* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah The Heartbeat
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
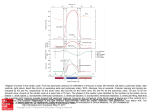
Chapter 26 Assessment of Cardiovascular Function Medical Surgical- Part B By Dr. Yousef Aljeesh Associated Professor Islamic University Dr. Motasem Salah PhD Nursing Administration Palestinian College 1 Objectives: On completion of this chapter, the learner will be able to: 1. Explain cardiac physiology in relation to cardiac anatomy and the conduction system of the heart. 2. Incorporate assessment of functional health patterns and cardiac risk factors into the health. 3. Identify the clinical significance and related nursing implications of the various tests and procedures used for diagnostic assessment of cardiac function. 4. Compare central venous pressure monitoring, pulmonary artery pressure monitoring, and systemic intra-arterial monitoring Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 2 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Three layers of the heart Four chambers Heart valves Coronary arteries Cardiac conduction system Diagnostic test Hemodynamic monitoring Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 3 The Heart The heart is a cone-shaped, muscular organ located between the lungs behind the sternum. The heart muscle forms the myocardium, the inner lining of the myocardium is called Endocardium and the outer layer cells is called the Epicardium. The pericardium (visceral) is the outer membranous sac with lubricating fluid. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 4 The heart has four chambers: two upper, thin- walled atria, and two lower, thick-walled ventricles. The ventricle are, the chambers that eject blood in to arteries. The functions of the atrium are to receive the incoming blood from the vein. The septum is a wall dividing the right and left sides. Coronary arteries: the vessels that supply blood to theDr.Yoused heartAljeesh muscle. Dr. Motasem Salah 5 Structure of the Heart Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 6 Cardiac Valves: Cardiac valves permit blood to flow in only one directions through I. Atrioventricular Valves: 1] Tricuspid valve: separates the Rt atrium from the Rt ventricle 2] Bicuspid valve [Mitral valve]: lies Lt atrium and Lt ventricle. II. Semilunar valves: 1] Pulmonic valve: the valve between the Rt ventricle and the pulmonary artery. 2] Aortic valve: the valve between the Lt ventricle and the aorta. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 7 Internal view of the heart Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 8 The Heartbeat Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. When the heart beats occur, the two atria contract together, then the two ventricles contract; then the whole heart relaxes. Systole is the contraction of heart chambers; diastole is their relaxation. The heart sounds, lub-dup, are due to the closing of the atrioventricular valves, followed by the closing of the semilunar valves. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 9 Conducting system of the heart Intrinsic Control of Heartbeat The SA (sinoatrial) node, or pacemaker, initiates the heartbeat approximately 60-100 impulses/min. The AV (atrioventricular) node conveys the stimulus and initiates contraction of the ventricles, located right Atrial wall, similar to S.A node but with impulses about 40-60/ min.. The signal for the ventricles to contract travels from the AV node through the atrioventricular bundle to the smaller Purkinje fibers. Purkinje fiber: heart muscle fibers that help carry the electrical signals that control heart contraction. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 10 Conduction system of the heart Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 11 Cardiac Conduction System Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 12 Extrinsic Control of Heartbeat A cardiac control center in the medulla oblongata speeds up or slows down the heart rate by way of the autonomic nervous system branches: parasympathetic system (slows heart rate) and the sympathetic system (increases heart rate). Hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla also stimulate faster heart rate. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 13 The Pulmonary Circuit The pulmonary circuit begins with the pulmonary trunk from the right ventricle which branches into two pulmonary arteries that take oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. In the lungs, oxygen diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood to be expelled by the lungs. Four pulmonary veins return oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 14 The Systemic Circuit The systemic circuit starts with the aorta carrying O2-rich blood from the left ventricle. The aorta branches with an artery going to each specific organ. The vein that takes blood to the vena cava often has the same name as the artery that delivered blood to the organ. Note: Stroke volume: the amount of blood ejected per heart beat. (Cardiac output) CO = SV X HR Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 15 Passage of Blood Through the Heart Blood follows this sequence through the heart: superior and inferior vena cava → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary semilunar valve → pulmonary trunk and arteries to the lungs → pulmonary veins leaving the lungs → left atrium → bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aortic semilunar valve → aorta → to the body. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 16 External heart anatomy Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 17 Diagnostic Test 1] Cardiac enzyme: CK & CK-MB: (Creatinine kinase 50-350) CK and in its isoenzyme CKMB are most specific enzymes analyzed in acute MI, and they are the first enzyme levels to increase (enzymes are released from injured cell when the cell membrane rupture). Note: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-BB (brain tissue), CK-MB (heart muscle). LDH: lactic dehydrogenase (analyzed only in select patients who have delayed seeking medical attention, because the blood levels of these substances peak in 2 to 3 days). 100-135 Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 18 Diagnostic Test SGOT: Serum glutamic oxalocetic transminase , found in heart, liver & muscle (0-40). Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 19 2] Lipid profile: Total cholesterol, Triglycerides and lipoproteins to evaluate atherosclerotic disease. 3] Serum electrolyte: Na : ↓ Na : hyponatremia. ↑ Na : hypernatremia. Ca: ↑ Ca : causes ECG changes or dysrhythmias K: ↓ K cause cardiac irritability. Glucose: many cardiac patients also have serum glucose level will ↑ with stress. 4] Chest x-ray: Usually used to determine size and position of the heart. E.g CHF, placement of cardiac catheters. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 20 5] Angiography: x-ray examination of blood vessels. 6] Echocardiography: Non invasive procedure ultrasound test used to examine the size + shape, useful in diagnosis of the heart murmur (turbulent flow of blood + the cause is narrowed valve, which allow regurgitation blood flow, can be heard at the apex or chest). Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 21 7. Cardiac Catheterization Invasive procedure used to measure cardiac chamber pressures and assess patency of the coronary arteries Requires ECG and hemodynamic monitoring; emergency equipment must be available Assessment prior to test; allergies, blood work Assessment of patient after procedure: circulation, potential for bleeding, potential for dysrhythmias Activity restrictions Patient education before & Dr.Yoused Aljeesh after procedure Dr. Motasem Salah 22 Rt heart catheterization: Involve passing a catheter from femoral vein- Rt atrium → Rt .ventricular → tricuspid valve. Lt heart catheterization: The same but passing a catheter through femoral artery. Cardiac catheterization Pre – operative : 1- fasting 8-12 hrs. Post – operative : 1- observe puncture sites, hematoma, peripheral pulses, every 15 minutes for 1 hr. then every 1-2 hrs until stable. 2- color of exterimities, pain, numbness. 3- observe cardiac monitor for dysrhythmias 4- nausea + vomiting , ↓ Bp. 5- supine position 2 head 30 degrees with leg straight. Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 23 6- analgesic medication, and report any chest pain. Hemodynamic Monitoring CVP Intra-arterial BP monitoring Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 24 Arterial Pressure Monitoring System Dr.Yoused Aljeesh Dr. Motasem Salah 25