses (C) – Sensitization: increase in synapses (D) ...
Forty3
... 3. Who/what was superstitious? 4. In the past 30 years there have been at least three congressional hearings on _________ _________. 5. Why would an American travel to Germany to study with Wundt? 6. Name one disorder that Kraeplin studied and described. ...
... 3. Who/what was superstitious? 4. In the past 30 years there have been at least three congressional hearings on _________ _________. 5. Why would an American travel to Germany to study with Wundt? 6. Name one disorder that Kraeplin studied and described. ...
1 - U-System
... 1. NMDA receptors and LTP in learning and memory - long term potentiation LTP; a neuron is given a brief, but rapid series of stimuli leaves neuron potentiated (highly responsive to new input of same type); LTP occurs in hippocampal neurons - LTP depends on activation of NMDA receptors - NMDA re ...
... 1. NMDA receptors and LTP in learning and memory - long term potentiation LTP; a neuron is given a brief, but rapid series of stimuli leaves neuron potentiated (highly responsive to new input of same type); LTP occurs in hippocampal neurons - LTP depends on activation of NMDA receptors - NMDA re ...
Does spike-time dependant plasticity occurs in dorsal horn neurons
... [3,16].Therefore, Wind-up is a long-lasting phenomenon that resembles a potentiation in dorsal horn. Furthermore, the introduction of the gate control theory of pain by Melzack and Wall in 1965 provided a convincing theory about the nature of pain and offered a theoretical basis for the effectivene ...
... [3,16].Therefore, Wind-up is a long-lasting phenomenon that resembles a potentiation in dorsal horn. Furthermore, the introduction of the gate control theory of pain by Melzack and Wall in 1965 provided a convincing theory about the nature of pain and offered a theoretical basis for the effectivene ...
Document
... 13. Capable of generating action potentials propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
... 13. Capable of generating action potentials propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
Doktryna neuronu
... Schaffer Collateral Pathway (SC), as well as to CA1 cells in the contralateral hippocampus via the Associational Commisural (AC) Pathway. CA1 neurons also receive inputs direct from the Perforant Path and send axons to the Subiculum (Sb). These neurons in turn send the main hippocampal output back t ...
... Schaffer Collateral Pathway (SC), as well as to CA1 cells in the contralateral hippocampus via the Associational Commisural (AC) Pathway. CA1 neurons also receive inputs direct from the Perforant Path and send axons to the Subiculum (Sb). These neurons in turn send the main hippocampal output back t ...
1) Propagated electrical signals - UW Canvas
... Ions pass through a gated aqueous pore. The voltage sensor regulates the gate. ...
... Ions pass through a gated aqueous pore. The voltage sensor regulates the gate. ...
Checkpoint Answers
... B. peripheral nervous system. C. peripheral ganglia. D. spinal nerves. 2. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located in the CNS. false 3. Sensory neurons A. are multipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. *B. are pseudounipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. C. are bipolar and carry imp ...
... B. peripheral nervous system. C. peripheral ganglia. D. spinal nerves. 2. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located in the CNS. false 3. Sensory neurons A. are multipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. *B. are pseudounipolar and carry impulses toward the CNS. C. are bipolar and carry imp ...
Synaptic Transmission
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements • mental deterioration ...
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements • mental deterioration ...
Molecular Basis for Induction of Ocular Dominance
... 1998). (The level of NMDA receptor activation must be appropriate, since strong activation induces synaptic potentiation instead.) The inhibition of this LTD induction mechanism may account for why NMDA receptor antagonists prevent deprivation-induced synaptic depression. However, there is now good ...
... 1998). (The level of NMDA receptor activation must be appropriate, since strong activation induces synaptic potentiation instead.) The inhibition of this LTD induction mechanism may account for why NMDA receptor antagonists prevent deprivation-induced synaptic depression. However, there is now good ...
biopsychology-2-synaptic-transmission
... • Can you think of any examples from the biological approach? ...
... • Can you think of any examples from the biological approach? ...
II. Systematic Approach to Biology of Cognition
... strength excited by sustained, low frequency stimulation [9]. These long lasting changes in the synaptic function are hypothesized to provide, at least in part, the cellular basis of learning and memory [8]. Perhaps the best-studied forms of synaptic plasticity are N-methyl-D-asparate (NMDA) recepto ...
... strength excited by sustained, low frequency stimulation [9]. These long lasting changes in the synaptic function are hypothesized to provide, at least in part, the cellular basis of learning and memory [8]. Perhaps the best-studied forms of synaptic plasticity are N-methyl-D-asparate (NMDA) recepto ...
04/16 PPT - Molecular and Cell Biology
... • During learning of a new motor task, subject makes mistakes, but the error reduces with practice • The standard notion is that the “error signal” causes changes in brain circuits involved in motor control (e.g., cerebellum), thus improving motor performance ...
... • During learning of a new motor task, subject makes mistakes, but the error reduces with practice • The standard notion is that the “error signal” causes changes in brain circuits involved in motor control (e.g., cerebellum), thus improving motor performance ...
Module 9: Synaptic Transmission
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
... neurons in the substantia nigra • Symptoms include – difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements – tremors at rest – stooped posture – rigidity – poor balance ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements • mental deterioration ...
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements • mental deterioration ...
The Nervous System
... • Chemical synapse transmision – The neurotransmitter is degraded and recycled. • After the neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane receptors, it is broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft. • Example – Acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase. – Degraded neurotransmitters are ...
... • Chemical synapse transmision – The neurotransmitter is degraded and recycled. • After the neurotransmitter binds to the postsynaptic membrane receptors, it is broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft. • Example – Acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase. – Degraded neurotransmitters are ...
chapt12 neuron_lecture
... – temporal summation occurs when single synapse receives many EPSPs in a short period of time – spatial summation occurs when single synapse receives many EPSPs from many presynaptic cells ...
... – temporal summation occurs when single synapse receives many EPSPs in a short period of time – spatial summation occurs when single synapse receives many EPSPs from many presynaptic cells ...
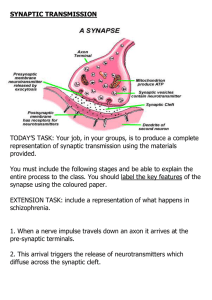
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...