science project 2012
... Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
... Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
Australia`s volcanic history is a lot more recent than you
... These volcanoes are part of a larger volcanic area or province in south-eastern Australia, where we Mt Elephant, at 190m, is the tallest scoria cone in can still expect another eruption. What will such an western Victoria. Credit: Jozua van Otterloo eruption look like and where will it happen? Looki ...
... These volcanoes are part of a larger volcanic area or province in south-eastern Australia, where we Mt Elephant, at 190m, is the tallest scoria cone in can still expect another eruption. What will such an western Victoria. Credit: Jozua van Otterloo eruption look like and where will it happen? Looki ...
3 types of Volcanoes Reading
... mountain on Earth. Measured from its base on the sea floor, Mauna Kea is taller than Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on land. Cinder cone volcanoes are small volcanic cones made entirely of pyroclastic material from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steeper slopes wi ...
... mountain on Earth. Measured from its base on the sea floor, Mauna Kea is taller than Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on land. Cinder cone volcanoes are small volcanic cones made entirely of pyroclastic material from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steeper slopes wi ...
1 GS104 Lab Quiz 2 Study Guide - Taylor Sections Use your lecture
... Igneous Rock - formed from the cooling of magma (intrusive) or lava (extrusive) Extrusive igneous rock = lava cools to form rock, via volcanic eruption fast cooling, small / microscopic crystals Intrusive igneous rock = magma cools to form rock, beneath Earth's surface slow cooling, large mineral cr ...
... Igneous Rock - formed from the cooling of magma (intrusive) or lava (extrusive) Extrusive igneous rock = lava cools to form rock, via volcanic eruption fast cooling, small / microscopic crystals Intrusive igneous rock = magma cools to form rock, beneath Earth's surface slow cooling, large mineral cr ...
Chapter 29: Formation of Rocks
... Learn about the role of plate tectonics in causing volcanoes and learn what causes eruptions to be gentle or highly explosive. Identify the main types of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones. Learn about other forms of volcanic activity such as geysers, hot springs, hydroth ...
... Learn about the role of plate tectonics in causing volcanoes and learn what causes eruptions to be gentle or highly explosive. Identify the main types of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones. Learn about other forms of volcanic activity such as geysers, hot springs, hydroth ...
Geology - Nayland College
... 2)Relating to or involving volcanic processes: "igneous activity". • Igneous … think ignite … think fire … think lava or magna ...
... 2)Relating to or involving volcanic processes: "igneous activity". • Igneous … think ignite … think fire … think lava or magna ...
Putting the Lava in the Lava Beds
... believed to be over a million years old. Covering almost the entire monument are small bits of pumice which formed as fallout from the eruptions of Glass Mountain and Little Glass Mountain about 1,000 years ago. This was the latest major volcanic activity. One other feature is known as tuff. This is ...
... believed to be over a million years old. Covering almost the entire monument are small bits of pumice which formed as fallout from the eruptions of Glass Mountain and Little Glass Mountain about 1,000 years ago. This was the latest major volcanic activity. One other feature is known as tuff. This is ...
Rock Cycle
... metamorphic rock - Rock deep within Earth’s crust that has been exposed to extreme heat and pressure causing changes to its appearance, structure, and composition ...
... metamorphic rock - Rock deep within Earth’s crust that has been exposed to extreme heat and pressure causing changes to its appearance, structure, and composition ...
76 Volcanism and Igneous Processes I. Introduction A. Volcanism
... Pumice- sand to gravel sized fragments of cooled lava with many air voids. Lapilli- walnut sized pyroclastic ejecta. Cinders- pea-sized basaltic particles Blocks and bombs- pyroclastic fragments larger than lapilli, blocks = comprised of ejected hardened lava, bombs=ejected as molten lava. ...
... Pumice- sand to gravel sized fragments of cooled lava with many air voids. Lapilli- walnut sized pyroclastic ejecta. Cinders- pea-sized basaltic particles Blocks and bombs- pyroclastic fragments larger than lapilli, blocks = comprised of ejected hardened lava, bombs=ejected as molten lava. ...
Word format
... A sedimentary bed contains three fossils: A, B, and C. Fossil A formed from an animal that only existed in the Cambrian and Ordovician Periods. Fossil B only existed in the Ordovician Period. Fossil C existed for a very long time on Earth- from the Cambrian to the Triassic Period. Based on this foss ...
... A sedimentary bed contains three fossils: A, B, and C. Fossil A formed from an animal that only existed in the Cambrian and Ordovician Periods. Fossil B only existed in the Ordovician Period. Fossil C existed for a very long time on Earth- from the Cambrian to the Triassic Period. Based on this foss ...
PDF format
... 37. Which type of metamorphism would NOT be expected to produce predominantly mechanical deformation? A. regional B. impact C. burial D. dynamic E. all of the above are dominated by mechanical deformation 38. What is meant by the term chronological sequence? A. it is one of the principles of stratig ...
... 37. Which type of metamorphism would NOT be expected to produce predominantly mechanical deformation? A. regional B. impact C. burial D. dynamic E. all of the above are dominated by mechanical deformation 38. What is meant by the term chronological sequence? A. it is one of the principles of stratig ...
Chapter 10: Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks
... that the gases in the magma can’t easily escape as the magma rises to the surface. This causes gas pressures to rise until…boom!--they finally escape in an explosive manner! A good analogy from cooking is the way that homemade spaghetti sauce (which is thick and rich) behaves when brought to a boil ...
... that the gases in the magma can’t easily escape as the magma rises to the surface. This causes gas pressures to rise until…boom!--they finally escape in an explosive manner! A good analogy from cooking is the way that homemade spaghetti sauce (which is thick and rich) behaves when brought to a boil ...
Volcanoes
... history, but not for long! It is a huge volcano, but it used to be bigger the eruption was so violent it blew some of it apart. ...
... history, but not for long! It is a huge volcano, but it used to be bigger the eruption was so violent it blew some of it apart. ...
Shield volcanoes
... Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. • Volcanic mountains form when layers of lava, ash, and other material build up around these openings. ...
... Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. • Volcanic mountains form when layers of lava, ash, and other material build up around these openings. ...
File
... • Composite volcanoes, sometimes known as strato volcanoes, are between the steep sided ash and cinder cones and the low-lying shield cones. • They are formed from layers of ash and [lava] flows. When composite volcanoes erupt they are sometimes explosive and sometimes less violent. • Shield Shield ...
... • Composite volcanoes, sometimes known as strato volcanoes, are between the steep sided ash and cinder cones and the low-lying shield cones. • They are formed from layers of ash and [lava] flows. When composite volcanoes erupt they are sometimes explosive and sometimes less violent. • Shield Shield ...
Volcanic Fatalities
... miles to the southeast, released a heavy cloud of toxic gas, killing 37 people. A third lake, Lake Kivu, on the Congo-Rwanda border in Central Africa, is also known to act as a reservoir of carbon dioxide and methane, which is a valuable natural gas that is gathered from the lake ...
... miles to the southeast, released a heavy cloud of toxic gas, killing 37 people. A third lake, Lake Kivu, on the Congo-Rwanda border in Central Africa, is also known to act as a reservoir of carbon dioxide and methane, which is a valuable natural gas that is gathered from the lake ...
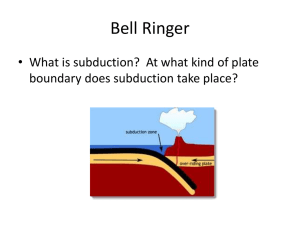
Bell Ringer
... • Cinder Cones – These are the most common and the smallest volcanoes – Large amounts of gas become trapped in the magma and violent eruptions happen. – Ash and lava are thrown from the vent. It falls down and forms the cone shape. ...
... • Cinder Cones – These are the most common and the smallest volcanoes – Large amounts of gas become trapped in the magma and violent eruptions happen. – Ash and lava are thrown from the vent. It falls down and forms the cone shape. ...
Review for Chapter 9 – Volcanoes
... 17. How is magma different from lava? 18. Crater Lake is an example of what volcanic landform? 19. At a Subduction boundary, where does the volcano normally form? 20. Lava plateaus (very broad flat land forms) form from what type of lava? 21. In our solar system, where are there active volcanoes? 2 ...
... 17. How is magma different from lava? 18. Crater Lake is an example of what volcanic landform? 19. At a Subduction boundary, where does the volcano normally form? 20. Lava plateaus (very broad flat land forms) form from what type of lava? 21. In our solar system, where are there active volcanoes? 2 ...
Slide 1
... volc. = islands. Eg. Hawaii, (Mauna Loa still active) Caldera…large crater, violent eruption may remove summit of volcaone causing it to collapse- often filled with a lake e.g. ...
... volc. = islands. Eg. Hawaii, (Mauna Loa still active) Caldera…large crater, violent eruption may remove summit of volcaone causing it to collapse- often filled with a lake e.g. ...
Geysers: Types: cone (has a cone of “geyserite” around a small vent
... Surtseyan Eruptions: Caused by rising magma hitting shallow water Terms: Siliceous sinter: Porous opaline silica, precipitated as an encrustation by a geyser or hot spring, a synonym for "geyserite" Tephra: fallen volcanic material 4 sizes of Tephra: dust/ash(<2mm), Lapilli(2-64mm), volcanic bombs/v ...
... Surtseyan Eruptions: Caused by rising magma hitting shallow water Terms: Siliceous sinter: Porous opaline silica, precipitated as an encrustation by a geyser or hot spring, a synonym for "geyserite" Tephra: fallen volcanic material 4 sizes of Tephra: dust/ash(<2mm), Lapilli(2-64mm), volcanic bombs/v ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
Homework04 n
... 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and s ...
... 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and s ...
Tuff

Tuff (from the Italian tufo) is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is compacted into a solid rock in a process called consolidation. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered tuffaceous. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Since it is common in Italy the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the moai statues in Easter Island.Tuff can be classified as either sedimentary or igneous rocks. They are usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although they are sometimes described using sedimentological terms.