VOLCANOES
... relative to the surrounding rocks causes it to rise. It will rise to the surface or to a depth that is determined by the density of the magma and the weight of the rocks above it. As the magma rises, bubbles start to form from the gas dissolved in the magma. The gas bubbles exert ...
... relative to the surrounding rocks causes it to rise. It will rise to the surface or to a depth that is determined by the density of the magma and the weight of the rocks above it. As the magma rises, bubbles start to form from the gas dissolved in the magma. The gas bubbles exert ...
ROCKS and how to identify them
... Volcanic in origin Cooling may be so rapid that glass is produced (Obsidian) ...
... Volcanic in origin Cooling may be so rapid that glass is produced (Obsidian) ...
LAVA FLOW—A SILENT VOLCANIC HAZARD IN HAWAII Thursday
... Thursday, October 30, to provide security to the Big Island community that was being threatened by the slow-moving river of molten lava creeping slowly towards the town's center. ...
... Thursday, October 30, to provide security to the Big Island community that was being threatened by the slow-moving river of molten lava creeping slowly towards the town's center. ...
Y10Ge U1B4 Hazards Nov 19 PP
... rocks are fresh the minerals are not available to plants. The rocks need thousands of years to become weathered and broken down before they form rich soils. When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. Places such as the African Rift Valley, Mt Elgon in Uganda, ...
... rocks are fresh the minerals are not available to plants. The rocks need thousands of years to become weathered and broken down before they form rich soils. When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. Places such as the African Rift Valley, Mt Elgon in Uganda, ...
Cascades?
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
WERE THE MONTEREGIAN HILLS VOLCANOES
... of volcanic activity is the explosive venting of gases to the surface as represented by the diatremes in the Montreal area. Petrographic, structural and other evidence suggests that the intrusive magmas themselves never reached the surface as volcanos or lava flows. Contrary to some popular notions, ...
... of volcanic activity is the explosive venting of gases to the surface as represented by the diatremes in the Montreal area. Petrographic, structural and other evidence suggests that the intrusive magmas themselves never reached the surface as volcanos or lava flows. Contrary to some popular notions, ...
Chapter 12 Section 4
... What is the most common volcanic gas? Water vapor What other gases can be expected? Carbon dioxide and sulfur compounds All of gasses that are expelled are super heated!! Evidence has shown that volcanoes contribute enough greenhouse gas to affect climate long after the eruption has ended! ...
... What is the most common volcanic gas? Water vapor What other gases can be expected? Carbon dioxide and sulfur compounds All of gasses that are expelled are super heated!! Evidence has shown that volcanoes contribute enough greenhouse gas to affect climate long after the eruption has ended! ...
Science 7 Definitions Topic 2
... The process by which sedimentary rock is formed from sediment, through the weight and pressure of water and other sediment. A type of rock made when high pressure and heat act on another type of rock and change it into a new form. Original rock that was acted on by high pressure and heat to form a ...
... The process by which sedimentary rock is formed from sediment, through the weight and pressure of water and other sediment. A type of rock made when high pressure and heat act on another type of rock and change it into a new form. Original rock that was acted on by high pressure and heat to form a ...
Assignment #22A - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... leaving holes = vesicles = cavities in extrusive rocks due to trapped gases when material cooled pumice = very viscous lava, lava churned into a ‘froth’ (like froth on top of soft drink when poured), cooled quickly, lots of air space in rock material, floats on water volcanic ‘bombs’ and ‘blocks’ = ...
... leaving holes = vesicles = cavities in extrusive rocks due to trapped gases when material cooled pumice = very viscous lava, lava churned into a ‘froth’ (like froth on top of soft drink when poured), cooled quickly, lots of air space in rock material, floats on water volcanic ‘bombs’ and ‘blocks’ = ...
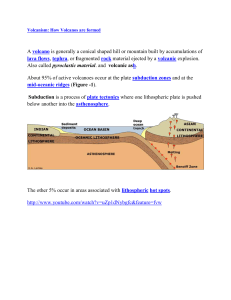
A volcano is generally a conical shaped hill or mountain built by
... occur along plate boundaries are the result of localized asthenosphere hot spots that melt through the Earth's crust. The Hawaiian Island chain of volcanoes was create by a hot spot. ...
... occur along plate boundaries are the result of localized asthenosphere hot spots that melt through the Earth's crust. The Hawaiian Island chain of volcanoes was create by a hot spot. ...
Monitoring Methods
... seismic, deformation and geochemistry. Worldwide, almost all monitored volcanoes have some kind of seismic monitoring system and it is usually the first technique applied when scientists begin to monitor a volcano. Ground Deformation — One of the key techniques used in volcano surveillance is monito ...
... seismic, deformation and geochemistry. Worldwide, almost all monitored volcanoes have some kind of seismic monitoring system and it is usually the first technique applied when scientists begin to monitor a volcano. Ground Deformation — One of the key techniques used in volcano surveillance is monito ...
File
... On August 24, 79AD Mount Vesuvius literally blew its top, erupting tons of molten ash, rocks, pumice and sulfuric gas miles into the atmosphere and it continued about 19 hours. Mt. Vesuvius is a composite type of volcano, which is formed by alternating layers of lava and rock fragments ...
... On August 24, 79AD Mount Vesuvius literally blew its top, erupting tons of molten ash, rocks, pumice and sulfuric gas miles into the atmosphere and it continued about 19 hours. Mt. Vesuvius is a composite type of volcano, which is formed by alternating layers of lava and rock fragments ...
Volcanoes by Marida Torosyan and Ani Tashyan
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts.
... Earth’s thin outer layer is made of cool rock, but most of Earth is made of extremely hot rock and molten metal. Some of the heat inside Earth escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain ...
... Earth’s thin outer layer is made of cool rock, but most of Earth is made of extremely hot rock and molten metal. Some of the heat inside Earth escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain ...
Eras, periods and epochs Dating by radioactive
... “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating throughout geologic time” Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) Source: University of Calgary ...
... “The same physical processes active in the environment today have been operating throughout geologic time” Hutton (1795), Lyell (1830) Source: University of Calgary ...
1ºESO SCIENCE: 9th October, 2007
... 10.Plutonic and sedimentary rocks are called igneous rocks. 11.Sometimes we use coal for the floor. 12.Schist is a metamorphic rock. 13.Basalts can have holes. 14.Geologists study rocks. 15.Gypsum rocks appear around volcanoes. 16.Sometimes there are fossils in the plutonic rocks. 17.There is a lot ...
... 10.Plutonic and sedimentary rocks are called igneous rocks. 11.Sometimes we use coal for the floor. 12.Schist is a metamorphic rock. 13.Basalts can have holes. 14.Geologists study rocks. 15.Gypsum rocks appear around volcanoes. 16.Sometimes there are fossils in the plutonic rocks. 17.There is a lot ...
Physical Geology - Volcanoes and Volcanic Rocks
... • Eruptions of volcanoes consisting of mafic magmas are relatively quiet because of the thin, fluid nature and the absence of gas under pressure • Mafic lava flows tend to travel long distances across the surface, and form broad-based volcanoes with gently sloping sides • Fissure eruptions on the si ...
... • Eruptions of volcanoes consisting of mafic magmas are relatively quiet because of the thin, fluid nature and the absence of gas under pressure • Mafic lava flows tend to travel long distances across the surface, and form broad-based volcanoes with gently sloping sides • Fissure eruptions on the si ...
Volcanoes
... »Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash and other debris »Move down the slopes of a volcano at speeds up to 200 kilometers per hour »May produce a lahar, which is a volcanic ...
... »Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash and other debris »Move down the slopes of a volcano at speeds up to 200 kilometers per hour »May produce a lahar, which is a volcanic ...
geothermal activity - Madison County Schools
... • A volcanic neck (or volcanic plug) forms when magma hardens in the pipe of a volcano. Softer rock around the pipe erodes away, leaving just the neck standing. A volcanic neck looks like a giant tooth stuck into the ground. ...
... • A volcanic neck (or volcanic plug) forms when magma hardens in the pipe of a volcano. Softer rock around the pipe erodes away, leaving just the neck standing. A volcanic neck looks like a giant tooth stuck into the ground. ...
Rocks in the Crust of the Earth
... Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary These are the rocks in the crust of the earth Igneous rocks are from the lava that flows From the mighty volcanoes When that lava is good and cool Igneous rocks will form, that’s the rule (chorus) M ...
... Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary These are the rocks in the crust of the earth Igneous rocks are from the lava that flows From the mighty volcanoes When that lava is good and cool Igneous rocks will form, that’s the rule (chorus) M ...
Types of Volcanoes
... An eruption begins when pressure on a magma chamber forces magma up through the conduit and out the volcano's vents. When the magma chamber has been completely filled, the type of eruption partly depends on the amount of gases and silica in the magma. The amount of silica determines how sticky (leve ...
... An eruption begins when pressure on a magma chamber forces magma up through the conduit and out the volcano's vents. When the magma chamber has been completely filled, the type of eruption partly depends on the amount of gases and silica in the magma. The amount of silica determines how sticky (leve ...
Volcano Study Guide Extinct – Unlikely to erupt ever again Active
... 2. What is the Ring of Fire? It is a major volcanic belt formed by the many volcanoes that surround the Pacific Ocean. 3. Describe how volcanoes form along the mid-ocean ridge. Volcanoes form when lava oozes out of cracks in the ocean floor. 4. How does subduction at convergent plate boundaries lead ...
... 2. What is the Ring of Fire? It is a major volcanic belt formed by the many volcanoes that surround the Pacific Ocean. 3. Describe how volcanoes form along the mid-ocean ridge. Volcanoes form when lava oozes out of cracks in the ocean floor. 4. How does subduction at convergent plate boundaries lead ...
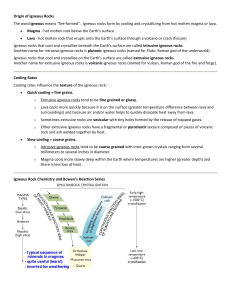
Origin of Igneous Rocks The word igneous means "fire
... Pumice - light in color; white to gray; may be glassy or dull. Fully riddled with holes. Very sponge-like. Floats. Used as an abrasive. (Pumice stone, Lava Soap). ...
... Pumice - light in color; white to gray; may be glassy or dull. Fully riddled with holes. Very sponge-like. Floats. Used as an abrasive. (Pumice stone, Lava Soap). ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.