ppt
... •allows K+ to flow out of the cell or Cl- to flow inside the cell •causing a slight hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell further from firing an action potential ...
... •allows K+ to flow out of the cell or Cl- to flow inside the cell •causing a slight hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell further from firing an action potential ...
fleming_Oct
... dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spinal cord and send their axons to the muscles or glands of the body. ...
... dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spinal cord and send their axons to the muscles or glands of the body. ...
the limbic system
... transduce the glutamate signal into electrical & biochemical events in the postsynaptic neuron. The -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptor opens {unconditionally} in response to glutamate binding and mediates most of the rapid excitatory postsynaptic curre ...
... transduce the glutamate signal into electrical & biochemical events in the postsynaptic neuron. The -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptor opens {unconditionally} in response to glutamate binding and mediates most of the rapid excitatory postsynaptic curre ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... excitatory synapse on another neuron, and the two nerve endings form an axoaxonal synapse. o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory a ...
... excitatory synapse on another neuron, and the two nerve endings form an axoaxonal synapse. o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory a ...
Sample Prelab Assignment - Neurobiology Laboratory
... in the postsynaptic neuron. Depolarization of the presynaptic neuron causes an influx of calcium at the nerve terminal, therefore allowing the release of synaptic vesicles. The transmitters in the vesicles then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. Th ...
... in the postsynaptic neuron. Depolarization of the presynaptic neuron causes an influx of calcium at the nerve terminal, therefore allowing the release of synaptic vesicles. The transmitters in the vesicles then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. Th ...
Excitatory and inhibitory transmission in the superior olivary complex
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
Pull out the stops for plasticity
... synapse as that analysed in the current study9. The activity of various metabotropic receptors, including mGlu1, can increase glutamatemediated responses through this pathway10. It will be interesting to investigate whether the mGlu1-triggered blockade of SK channels identified by Tigaret et al. act ...
... synapse as that analysed in the current study9. The activity of various metabotropic receptors, including mGlu1, can increase glutamatemediated responses through this pathway10. It will be interesting to investigate whether the mGlu1-triggered blockade of SK channels identified by Tigaret et al. act ...
9-18-04 Nervous System Peripheral No1
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
Boardworks Respiration
... The heart pumps blood around the body in the blood vessels. Each time it pumps it causes the blood vessels to throb. This is called a pulse. To take your pulse: 1. Hold out one hand with the palm facing up. 2. Put the index and middle fingers of your other hand together. 3. Press these fingers light ...
... The heart pumps blood around the body in the blood vessels. Each time it pumps it causes the blood vessels to throb. This is called a pulse. To take your pulse: 1. Hold out one hand with the palm facing up. 2. Put the index and middle fingers of your other hand together. 3. Press these fingers light ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... discussed in our recent papers where we addressed it by using a Brownian model for diffusion of glutamate molecules in the synaptic cleft (Di Maio and Ventriglia, 2000; Ventriglia and Di Maio, 2000a, 2000b, 2001). 2. Model and Simulation results The Brownian motion model of synaptic transmission use ...
... discussed in our recent papers where we addressed it by using a Brownian model for diffusion of glutamate molecules in the synaptic cleft (Di Maio and Ventriglia, 2000; Ventriglia and Di Maio, 2000a, 2000b, 2001). 2. Model and Simulation results The Brownian motion model of synaptic transmission use ...
The synapse.
... Advantages of the double-barrel electrode. The preceding slide was a drawing of the electrode tips. Real tips of the two barrels is not likely to be of the same length. The drawing at the right is more likely to occur. What this allows is to record differentially where the longer electrode is intra ...
... Advantages of the double-barrel electrode. The preceding slide was a drawing of the electrode tips. Real tips of the two barrels is not likely to be of the same length. The drawing at the right is more likely to occur. What this allows is to record differentially where the longer electrode is intra ...
Chapter 3 Synapses
... • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs Spatial Summation • Synaptic inputs from separate locations combine their effects on a neuron ...
... • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs Spatial Summation • Synaptic inputs from separate locations combine their effects on a neuron ...
Exam 3 suggested answers
... [Total on this part of the exam was 62, but it is counted as being out of 60, i.e. there were 2 free points.] (1) What general question about visual system plasticity are these experiments designed to answer? [4 points; 1 sentence] Is LTP the cellular mechanism that undelies ocular dominance plastic ...
... [Total on this part of the exam was 62, but it is counted as being out of 60, i.e. there were 2 free points.] (1) What general question about visual system plasticity are these experiments designed to answer? [4 points; 1 sentence] Is LTP the cellular mechanism that undelies ocular dominance plastic ...
Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... • Only 2.5 nm apart • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
... • Only 2.5 nm apart • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
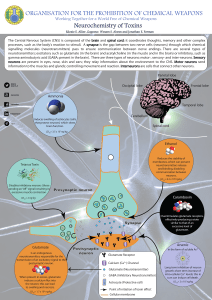
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
The Synapse
... thousands of these messages and integrates this input to bring about only one of two possible outcomes - the neuron stays in a resting state or it generates an action potential to communicate with another neuron. ...
... thousands of these messages and integrates this input to bring about only one of two possible outcomes - the neuron stays in a resting state or it generates an action potential to communicate with another neuron. ...
Part 1: True/False
... 2. __ T The EPSPs in the central nervous system are much smaller than end plate potentials. 3. __ T An IPSP can depolarize or hyperpolarize a cell. 4. __ F All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ F The two main families o ...
... 2. __ T The EPSPs in the central nervous system are much smaller than end plate potentials. 3. __ T An IPSP can depolarize or hyperpolarize a cell. 4. __ F All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ F The two main families o ...
2014 chemical signal..
... -A substance released by one neuron and acting rapidly, briefly and at short range on the membrane of adjacent (postsynaptic) neuron, causing excitation or inhibition. ...
... -A substance released by one neuron and acting rapidly, briefly and at short range on the membrane of adjacent (postsynaptic) neuron, causing excitation or inhibition. ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
Part 1: True/False
... 13. Which of the following is a metabotropic receptor? A. nACh receptor B. AMPA receptor C. NMDA receptor D. muscarinic receptor E. Kinate receptor 14. Which is the strongest piece of evidence that Otto Loewi provided proving that chemical synaptic transmission exists: A. Showing that stimulating th ...
... 13. Which of the following is a metabotropic receptor? A. nACh receptor B. AMPA receptor C. NMDA receptor D. muscarinic receptor E. Kinate receptor 14. Which is the strongest piece of evidence that Otto Loewi provided proving that chemical synaptic transmission exists: A. Showing that stimulating th ...