* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marfan-HOCM Fact Sheet
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Williams syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
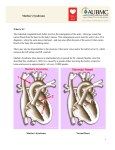
Information Sheet Marfan Syndrome and Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Blessing Hospital, Heart and Vascular Center will be providing free cardiac ultrasounds to children of Blessing Associates to look for two rare diseases - Marfan syndrome and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy - which are particularly important to detect early in young athletes. In order to provide you more information on these conditions and their possible effects, we have prepared the following descriptions. Marfan Syndrome Marfan syndrome is a disease that affects the connective tissue. Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue in the body and is a vital component to supporting the body's organs. For people with Marfan syndrome, the chemical makeup of the connective tissue isn't normal and as a result is not as strong as it should be. In the heart, the valves and/or main artery attached to the heart can be affected by Marfan syndrome. The valve leaflets become floppy and do not close tightly, allowing blood to leak backwards across the valve. The aorta may become enlarged and could rupture. An echocardiogram can detect changes in the heart. Marfan syndrome is rare, affecting 1 person in 20,000. For more information on Marfan syndrome, visit the National Marfan Foundation’s website at www.marfan.org. Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) is a form of cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle) involving enlargement and thickening of the heart muscle. This enlargement interferes with the function of the heart. This disease is also rare, affecting 1 or 2 in 1,000. In this condition, heart muscle becomes too thick to function properly. It may interfere with the functioning of the heart by reducing the size of the ventricular chamber, and may also reduce the ability of the valves to work properly. The enlargement may, in some circumstances, obstruct the flow of blood out of the heart. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of the disease, but HOCM may be diagnosed in people of all ages. HOCM is also the most common cause of sudden death in American athletes. For more information on HOCM, you can visit the website of the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Association at www.4hcm.org. Again, these diseases are rare, but we feel it is important to screen for and detect them early in young athletes in order to treat them appropriately.