* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Med Prep final review guide File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
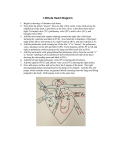
Final Exam Med Prep Spring 2015 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1-6 Label the above diagram with correct cavity or term. Multiple Choice 7.Groups of cells that have a common function are termed __________. a. system c. organ b. tissues d. cavity 8.The heart and blood vessels are the primary organs of the __________ system. a. circulatory c. digestive b. respiratory d. reproductive 9.The body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions is referred to as __________. a. metabolism c. homeostasis b. mechanical control d. physiology 10.The right and left iliac (inguinal) regions are lateral to the __________ region. a. hypogastic c. hypochondriac b. epigastric d. umbilical 11.The cranial and spinal cavities are subdivisions of the __________ cavity. a. cranial c. vental b. frontal d. dorsal 12.The abdominopelvic cavity has __________ quadrants and __________ regions. a. 4, 9 c. 9, 4 b. 4, 6 d. 4, 4 In the space provided give the meaning for the following terms: 13.hypoglycemia ____________________ H 14.gastroenteritis____________________ 15.bradycardia______________________ 17.hydrophobia_____________________ 18.cyanosis________________________ 24.intercostal______________________ 27.tachycardia_____________________ 29. The study of the function of the body and body parts is called: a. anatomy b. physiology c. homeostasis d. negative feedback 30. a. b. c. d. Hematopoiesis, or blood cell formation, is a function of the: muscular system respiratory system skeletal system nervous system 31.Which system covers the external surface of the body and protects deeper tissues: a. endocrine system b. integumentary system c. nervous system d. lymphatic system 34.When correctly situated in anatomical position, where are your feet in relation to your knees: a. proximal b. medial c. superior d. distal e Deep a. 35.Which of the following orientation terms have opposite meanings (in humans): a. superficial and proximal b. distal and proximal c. medial and distal d. medial and anterior 37.The lungs and heart are situated in the _____ body cavity. a. dorsal b. spinal c. thoracic d. cranial e. abdominopelvic 38.A section that divides the body on the longitudinal plane into equal right and left parts is called: a. median (midsagittal) b. frontal c. transverse d. oblique e. coronal 39.Which set of regions in the abdominopelvic cavity is medial: a. umbilical, right lumbar, and left lumbar regions b. epigastric, umbilical, and hypogastric regions c. iliac (inguinal), lumbar, and hypogastric regions d. epigastric, right, and left hypochondriac regions e. right and left iliac (inguinal), and hypogastric regions 40.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the location of the stomach: a. the stomach is located in the left upper quadrant b. the stomach is located in the right upper quadrant c. the stomach is located medially d. the stomach is located in the left lower quadrant e. the stomach is located in the right lower quadrant 21. "Goosebumps" are caused by contractions of the ______________ ____________ muscles. 22. The type of burn that involves injury to the epidermis and the upper region of the dermis and is red, blistered, and painful is termed as a __________-degree burn. 25. The letters in the ABCD rule for recognizing melanomas stand for _____________ ____________ _____________ _______________. 30. The skin and its derivatives (nails, glands, and hairs) form the: A) skeletal system B) integumentary system C) endocrine system D) immune system E) lymphatic system 34. The "tanning" effect (darkening of the skin) that occurs when a person is exposed to the sun is due to: A) melanin B) keratin C) oil D) Langerhans cells E) sweat 38. Which of the following abnormal skin colors results from liver disorders: A) cyanosis B) pallor C) erythema D) jaundice E) bruising 1. The proximal epiphysis is represented by letter __________. 2. The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter __________. 3. The area that serves as a storage area for fat in adults is indicated by letter __________. 4. The diaphysis is indicated by letter __________. 5. The periosteum, a connective tissue covering on the diaphysis, is represented by letter __________. 6. The area that contains glassy hyaline cartilage that provides a smooth slippery surface which decreases friction is indicated by letter __________. 7. Yellow marrow is a storage area for __________. 10.The skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage form the __________ skeleton. 11. The thigh bone is called the __________. Using Figure 5.2, identify the following: 14. The frontal bone is indicated by letter __________. 15. The femur is indicated by letter __________. 16. The tibia is indicated by letter __________. 17. The sternum is indicated by letter __________. 18. The radius bone is indicated by letter __________. 19. The mandible is indicated by letter __________. 20. The carpals indicated by letter __________. 21. The ilium, pubis, and ischium fuse to form the bone marked by letter __________. 24.The femur, tibia, humerus, and radius are all classified as: a. compact bones b. irregular bones c. flat bones d. long bones e. sesamoid bones ____ 33. Which two bones constitute the forearm: a. radius and humerus b. humerus and scapula c. fibula and tibia d. ulna and radius e. femur and fibula 41.Explain the five functions of the skeletal system. (10pts) 8. The bulk of the tissue of a muscle tends to lie (proximal or distal) to the part of the body it causes to move. 9. Contractions in which muscles do not produce movement or shortening are termed __________. 10. The movement that is commonly seen in a ball-in-socket joint, that includes a combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, is called __________. 11. Muscles that perform opposite actions to one another are termed __________. 12. the __________. 13. The muscle referred to as the "smiling" muscle because it raised the corners of the mouth upward is The muscle that raises you eyebrows is_________________. 15.Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d. cardiac muscle e. dense irregular 18.Which of the following is NOT a function of the muscular system: a. production of movement b. maintenance of posture c. stabilization of joints d. generation of heat e. hematopoiesis ____ 19. Isometric contractions produce: a. contractions b. movement c. muscle shortening d. contractions and movement, but not shortening e. contractions and shortening, but not movement ____ 20. The movement opposite to abduction is: a. flexion b. rotation c. circumduction d. adduction e. supination ____ 21. Which of the following muscles closes the jaw: a. buccinator b. zygomaticus c. frontalis d. sternocleidomastoid e. both masseter and temporalis 23.What is the main function of the quadriceps femoris group a. arm flexion b. hand supination c. thigh abduction d. knee extension e. foot inversion 26. While doing "jumping jacks" during an exercise class, your arms and legs move laterally away from the midline of your body. This motion is called: a. extension b. flexion c. abduction d. adduction e. circumduction ____ 27. Which of the following muscles are antagonists: a. biceps brachii and triceps brachii b. bicpes femoris and biceps brachii c. vastus medialis and vastus lateralis d. masseter and temporalis e. gastrocnemius and soleus Match the following: a. pronation b. rotation c. dorsiflexion d. flexion e. adduction f. circumduction g. abduction h. supination i. extension ____ 41. Type of movement that decreases the angle of the joint ____ 42. Type of movement that results when the forearm rotates laterally so that the palm faces anteriorly ____ 43. The movement of a limb toward the body midline ____ 44. Type of movement that increases the angle of the joint ____ 45. The movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis ____ 46. The movement of a limb away from the body midline ____ 47. Type of movement that results when the forearm rotates medially so the palm faces posteriorly 49.What types of movements are demonstrated by your feet and ankles when you drive a car? Describe these movements. 26.Pulmonary circulation involves blood flow to and from the heart and the: a. body b. digestive organs c. skin d. lungs e. brain 27.The right AV valve is known as the: a. aortic semilunar valve b. tricuspid valve c. mitral valve d. pulmonary semilunar valve e. bicuspid valve ____ 28. Pulmonary veins: a. transport oxygenated blood to the lungs b. transport blood rich in carbon dioxide to the lungs c. transport oxygenated blood to the heart d. split off the pulmonary trunk e. return blood to the right atrium of the heart ____ 29. When the ventricles contract, the bicuspid (mitral) valve prevents blood from flowing from the: a. right ventricle to the right atrium b. left ventricle to the left atrium c. left atrium to the right atrium d. right atrium to the left atrium e. left ventricle to the right ventricle ____ 30. The tricuspid valve is located between the: a. right atrium and left atrium b. right atrium and right ventricle c. left ventricle and pulmonary artery d. left ventricle and aorta e. right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk ____ 31. Deoxygenated blood is returned to the right side of the heart by the: a. superior and inferior vena cavea b. pulmonary trunk c. aorta d. pulmonary veins e. pulmonary arteries ____ 32. Which one of the following blood vessels carries oxygenated blood: a. superior vena cava b. inferior vena cava c. coronary sinus d. pulmonary artery e. pulmonary vein ____ 33. Which valve guards the base of the aorta and opens when the ventricles are contracting: a. mitral valve b. aortic semilunar valve c. bicuspid valve d. pulmonary semilunar valve e. tricuspid valve ____ 34. The sinoatrial node is located in the: a. aorta b. right atrium c. left atrium d. right ventricle e. interventricular septum Veins: a. b. c. d. e. carry blood away from the heart branch into smaller vessels called arterioles transport oxygen-rich blood operate under high pressure often have valves to prevent the backflow of blood ____ 38. Which of the following vessels has the lowest blood pressure: a. veins b. capillaries c. venae cavae d. arteries e. arterioles ____ 39. Coronary heart disease results from: a. persistent parasympathetic nervous system stimulation of the heart b. the accumulation of fatty substances within blood vessels c. temporary loss of oxygen to the heart d. incompetent venous valves e. scar tissue in the myocardium of the heart from repeated myocardial infarctions Matching Match the following: a. right ventricle b. left atrium c. right atrium d. left ventricle ____ 40. Heart chamber with the thickest wall ____ 41. Inferior discharging chamber on the left side of the heart ____ 42. Heart chamber that pumps blood to the pulmonary trunk ____ 43. Heart chamber that contains the sinoatrial node ____ 44. Roof of this chamber contains the bicuspid valve ____ 45. The coronary sinus empties blood from cardiac circulation into this chamber ____ 46. The four pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to this chamber ____ 47. This chamber sends blood into the aorta Color the heart diagram red or blue depending on whether the vessel or chamber is filled with oxygenated or unoxygenated blood