Un - KTH
... and the number one cause of death in the world. Many of the cardiac diseases lead to deformations of the geometry of the heart and thereby also to changes in the qualitative and quantitative properties of the blood flow in the heart. Our goal is to apply numerical simulation to study such effects of ...
... and the number one cause of death in the world. Many of the cardiac diseases lead to deformations of the geometry of the heart and thereby also to changes in the qualitative and quantitative properties of the blood flow in the heart. Our goal is to apply numerical simulation to study such effects of ...
important points
... -Horner’s syndrome happens if lesion above T1 -in the cerebellum..granule cells is the only excitatory neurons while all others are inhibitory -trouble going downstairs==Trochlearnerve damage -trigeminal neuralgia—v2+v3 -Glossopharyngeal nerve supplies carotid body and parotid gland -loss of accommo ...
... -Horner’s syndrome happens if lesion above T1 -in the cerebellum..granule cells is the only excitatory neurons while all others are inhibitory -trouble going downstairs==Trochlearnerve damage -trigeminal neuralgia—v2+v3 -Glossopharyngeal nerve supplies carotid body and parotid gland -loss of accommo ...
Cardiac Tamponade - Jefferson EM Ultrasound
... Can be loculated (post-Cardiac surgery patients) ...
... Can be loculated (post-Cardiac surgery patients) ...
NOTES: Normal Heart - Children`s Heart Clinic
... arise from the ascending aorta. There is a single truncal valve with two, three, or four leaflets and is often incompetent, resulting in regurgitation (backflow of blood). A large perimembranous ventricular septal defect (VSD) is present directly below the truncus in all cases. This allows for mixin ...
... arise from the ascending aorta. There is a single truncal valve with two, three, or four leaflets and is often incompetent, resulting in regurgitation (backflow of blood). A large perimembranous ventricular septal defect (VSD) is present directly below the truncus in all cases. This allows for mixin ...
Unit Four (4.1.1) ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the structures
... An anatomical cavity or passage; especially a chamber of the heart that receives blood from the veins and forces it into a ventricle or ventricles. The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed o ...
... An anatomical cavity or passage; especially a chamber of the heart that receives blood from the veins and forces it into a ventricle or ventricles. The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed o ...
Heart Anatomy - Dr. M`s Class
... – Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary arteries ...
... – Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary arteries ...
Marfan-HOCM Fact Sheet
... young athletes. In order to provide you more information on these conditions and their possible effects, we have prepared the following descriptions. Marfan Syndrome Marfan syndrome is a disease that affects the connective tissue. Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue in the body and is a vi ...
... young athletes. In order to provide you more information on these conditions and their possible effects, we have prepared the following descriptions. Marfan Syndrome Marfan syndrome is a disease that affects the connective tissue. Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue in the body and is a vi ...
Airgas template - Morgan Community College
... How will each of these factors affect arteriole size and peripheral resistance? Lactic acid • Low PO2 Cold • Histamine Endothelin • Heat NO • Adenosine ...
... How will each of these factors affect arteriole size and peripheral resistance? Lactic acid • Low PO2 Cold • Histamine Endothelin • Heat NO • Adenosine ...
Med Prep final review guide File
... a. superior and inferior vena cavea b. pulmonary trunk c. aorta d. pulmonary veins e. pulmonary arteries ____ 32. Which one of the following blood vessels carries oxygenated blood: a. superior vena cava b. inferior vena cava c. coronary sinus d. pulmonary artery e. pulmonary vein ____ 33. Which valv ...
... a. superior and inferior vena cavea b. pulmonary trunk c. aorta d. pulmonary veins e. pulmonary arteries ____ 32. Which one of the following blood vessels carries oxygenated blood: a. superior vena cava b. inferior vena cava c. coronary sinus d. pulmonary artery e. pulmonary vein ____ 33. Which valv ...
Structures of the Heart - California Health Information Association
... the two layers, serous fluid, known as pericardial fluid, lubricates and helps the heart move fluidly when beating. The heart wall is made up of three tissue layers: the epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium. The epicardium, which is the outermost layer, is also known as the visceral peric ...
... the two layers, serous fluid, known as pericardial fluid, lubricates and helps the heart move fluidly when beating. The heart wall is made up of three tissue layers: the epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium. The epicardium, which is the outermost layer, is also known as the visceral peric ...
Heart
... Na+ constantly leaks into the cells, decreasing the voltage until threshold voltage is reached Thereafter: contraction similar to what we discussed for skeletal muscle: Action potential moves along sarcolemma and into the cell through transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum ...
... Na+ constantly leaks into the cells, decreasing the voltage until threshold voltage is reached Thereafter: contraction similar to what we discussed for skeletal muscle: Action potential moves along sarcolemma and into the cell through transverse tubules Sarcoplasmic reticulum ...
Circulatory System
... blood to heart from upper portions of body. • Inferior vena cava: brings oxygen-poor blood to heart from lower portions of body • Right and left pulmonary arteries: brings oxygen-poor blood from heart to lungs • Right and left pulmonary veins: brings oxygenated blood from lungs back to heart ...
... blood to heart from upper portions of body. • Inferior vena cava: brings oxygen-poor blood to heart from lower portions of body • Right and left pulmonary arteries: brings oxygen-poor blood from heart to lungs • Right and left pulmonary veins: brings oxygenated blood from lungs back to heart ...
Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah The Heartbeat
... lipoproteins to evaluate atherosclerotic disease. 3] Serum electrolyte: Na : ↓ Na : hyponatremia. ...
... lipoproteins to evaluate atherosclerotic disease. 3] Serum electrolyte: Na : ↓ Na : hyponatremia. ...
Lecture #1 - Jewish Hospital Cardiothoracic Surgical Research
... (a) Phase I (D – Diastolic Filling) - blood passively fills from atrium into ventricle, followed by additional volume due to atrial contraction. Characteristics: mitral/tricuspid valve open and aortic/pulmonic valve closed, low pressure changes, high volume changes. (b) Phase II (IC - Isovolumic Con ...
... (a) Phase I (D – Diastolic Filling) - blood passively fills from atrium into ventricle, followed by additional volume due to atrial contraction. Characteristics: mitral/tricuspid valve open and aortic/pulmonic valve closed, low pressure changes, high volume changes. (b) Phase II (IC - Isovolumic Con ...
Right Atrium
... Thank you for completing this lesson on the Cardiovascular System. Please complete the evaluation form you have been provided. ...
... Thank you for completing this lesson on the Cardiovascular System. Please complete the evaluation form you have been provided. ...
Ventricular systole
... signal from the heart's upper to lower chambers is impaired or doesn't transmit. ...
... signal from the heart's upper to lower chambers is impaired or doesn't transmit. ...
File
... • Tricuspid & bicuspid valves forced closed due to an increase in ventricular pressure. • Ventricles contract to force blood from the heart. • Pulmonary & aortic semi-lunar valves are open. ...
... • Tricuspid & bicuspid valves forced closed due to an increase in ventricular pressure. • Ventricles contract to force blood from the heart. • Pulmonary & aortic semi-lunar valves are open. ...
Introduction: Basic Anatomy of the Heart
... flow of blood through the heart? Start with the right atrium. List all the major structures along the way (chambers, valves, and vessels). Refer to the diagram on page 602. Example: Rt. atrium > ? valve> ? (chamber) > ? valve up the pulmonary trunk which divides into the > ? arteries (which send the ...
... flow of blood through the heart? Start with the right atrium. List all the major structures along the way (chambers, valves, and vessels). Refer to the diagram on page 602. Example: Rt. atrium > ? valve> ? (chamber) > ? valve up the pulmonary trunk which divides into the > ? arteries (which send the ...
The heart
... beats/minute. During rest and sleep, the heart may beat less than 60 beats/minute but usually does not fall below 50 beats/minute. 2. Tachycardia refers to a heart rate over 100 beats/minute. 3. Sinus arrhythmia is a regular variation in heart rate due to changes in the rate and depth of breathing. ...
... beats/minute. During rest and sleep, the heart may beat less than 60 beats/minute but usually does not fall below 50 beats/minute. 2. Tachycardia refers to a heart rate over 100 beats/minute. 3. Sinus arrhythmia is a regular variation in heart rate due to changes in the rate and depth of breathing. ...
Infective Endocarditis
... leads II, III, aVF, and V2 to V6. There is also subtle PR segment deviation (positive in aVR, negative in most other leads). ST segment elevation is due to a ventricular current of injury associated with epicardial inflammation; similarly, the PR segment changes are due to an atrial current of injur ...
... leads II, III, aVF, and V2 to V6. There is also subtle PR segment deviation (positive in aVR, negative in most other leads). ST segment elevation is due to a ventricular current of injury associated with epicardial inflammation; similarly, the PR segment changes are due to an atrial current of injur ...
click - Uplift North Hills Prep
... 3. Identify the major blood vessels that leave the heart. Stick a probe or your finger through each vessel to determine from which chamber it leaves or enters. You may want to place marked pencils in each vessel to indicate which is which. a. Superior vena cava – Turn the heart so that its posterio ...
... 3. Identify the major blood vessels that leave the heart. Stick a probe or your finger through each vessel to determine from which chamber it leaves or enters. You may want to place marked pencils in each vessel to indicate which is which. a. Superior vena cava – Turn the heart so that its posterio ...
The RESPIRATORY System
... chest pain radiating to the neck, jaw, abdomen, shoulder or left arm – Nausea – Vomiting – Difficulty breathing – Anxiety or fear ...
... chest pain radiating to the neck, jaw, abdomen, shoulder or left arm – Nausea – Vomiting – Difficulty breathing – Anxiety or fear ...
1439573491-2 Heart anatomy
... Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta Thicker myocardium due to greater work load Pulmonary circulation supplied by right ventricle is a much low pressure system requiring less energy output by ventricle Systemic circulation supplied by le ...
... Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta Thicker myocardium due to greater work load Pulmonary circulation supplied by right ventricle is a much low pressure system requiring less energy output by ventricle Systemic circulation supplied by le ...
Slide ()
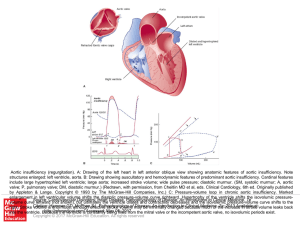
... Aortic insufficiency (regurgitation). A: Drawing of the left heart in left anterior oblique view showing anatomic features of aortic insufficiency. Note structures enlarged: left ventricle, aorta. B: Drawing showing auscultatory and hemodynamic features of predominant aortic insufficiency. Cardinal ...
... Aortic insufficiency (regurgitation). A: Drawing of the left heart in left anterior oblique view showing anatomic features of aortic insufficiency. Note structures enlarged: left ventricle, aorta. B: Drawing showing auscultatory and hemodynamic features of predominant aortic insufficiency. Cardinal ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.