egypt study guide
... OLD KINGDOM (2750-2260 B.C.) King Menes, the king of upper Egypt, conquered Lower Egypt and united the kingdoms. He became the first pharaoh, made Egypt stronger, and formed the first dynasty. Great pyramids were built for pharaohs (ex. The Step Pyramid for King Zoser). MIDDLE KINGDOM (2061-1784 ...
... OLD KINGDOM (2750-2260 B.C.) King Menes, the king of upper Egypt, conquered Lower Egypt and united the kingdoms. He became the first pharaoh, made Egypt stronger, and formed the first dynasty. Great pyramids were built for pharaohs (ex. The Step Pyramid for King Zoser). MIDDLE KINGDOM (2061-1784 ...
The Middle Kingdom was a period of stable
... vowed that outsiders would never again control any part of Egypt. ...
... vowed that outsiders would never again control any part of Egypt. ...
Chapter 2 section 1 and 2 Test Review (with answers) (Section 1
... What was their system of writing known as? Cuneiform How many laws did Hammurabi have in his code? 282 (Chapter 2 Section 2 material) Delta: land formed by silt deposits at mouth of a river Narmer: Egyptian king that united Upper and Lower Egypt. Pharaoh: Kings of Egypt, considered to be gods by Egy ...
... What was their system of writing known as? Cuneiform How many laws did Hammurabi have in his code? 282 (Chapter 2 Section 2 material) Delta: land formed by silt deposits at mouth of a river Narmer: Egyptian king that united Upper and Lower Egypt. Pharaoh: Kings of Egypt, considered to be gods by Egy ...
Ancient Egypt - TReavis
... What was the main food eaten by Egyptians? What did most Egyptians live in? What was Egyptian language called? What is an Egyptian king called? What was the “afterlife?” Describe the mummification process. Name four contributions of Ancient Egypt. ...
... What was the main food eaten by Egyptians? What did most Egyptians live in? What was Egyptian language called? What is an Egyptian king called? What was the “afterlife?” Describe the mummification process. Name four contributions of Ancient Egypt. ...
Anstey Junior School Long Term Planning Year 4 Awesome Egyptians
... Rationale: The life of the Ancient Egyptians provides an amazing study into a period of Ancient history. Research can be carried out by using second hand sources – including the internet and first hand artefacts. Children will use sources of information and artefacts to follow the six step approach ...
... Rationale: The life of the Ancient Egyptians provides an amazing study into a period of Ancient history. Research can be carried out by using second hand sources – including the internet and first hand artefacts. Children will use sources of information and artefacts to follow the six step approach ...
Name: Date: Social Studies 6 Egypt Study Guide Vocabulary to
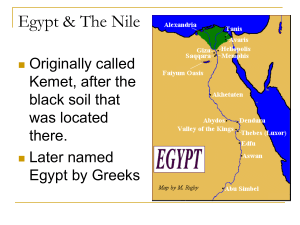
... Nile River valley is the harsh deserts that border the civilization. The Libyan Desert is on the west and to the east of the river is the Western Desert which extends all the way to the Red Sea. Egyptians called this area the “Red Land” because of the scorching heat. These deserts helped keep Egypt ...
... Nile River valley is the harsh deserts that border the civilization. The Libyan Desert is on the west and to the east of the river is the Western Desert which extends all the way to the Red Sea. Egyptians called this area the “Red Land” because of the scorching heat. These deserts helped keep Egypt ...
Ancient Mediterranean Culture- Egypt
... Ancient Egypt The culture of ancient Egypt developed from a network of pastoral and agricultural societies that existed near the Nile River Valley during the 4th and 5th millennia BC. These independent villages and towns were called nomes, or city-states, and were ruled by nomarchs. Around the year ...
... Ancient Egypt The culture of ancient Egypt developed from a network of pastoral and agricultural societies that existed near the Nile River Valley during the 4th and 5th millennia BC. These independent villages and towns were called nomes, or city-states, and were ruled by nomarchs. Around the year ...
Station 1: Explain why Egyptian civilization began in the Nile River
... 1. wild rapids found on the Nile River. CATARACTS ...
... 1. wild rapids found on the Nile River. CATARACTS ...
File - Rowland Social Studies 9
... using pyramids to bury their rulers. They also built new temples to Egyptian gods and restored old temples. The Kushites also worked to preserve Egyptian writings. Kush also used Egyptian as the language of the region, their people used Egyptian names, they wore Egyptian-style clothing, and adapted ...
... using pyramids to bury their rulers. They also built new temples to Egyptian gods and restored old temples. The Kushites also worked to preserve Egyptian writings. Kush also used Egyptian as the language of the region, their people used Egyptian names, they wore Egyptian-style clothing, and adapted ...
Ancient Egypt
... a.) It was believed that cats were able to protect homes and children. 2. Hurting a cat was a serious crime. a.) A person could be sentenced to death for killing a cat. ...
... a.) It was believed that cats were able to protect homes and children. 2. Hurting a cat was a serious crime. a.) A person could be sentenced to death for killing a cat. ...
The Kingdom of Egypt Nile
... • Worshipped only one god called Aten • Changed his name to Akhenaton to honor Aten • Hated by priests and followers of many gods ...
... • Worshipped only one god called Aten • Changed his name to Akhenaton to honor Aten • Hated by priests and followers of many gods ...
Ancient Egypt
... As early as 5000 years ago man began to settle in the Nile valley. Leaders united these early peoples into kingdoms. By 4000 BCE two main kingdoms dominated. Upper- southern Egypt Lower- northern Egypt ...
... As early as 5000 years ago man began to settle in the Nile valley. Leaders united these early peoples into kingdoms. By 4000 BCE two main kingdoms dominated. Upper- southern Egypt Lower- northern Egypt ...
The New Kingdom - Mr Barck`s Classroom
... a. The Old Kingdom fell apart due to weak leadership b. ...
... a. The Old Kingdom fell apart due to weak leadership b. ...
Egypt: Gift of the Nile - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Around 3100 B.C. Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt were united by a king named Menes, kings who followed wore a double crown ...
... Around 3100 B.C. Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt were united by a king named Menes, kings who followed wore a double crown ...
Ancient Egypt : The Old Kingdom
... • Most of Egypt was desert. • The Nile’s floods were easier to predict than flood in Mesopotamia. • The Nile flooded upper Egypt in midsummer and lower Egypt in the fall. • The silt from the Nile made the soil ideal for farming. • Without floods, people never could have settled in Egypt. ...
... • Most of Egypt was desert. • The Nile’s floods were easier to predict than flood in Mesopotamia. • The Nile flooded upper Egypt in midsummer and lower Egypt in the fall. • The silt from the Nile made the soil ideal for farming. • Without floods, people never could have settled in Egypt. ...
Name: Hour:______ Kingdoms Study Guide Use pages 58
... 12. What was the Hebrew kingdom from 1020 to 922BC? 13. When the Hebrew kingdom divided, what was the kingdom in the south known as? 14. What was a tribute? 15. What Asiatic invaders ruled Egypt from 1640-1570 BC? 16. Which Egyptian pharaoh negotiated with the Hittite king in 1285BC? 17. Which kingd ...
... 12. What was the Hebrew kingdom from 1020 to 922BC? 13. When the Hebrew kingdom divided, what was the kingdom in the south known as? 14. What was a tribute? 15. What Asiatic invaders ruled Egypt from 1640-1570 BC? 16. Which Egyptian pharaoh negotiated with the Hittite king in 1285BC? 17. Which kingd ...
WH 3.1 Red Flag Questions
... Who conquered Egypt in 332 BC ending Egypt’s history as an independent kingdom? ...
... Who conquered Egypt in 332 BC ending Egypt’s history as an independent kingdom? ...
The Egyptian and Nubian Empires
... though the Nubians adopted Egyptian ways, they didn’t abandon their cultural identity. In many of these religious and funeral practices, the Nubians blended Egyptian customs with their own traditions. ...
... though the Nubians adopted Egyptian ways, they didn’t abandon their cultural identity. In many of these religious and funeral practices, the Nubians blended Egyptian customs with their own traditions. ...
The Egyptian and Nubian Empires
... though the Nubians adopted Egyptian ways, they didn’t abandon their cultural identity. In many of these religious and funeral practices, the Nubians blended Egyptian customs with their own traditions. ...
... though the Nubians adopted Egyptian ways, they didn’t abandon their cultural identity. In many of these religious and funeral practices, the Nubians blended Egyptian customs with their own traditions. ...
Pharaoh
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
Ancient Egypt Notes 9/5
... • Developed a 365 day calendar to keep track of 2me between floods and seasons. • Developed a system of numbers for coun2ng, adding, and subtrac2ng. – Used geometry to build pyramids and other ...
... • Developed a 365 day calendar to keep track of 2me between floods and seasons. • Developed a system of numbers for coun2ng, adding, and subtrac2ng. – Used geometry to build pyramids and other ...
Egypt Test
... provided. Note there will be two words not used. 1.The period of order and stability that lasted from 2050 BC until about 1750 BC was called the ...
... provided. Note there will be two words not used. 1.The period of order and stability that lasted from 2050 BC until about 1750 BC was called the ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.