Brains, Synapses and Neurotransmitters
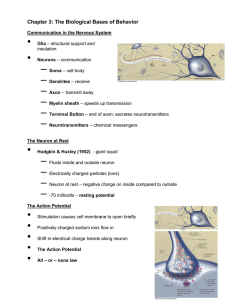
... Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
... Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
Synaptic transmission
... • In most of the areas of brain, norepinephrine probably activates excitatory receptors, but in a few areas, it activates inhibitory receptors instead. Norepinephrine is also secreted by most postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, where it excites some organs but inhibits others. ...
... • In most of the areas of brain, norepinephrine probably activates excitatory receptors, but in a few areas, it activates inhibitory receptors instead. Norepinephrine is also secreted by most postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, where it excites some organs but inhibits others. ...
Uncaging Compunds: - Florida State University
... and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to bind onto receptors on the postsynaptic spine. – 1:1 correspondence between ...
... and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to bind onto receptors on the postsynaptic spine. – 1:1 correspondence between ...
Neural Control II
... chemically-mediated signal may cause cells to lose the ability to respond to it; habituation • When receptor proteins are exposed to high levels of neurotransmitter molecules for prolonged periods, the postsynaptic cell often responds by decreasing the number of receptor proteins in its membrane; ma ...
... chemically-mediated signal may cause cells to lose the ability to respond to it; habituation • When receptor proteins are exposed to high levels of neurotransmitter molecules for prolonged periods, the postsynaptic cell often responds by decreasing the number of receptor proteins in its membrane; ma ...
Neuron_glia interaction
... Diffuses into the ECS. Presynaptic bind and inhibition of its own release. ...
... Diffuses into the ECS. Presynaptic bind and inhibition of its own release. ...
Chemistry of Neurotransmitters
... • They are ligand-gated ion channels. The receptors for stimulatory transmitters mediate the inflow of cations (mainly Na+). When these open after binding of the transmitter, local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane occurs. ...
... • They are ligand-gated ion channels. The receptors for stimulatory transmitters mediate the inflow of cations (mainly Na+). When these open after binding of the transmitter, local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane occurs. ...
The Nervous System
... • Found in the brain • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
... • Found in the brain • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
Learning Objectives
... They are ligand-gated ion channels. The receptors for stimulatory transmitters mediate the inflow of cations (mainly Na+). When these open after binding of the transmitter, local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane occurs. By contrast, inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine) allow Cl ...
... They are ligand-gated ion channels. The receptors for stimulatory transmitters mediate the inflow of cations (mainly Na+). When these open after binding of the transmitter, local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane occurs. By contrast, inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine) allow Cl ...
The basic Hebb rule
... • Models of such intrinsic plasticity show that neurons can be remarkably robust to external perturbations if they adjust their conductances to maintain specified functional characteristics • Intrinsic and synaptic plasticity can interact in interesting ways. For example, shifts in intrinsic excitab ...
... • Models of such intrinsic plasticity show that neurons can be remarkably robust to external perturbations if they adjust their conductances to maintain specified functional characteristics • Intrinsic and synaptic plasticity can interact in interesting ways. For example, shifts in intrinsic excitab ...
Document
... Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters Typically composed of two parts: ...
... Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters Typically composed of two parts: ...
Slide 1
... 2. Allow the simulation of different neuron models 3. Allow the incorporation of new neural features into neuron models without needing to modify the simulator code. 4. Real-time simulation of middle-scale neural networks (thousands of neurons). ...
... 2. Allow the simulation of different neuron models 3. Allow the incorporation of new neural features into neuron models without needing to modify the simulator code. 4. Real-time simulation of middle-scale neural networks (thousands of neurons). ...
Can You Remember My Name? Part 2
... • Short-term plasticities – Facilitation (paired pulse facilitation): 100-200 ms; increased Ca++ increased p(NT release) – Post-tetanic potentiation: 5-10 sec – Depression: hundreds of ms – few minutes; caused by repetitive stimulation causing a decrease in p(NT release). ...
... • Short-term plasticities – Facilitation (paired pulse facilitation): 100-200 ms; increased Ca++ increased p(NT release) – Post-tetanic potentiation: 5-10 sec – Depression: hundreds of ms – few minutes; caused by repetitive stimulation causing a decrease in p(NT release). ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere from five to 15 minutes. But then the drug begins to wear off, leaving the person feeling let-down and depressed, resulting in a desire to smoke mo ...
... such as eating and having sex. But in cocaine users, dopamine keeps stimulating those cells, creating a "high" -- a euphoric feeling that lasts anywhere from five to 15 minutes. But then the drug begins to wear off, leaving the person feeling let-down and depressed, resulting in a desire to smoke mo ...
Threshold Stimulus
... Synaptic Transmission • Neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft toward postsynaptic ...
... Synaptic Transmission • Neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft toward postsynaptic ...
Neurotransmitters & Synapses - IB
... • Which NT diffused? • Which receptors do they bind to? • Which ions flow in/out of the post-synaptic neurone? • Whether or not depolarization reaches threshold ...
... • Which NT diffused? • Which receptors do they bind to? • Which ions flow in/out of the post-synaptic neurone? • Whether or not depolarization reaches threshold ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
... Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
John F. MacDonald 2014 - Canadian Association for Neuroscience
... mammalian central nervous system. These receptors (eventually termed NMDA receptors) were later found to be blocked by magnesium in a voltage-dependent manner, and required for long-term synaptic modifications thought to underlie some forms of learning. By virtue of their voltage-dependence, NMDA re ...
... mammalian central nervous system. These receptors (eventually termed NMDA receptors) were later found to be blocked by magnesium in a voltage-dependent manner, and required for long-term synaptic modifications thought to underlie some forms of learning. By virtue of their voltage-dependence, NMDA re ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... Estimated number of synapses established by parallel fibers on a Purkinje cell Speed of fast anterograde transport ...
... Estimated number of synapses established by parallel fibers on a Purkinje cell Speed of fast anterograde transport ...
Lipids
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 22 of 12 ...
... A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape. There are up to four levels of structure in a protein: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Each of these play an important role in the overall structure and function of the protein. 22 of 12 ...
PNS and Transmission
... Transmission • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and ...
... Transmission • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and ...
Membrane Biophysics and Synaptic Physiology
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...